Parallel method for large-area drainage basin extraction
A large-area and watershed technology, applied in the parallel field of watershed extraction, can solve problems such as decision-making errors, national and people's economic losses, and increased computing costs, and achieve the effects of reducing the impact of computing efficiency, expanding application breadth, and ensuring load balancing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0047] In the present invention, data division, fusion strategy and parallel I / O mechanism under data parallel mode:
[0048] 1. Data partition strategy
[0049] (1) Division method
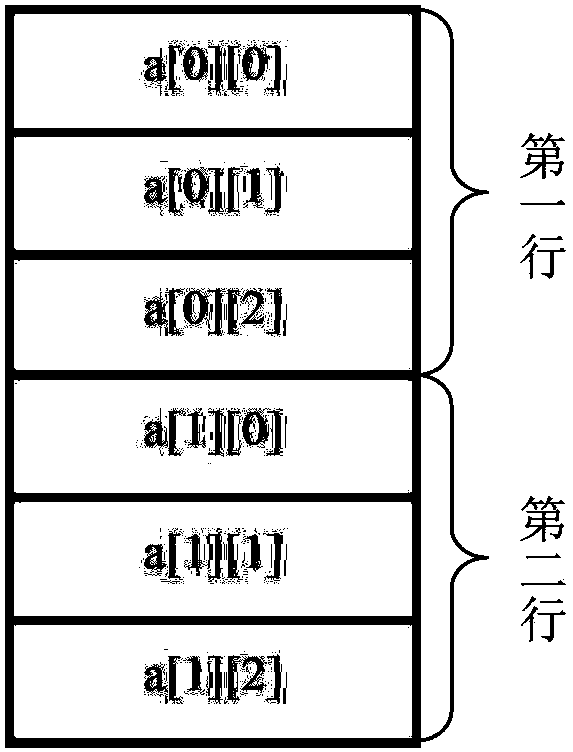
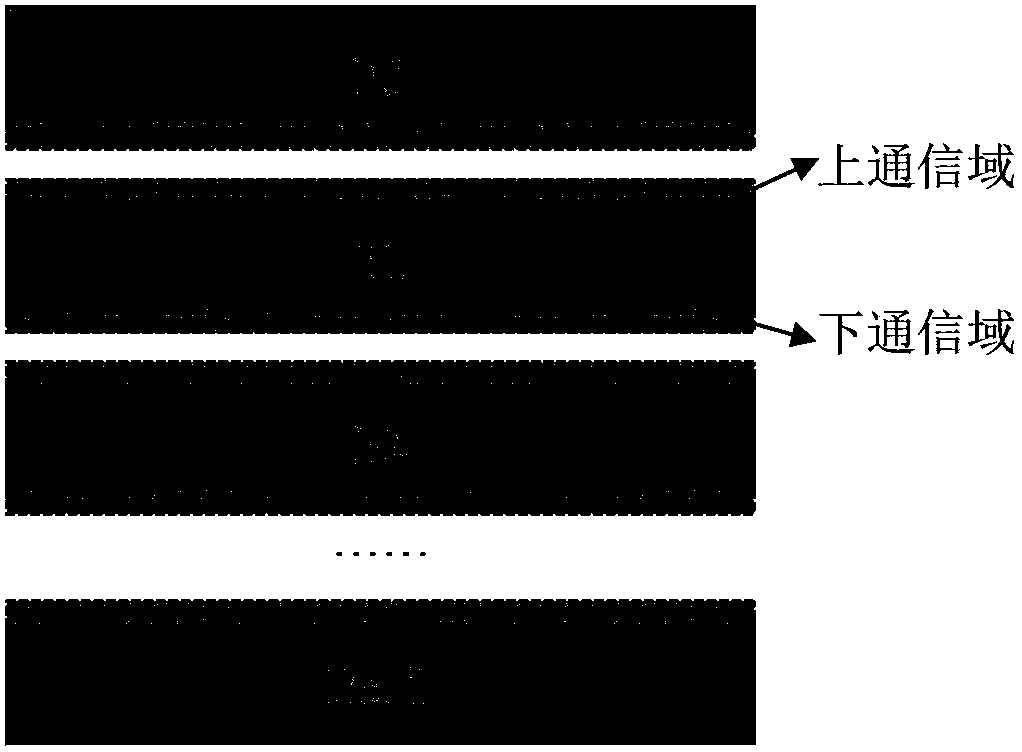
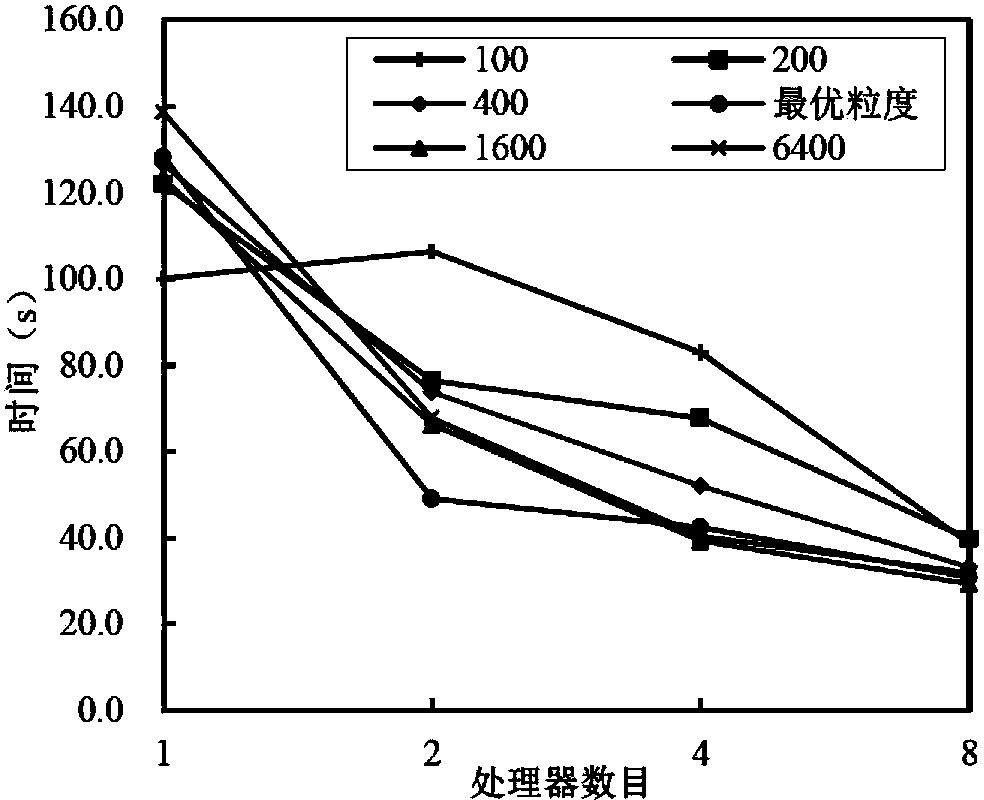
[0050] Row Band Communication Partition (RBCP): When DEM data is calculated, it is in the form of a matrix of m rows × n columns, which can be organized in a two-dimensional array. The storage form of DEM data based on two-dimensional arrays at the physical layer is row-by-row storage (such as figure 1 shown) and load balancing is an important factor for each computing node to achieve maximum computing efficiency in the parallel computing process. Considering two aspects, when the present invention divides DEM data, it uses row band redundancy division. The row-band communication domain division refers to the way of dividing the DEM into bands includi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com