Thin-film magnetoresistive sensor element and thin-film magnetoresistive bridge
A magnetoresistive sensor and thin-film technology, applied in the field of half-bridge and full-bridge bridges, can solve the problems affecting sensor performance, limiting chip design, limited bias magnetic field, etc., achieving small hysteresis, low cost, high precision and high linearity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1 Thin film magnetoresistive sensor element
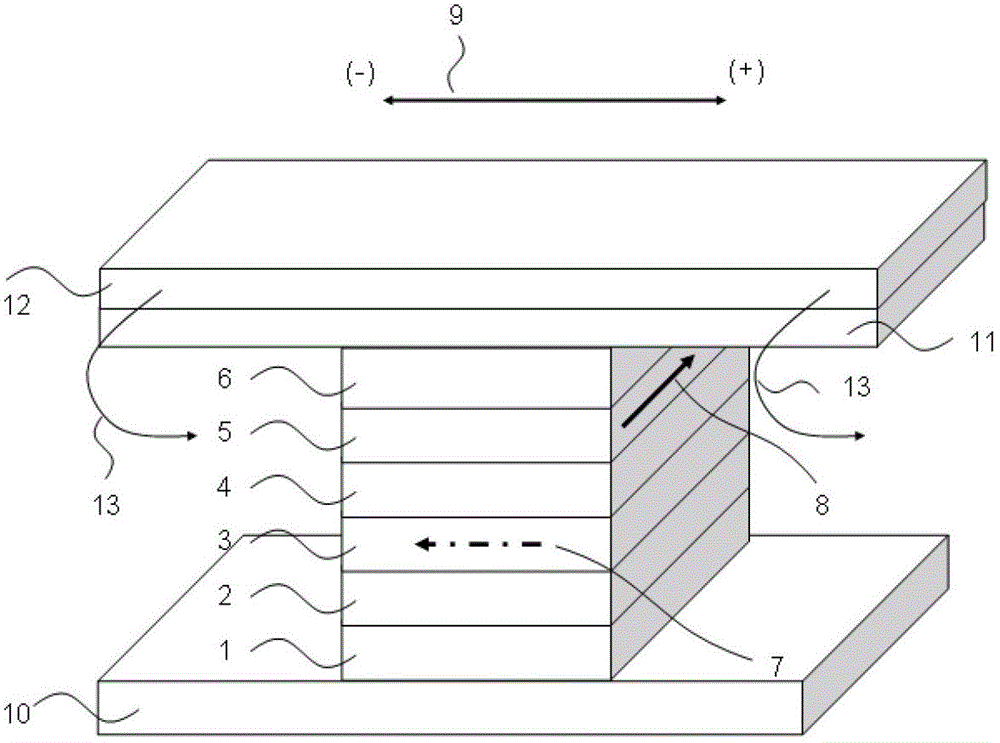
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, the structure of the thin film magnetoresistive sensor element is composed of nanoscale multilayer films: lower electrode 10, seed layer 1, antiferromagnetic pinning layer 2, magnetic pinned layer 3 structure, nonmagnetic isolation layer 4, magnetic Free layer 5 , protective layer 6 , upper electrode 11 , and bias layer 12 . The magnetic moment direction of the magnetic pinned layer 3 is shown in 7, the magnetic moment direction 8 of the magnetic free layer 5 is biased by the constant external magnetic field 13 produced by the bias layer 12, and the magnetic moment direction 8 of the magnetic free layer 5 is in line with The magnetic moment directions 7 of the magnetic pinned layers 3 are perpendicular to each other. The magnetic moment direction 8 of the magnetic free layer 5 changes with the magnitude and direction of the applied magnetic field 9 .
[0033] The working princi...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 Thin film magnetoresistive bridge half bridge
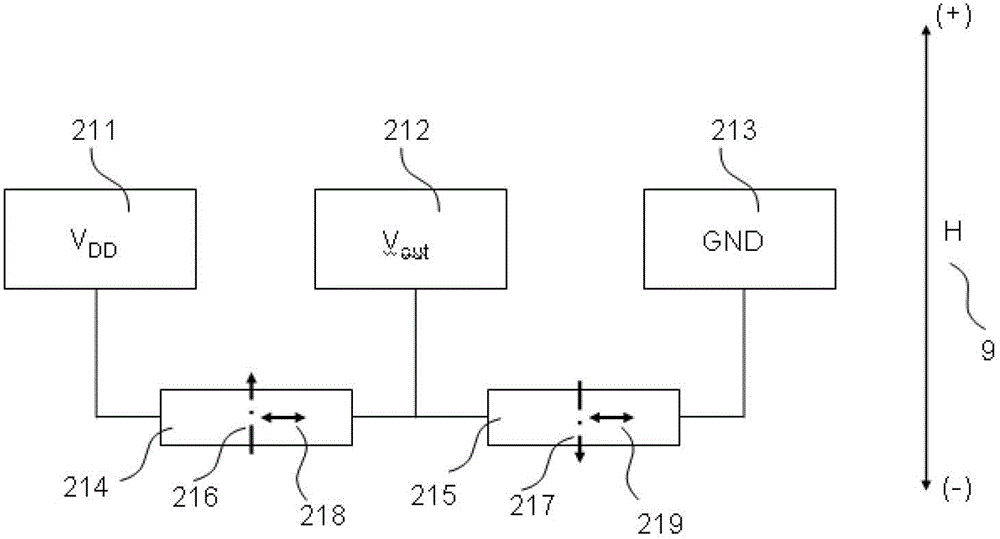
[0035] The structure of the thin film magnetoresistive bridge half bridge, such as image 3As shown, two thin film magnetoresistive elements 214 and 215 are formed. The magnetic moment direction 216 of the magnetic pinned layer of the thin film magnetoresistive element 214 is antiparallel to the magnetic moment direction 217 of the magnetic pinned layer of the thin film magnetoresistive element 215 . The directions 218 and 219 of the magnetic free layers of the thin film magnetoresistive elements 214 and 215 are parallel to each other. The electrodes 211 and 213 are the voltage input terminals of the half-bridge of the thin-film magnetoresistive bridge, and the electrode 212 is the voltage output terminal of the half-bridge of the thin-film magnetoresistive bridge.
