Conversion method of virtual and real addresses of many-core processor
A technology of many-core processors and virtual and real addresses, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as large overhead, inapplicability to many-core processors, affecting processor system performance, etc., and achieve the effect of small overhead, small overhead, and reduced overhead.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
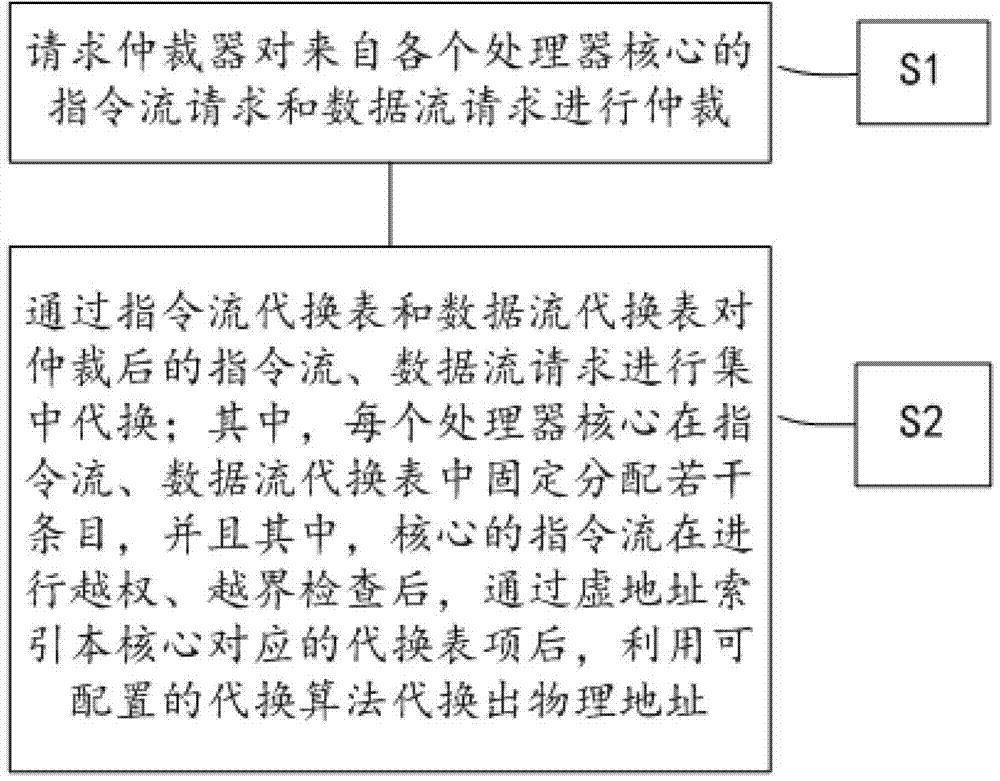
[0035] figure 1 A flow chart of a virtual-to-real address translation method for a many-core processor according to the first embodiment of the present invention is schematically shown. Such as figure 1 As shown, the many-core processor virtual-to-real address conversion method according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0036] The first step S1: the request arbitrator arbitrates the instruction flow requests and data flow requests from each processor core; wherein, preferably, the request arbitrator can be divided into multiple stages according to the scale of many-core processor cores.
[0037] Second step S2: Centrally replace the arbitrated instruction flow and data flow requests through the instruction flow substitution table and the data flow substitution table; wherein, each processor core is fixed in the instruction flow and data flow substitution table Allocate a number of entries, and among them, after the instruction ...
