Method and device for synchronous cell maintenance of multi-carrier communication system
A multi-carrier communication and cell synchronization technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of not giving synchronization status maintenance, unable to maintain cell synchronization status, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring backward compatibility and reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
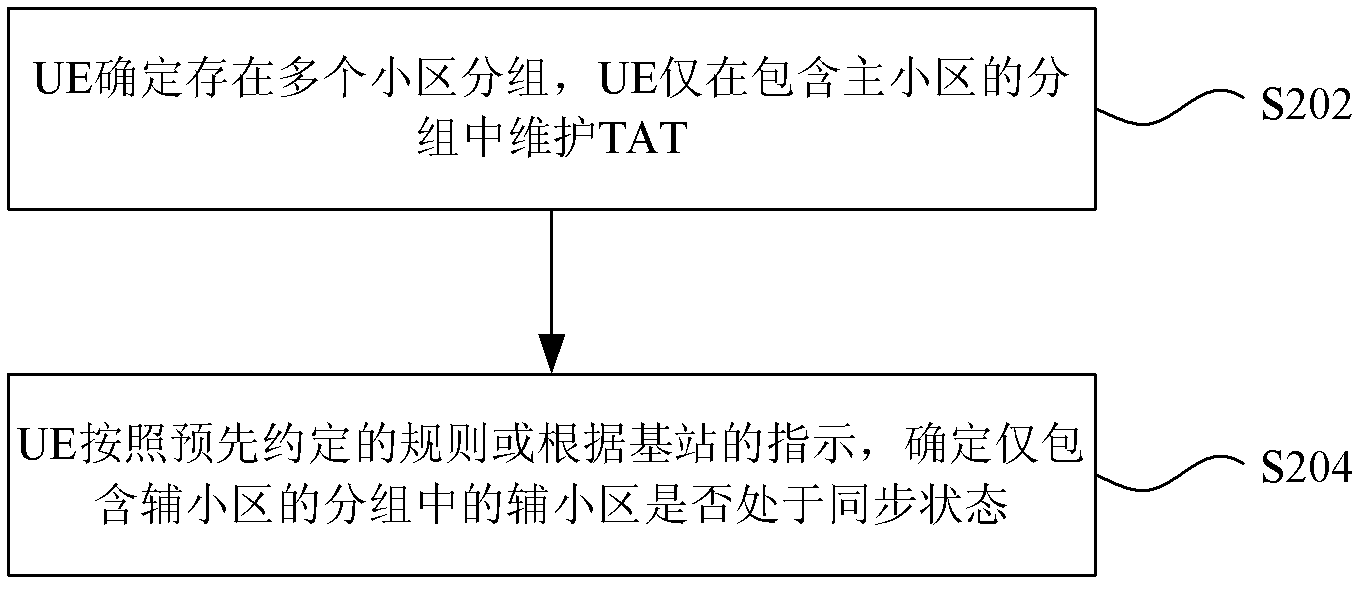
[0054] In this embodiment, the TAT maintenance process, the synchronization / out-of-synchronization maintenance of the secondary cell in the group containing only the secondary cell, and the TAT timeout processing are respectively described by adopting the technical solution provided by the embodiment of the present invention.
[0055] 1. TAT maintenance process
[0056] In this embodiment, the UE starts the TAT when receiving the RAR during the random access process of the primary cell, and restarts the TAT when the UE receives the MAC control element (ie TAC) including the time adjustment of the primary cell. However, addition, activation, deactivation, uplink synchronization and deletion of the secondary cell do not have any impact on the TAT.
[0057] When the UE receives the TAC for time adjustment of the packet containing only the secondary cell, it does not have any impact on the above TAT. The TAC used by the group containing only the secondary cell can be received by th...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Figure 4 is the signaling flow chart of Embodiment 2 of the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown, the synchronization state maintenance in this embodiment mainly includes the following steps:
[0087] Step 401: The UE initiates an RRC connection on CC1, and starts TAT after receiving the TA in the random access response message during the random access process on CC1; the base station configures the information of CC2 and CC3 to the UE in the RRC connection reconfiguration message and group information. CC1 is the primary serving cell, forming group 1, CC2 and CC3 are secondary serving cells, forming group 2; configure the TAT duration on CC1 as 1280ms; configure the secondary cell deactivation timers of CC2 and CC3 as infinite in the base station; after the secondary cells are activated If no uplink synchronization command from the base station is received within a certain period of time, it is considered that there is no need to initiate uplink synchroni...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Figure 5 It is a signaling flowchart of cell synchronization state maintenance in the multi-carrier communication system in Embodiment 3 of the present invention, as shown in Figure 5 As shown, the cell synchronization state maintenance in this embodiment mainly includes the following steps:
[0100] Step 501: The UE initiates an RRC connection on CC1, and starts TAT after receiving the TA in the random access response message during the random access process on CC1; the base station configures the information of CC2 and CC3 to the UE in the RRC connection reconfiguration message and group information. CC1 is the primary serving cell, forming group 1, CC2 and CC3 are secondary serving cells, forming group 2; configure the TAT duration on CC1 as 1280ms; configure the secondary cell deactivation timers of CC2 and CC3 as infinite in the base station; after the secondary cells are activated If no uplink synchronization command from the base station is received within ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com