Low-hydration-heat early-strength cement for well cementation
An early-strength cement and cementing technology, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, drilling compositions, etc., can solve the problems of shortening the well construction period, instability of permafrost or deep-water hydrate layer, cementing gas channeling, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of improved stability and compactness, excellent anti-gas channeling ability, and short thickening transition time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
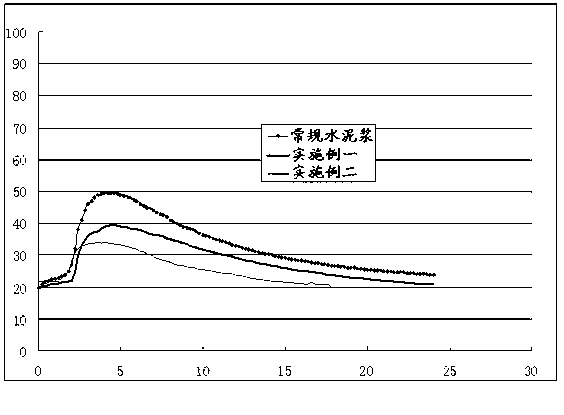
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: The formulation of early-strength cement with low heat of hydration of the present invention and performance evaluation of heat of hydration:
[0028] Cement component A: 60% of low-temperature early-strength cement, 25% of pozzolanic materials, and 15% of fine spherical particles.
[0029] Cement component B: 40% of low-temperature early-strength cement, 40% of pozzolanic materials, and 20% of fine spherical particles.
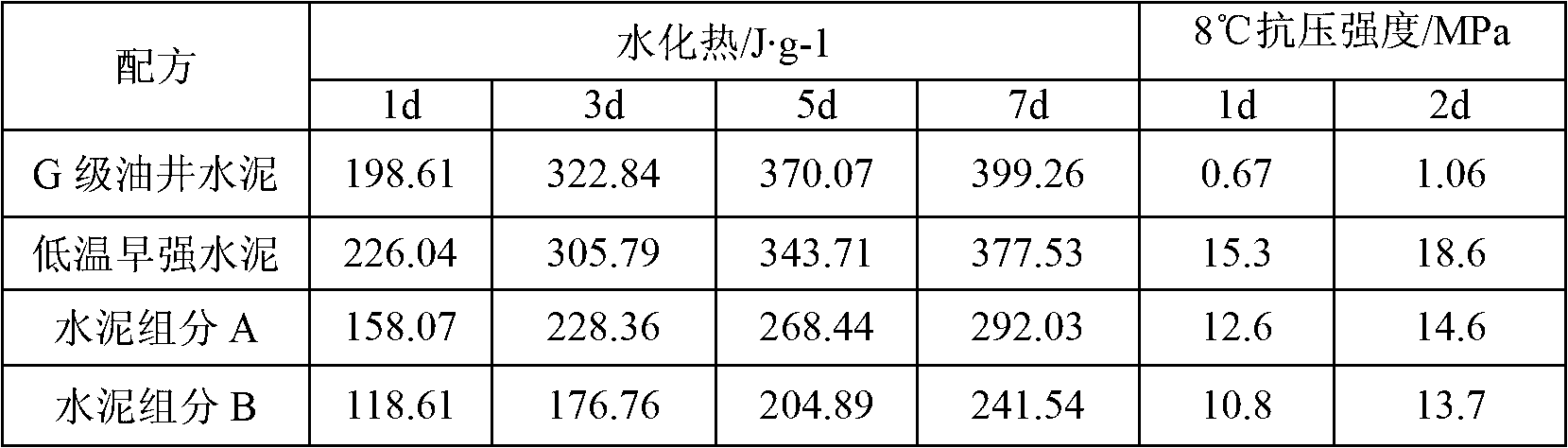
[0030] According to GB / T 12959-2008 "Method for Determination of Heat of Hydration of Cement", the hydration heat of cement with different formulations was tested, and compared with G-grade cement and low-temperature early-strength cement, the results are as follows.
[0031] Table 1
[0032]
[0033] It can be seen that after adding low heat of hydration materials, the heat of hydration of cement is greatly reduced, and the heat of hydration of cement component B is 51% of that of low-temperature early-strength cement, but its streng...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Low hydration heat cement slurry formula 1
[0035] Cement slurry formula 1: remaining cement component A + 20% hollow microspheres + 52% water + 1% sodium silicate + 0.5 retarder, cement slurry density: 1.5g / cm 3 .
[0036] The cement slurry was prepared and the performance of the cement slurry was tested with reference to the petroleum and natural gas industry standard ISO 10426-3-2003 "Cement and Materials for Oil Well Cementing Part 3: Deep Water Well Cement Formulation Test". The properties of cement paste are shown in Table 2.
[0037] Table 2
[0038]
Embodiment 3
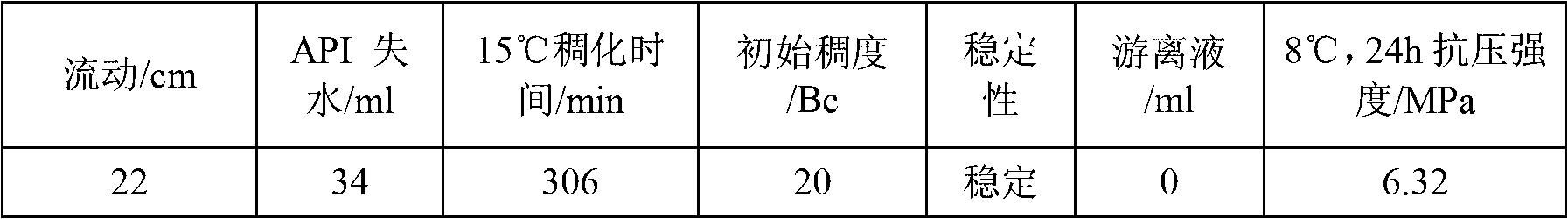
[0039] Embodiment 3: low hydration hot water slurry formula 2
[0040] Cement slurry formula 2: remaining cement component B + 30% hollow microspheres + 62% water + 1.2% sodium silicate + 0.4 retarder, cement slurry density: 1.35g / cm 3 .
[0041] The performance of cement slurry is shown in Table 3
[0042] table 3
[0043]
[0044]The heat of hydration of the cement of the present invention is only 1 / 2 of that of conventional cement, and the low-temperature strength develops rapidly, so cement slurry with low heat of hydration can be prepared, and the technical effect of being used for cementing wells in hydrate-containing layers is as follows:
[0045] 1. The early-strength cement with low heat of hydration for well cementing of the present invention develops strength rapidly at low temperature, and the heat of hydration is about 1 / 2 of that of conventional low-temperature early-strength cement. The temperature of the cement slurry is lowered during the waiting time, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com