Artificial transcription factor of hepatitis B virus (HBx) genes and application of artificial transcription factor
A hepatitis B virus, gene transcription technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of time-consuming and laborious, and achieve the effect of high inhibitory activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1, construction and screening of phage display library
[0044] 1. Construction of library
[0045] According to the literature [Mark I, Yen C. Rapid, high-throughput engineering of sequence-specific zinc finger DNA-binding proteins. Methods Enzymol, 2001, 340: 593-609], 18 common sequences were designed, including randomized sites 108 sequences. Phosphate addition, annealing, and ligation of the zinc finger fragments of the zinc finger library Lib12 and Lib23 are routine operations, carried out in accordance with the Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Second Edition).
[0046] design primers
[0047] Lib-top: 5'-TCGCGGCCCAGCCGGCCATGGCGGAAGAGA-3'(30nt)
[0048] Lib-end: 5'-TGTAGCGGCCGCCTTCTGTCTTAAATG-3'(27nt),
[0049] The ligation products of the zinc finger fragments of Lib12 and Lib23 were amplified by PCR, and restriction sites of SfiI and NotI were introduced at both ends of the fragments.
[0050] The conditions of PCR are: using conventional Taq enz...
Embodiment 2
[0108] Example 2, Affinity and specificity identification of phage display zinc finger library
[0109] 1. The affinity of zinc fingers screened by ELISA detection
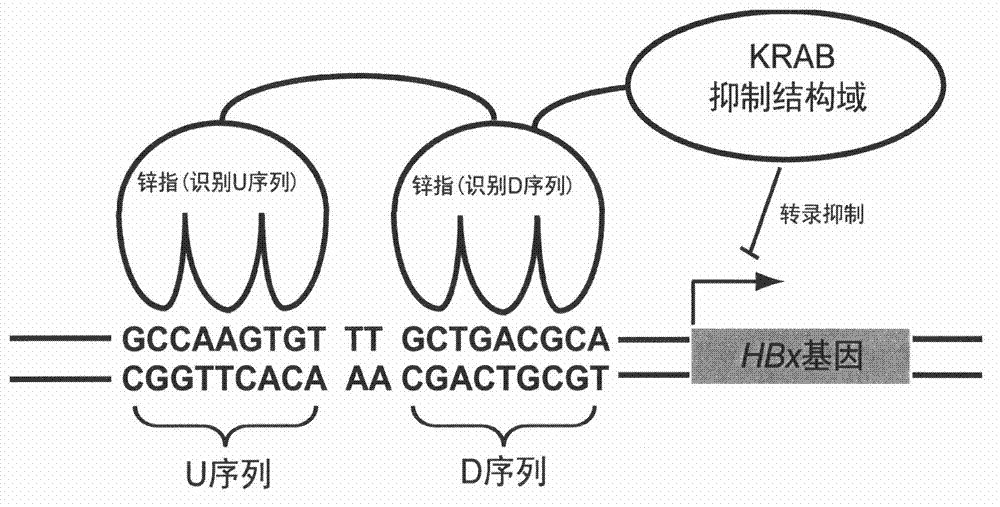
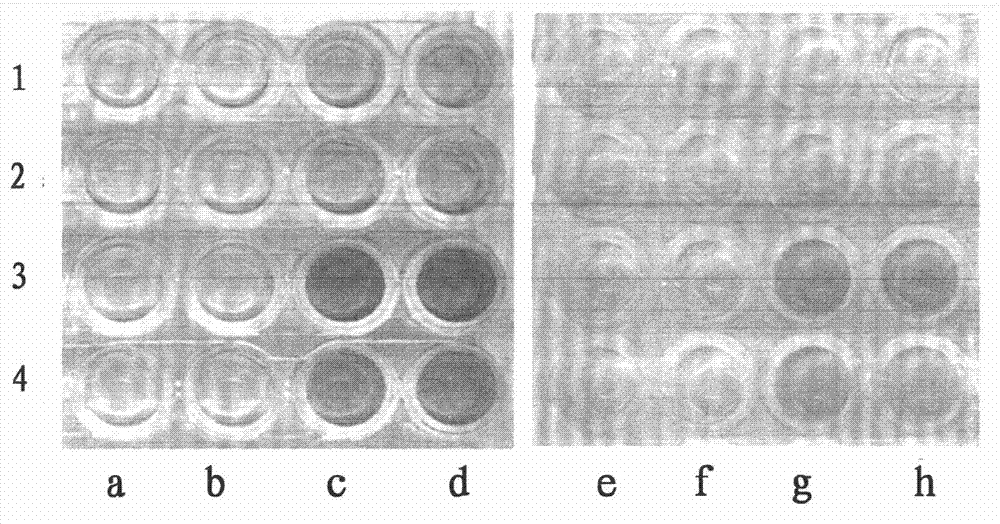
[0110] The test procedure is the same as part vi of Example 1. Such as image 3 As shown, three zinc finger clones U5 and U37 have good affinity for their screening target sequence GCCAAGTGT (U sequence), while three zinc finger clones D13 and D46 have good affinity for their screening target sequence GCTGACGCA (D sequence). Affinity.
[0111] 2. Detection of specificity of zinc finger clones by single base mutation test of target sequence
[0112] Synthesize 9 pairs of biotin-labeled new target sequences, each pair of sequences contains a base conversion relative to the original 9bp target sequence ( or ) mutation. The nine pairs of mutant sequences and the original target sequence were respectively wrapped in a streptavidin plate, and the difference in the affinity of each sequence to the rescue supernat...
Embodiment 3
[0160] Example 3, construction of six zinc finger proteins
[0161] To ensure specificity, artificial transcription factors should only act on their own target sequences when regulating gene expression. Since the human genome contains about 3×10 9 bp, so usually a sequence of 17 bp (417 possible combinations) or longer can guarantee that it has only a single copy in the human genome. As mentioned above, each zinc finger unit usually recognizes a 3bp sequence, so the DNA binding domain of an artificial transcription factor should consist of six or more zinc finger units. At present, most of the structures obtained through library screening are three-zinc-finger structures, so it is often necessary to connect multiple zinc-finger units in series through linkers.
[0162] The three zinc finger protein D13 for the D sequence is fused with the three zinc finger protein U5 for the U sequence through the linker peptide shown in SEQ ID NO20 to construct the six zinc finger protein U...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com