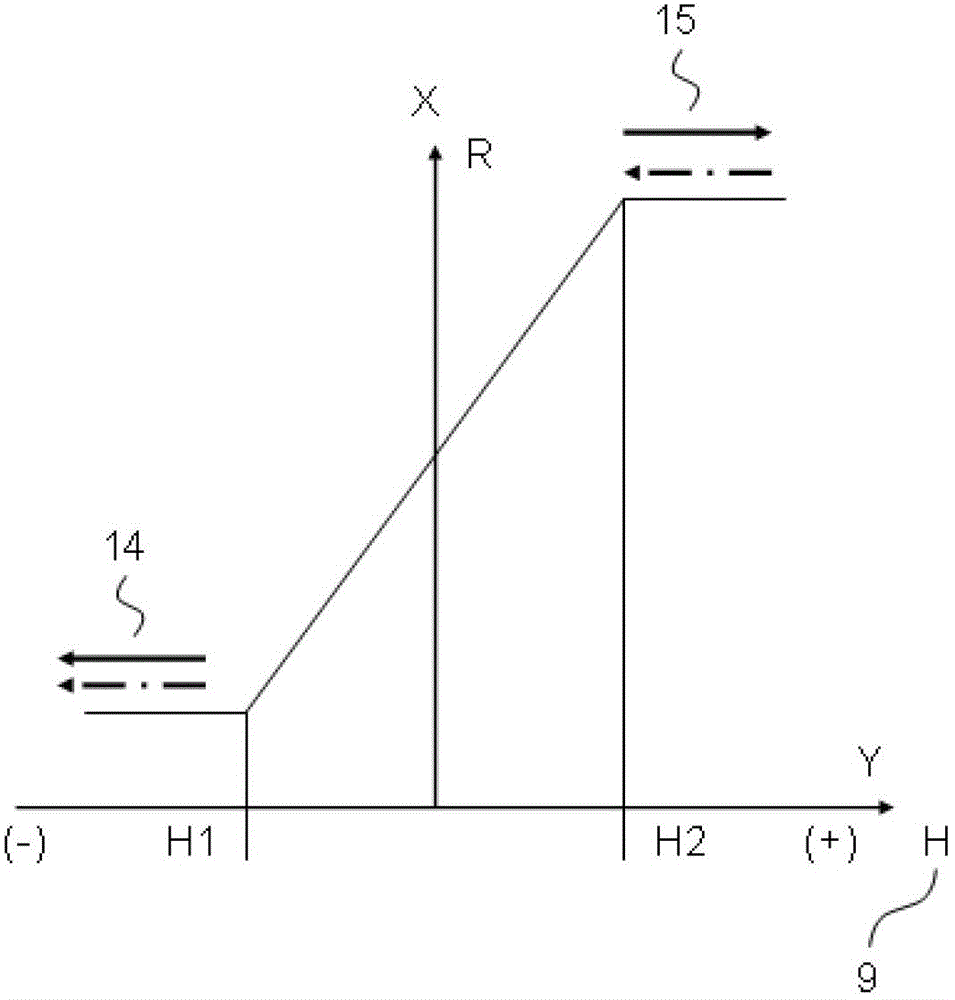
[0036] The working principle of the thin film magnetoresistive bridge half bridge, such as Figure 4 As shown, the output voltage V of the hal...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3 Thin film magnetoresistive bridge full bridge
[0038] The structure of the thin film magnetoresistive bridge full bridge, such as Figure 5 As shown, it consists of four thin film magnetoresistive elements 311, 312, 313, 314. The magnetic moment directions 321 , 323 of the magnetic pinned layers of the thin film magnetoresistive elements 311 and 314 are antiparallel to the magnetic moment directions 322 , 324 of the magnetic pinned layers of the thin film magnetoresistive elements 312 , 313 . The directions 331 , 332 , 333 , 334 of the magnetic free layers of the thin film magnetoresistive elements 311 , 312 , 313 , 314 are parallel to each other. The electrodes 315 and 316 are the voltage input ends of the full bridge of the thin film magnetoresistive bridge, and the electrodes 317 and 318 are the voltage output ends of the full bridge of the thin film magnetoresistive bridge.
[0039] The working principle of the thin film magnetoresistive bridge full ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com