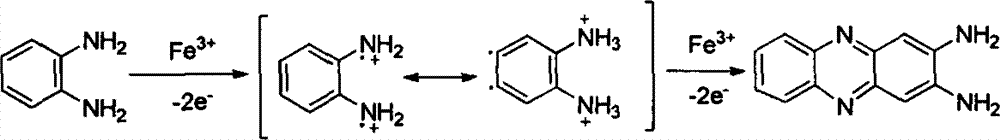
Method for removing o-phenylenediamine (OPD) in wastewater
An o-phenylenediamine and waste water technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as troublesome regeneration or replacement, high operating cost, and easy adsorption and saturation of activated carbon. , to achieve the effect of improving biodegradation performance and no secondary pollution problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
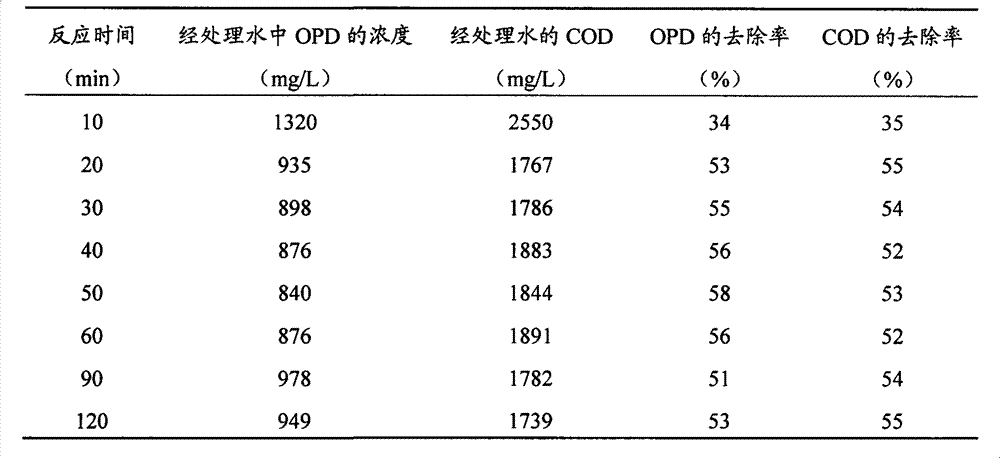
[0022] O-phenylenediamine (chemically pure) and distilled water were used to prepare simulated wastewater containing OPD. The OPD concentration and COD (COD value was measured by potassium dichromate method, the same below) were 2,000mg / L and 3,900mg / L, respectively. Take 200mL of simulated wastewater and put it in an 800mL beaker, adjust the pH value to about 2 with concentrated sulfuric acid, and then add 7g / L of solid analytically pure ferric sulfate. At room temperature (15° C. to 35° C., the same below), magnetic stirring was used for 20 minutes to 120 minutes, and samples were taken at intervals. See Table 1 for the processing results.
[0023] Table 1
[0024]
[0025] It can be seen from Table 1 that when water-soluble iron salts are used to oxidize the simulated wastewater containing OPD for more than 20 minutes, the reaction time has little effect on the removal of OPD by iron ions.
Embodiment 2
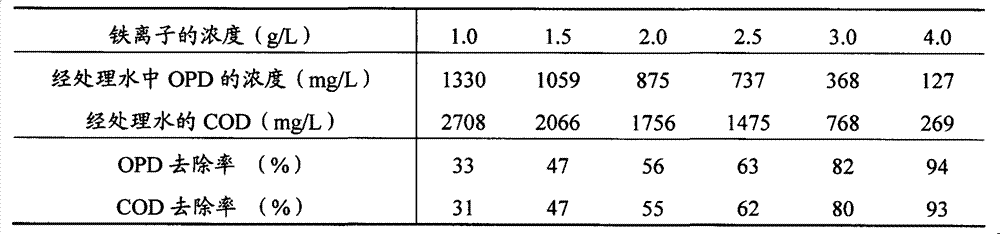
[0027] O-phenylenediamine (chemically pure) and distilled water were used to prepare simulated wastewater containing OPD. The OPD concentration and COD were 2,000mg / L and 3,900mg / L, respectively. Take several simulated wastewaters with a volume of 200mL and place them in different 800mL beakers, adjust their pH values to about 2 with concentrated sulfuric acid, and add different amounts of solid ferric sulfate (analytical pure) to these simulated wastewaters. , and then magnetically stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes to investigate the treatment effect of ferric sulfate at different concentrations. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0028] Table 2
[0029]
[0030] It can be seen from Table 2 that in the wastewater treatment system containing OPD, the concentration of iron ions is a key factor affecting the removal rate of OPD and COD in wastewater.
Embodiment 3
[0032] O-phenylenediamine (chemically pure) and distilled water were used to prepare simulated wastewater containing OPD. The OPD concentration and COD were 2,000mg / L and 3,900mg / L, respectively. Take several parts of simulated wastewater with a volume of 200mL and place them in different 800mL beakers, use concentrated sulfuric acid to adjust their pH value to about 2, and add 9g / L solid analytically pure iron sulfate (Fe3+ Concentration of 2.5g / L), magnetically stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes, and then added different amounts of hydrogen peroxide to these several simulated waste water, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 60 minutes, finally with solid sodium hydroxide The pH values of these several reaction systems were all adjusted to 8-9, left to settle, and the filtrate was taken for measurement. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0033] table 3
[0034]
[0035] It can be seen from Table 3 that when the dosages of ferric ions and hydrogen p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com