no. 2 example
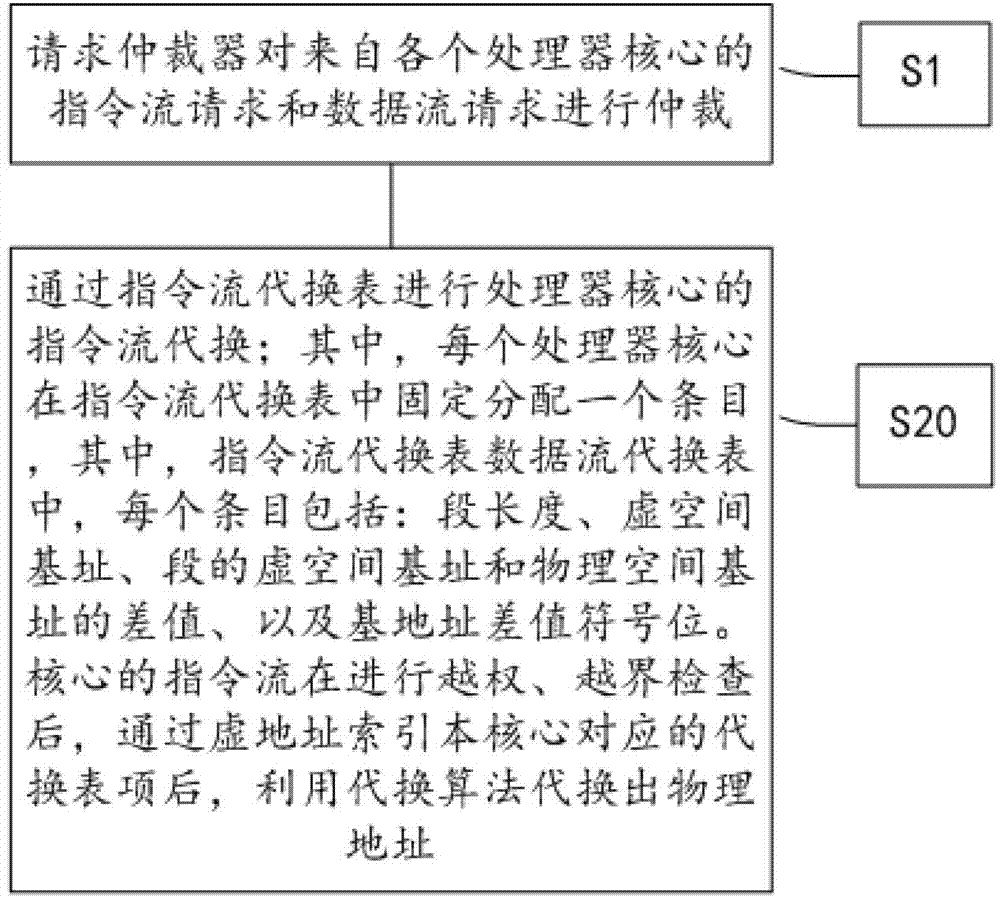
[0049] figure 2 A flow chart of a virtual-to-real address conversion method for a many-core processor according to the second embodiment of the present invention is schematically shown. Such as figure 2 As shown, the many-core processor virtual-real address translation method according to the second embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0050] The first step S1: the request arbitrator arbitrates the instruction flow requests and data flow requests from each processor core; wherein, preferably, the request arbitrator can be divided into multiple stages according to the core scale of the many-core processor.
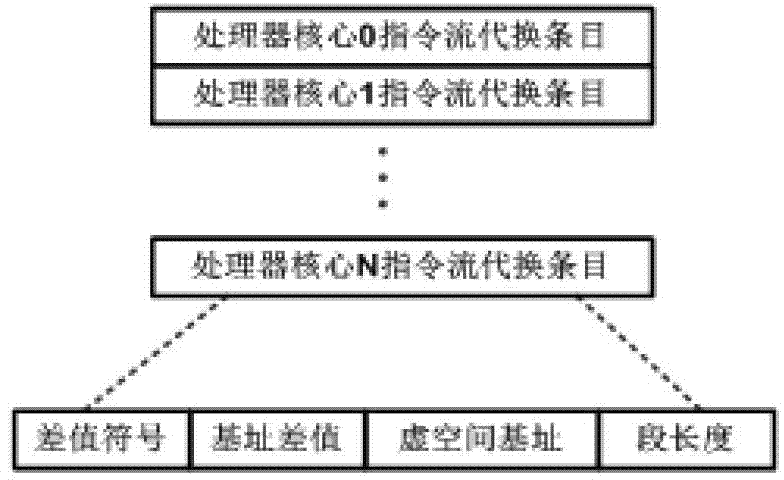
[0051] The second step S20: perform the instruction stream substitution of the processor core through the instruction stream substitution table; wherein, each processor core fixedly allocates an entry in the instruction stream substitution table (such as image 3 shown), where, in the instruction stream substitution table and the data stre...
no. 3 example
[0053] The second embodiment above corresponds to the case where each processor core permanently allocates one entry in the instruction stream substitution table, and correspondingly, for the case where each processor core permanently allocates multiple entries in the instruction stream substitution table, Figure 4 A flow chart of a virtual-to-real address conversion method for a many-core processor according to the third embodiment of the present invention is schematically shown. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the many-core processor virtual-to-real address conversion method according to the third embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0054] The first step S1: the request arbitrator arbitrates the instruction flow requests and data flow requests from each processor core; wherein, preferably, the request arbitrator can be divided into multiple stages according to the core scale of the many-core processor.
[0055] The second step S20: perform the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com