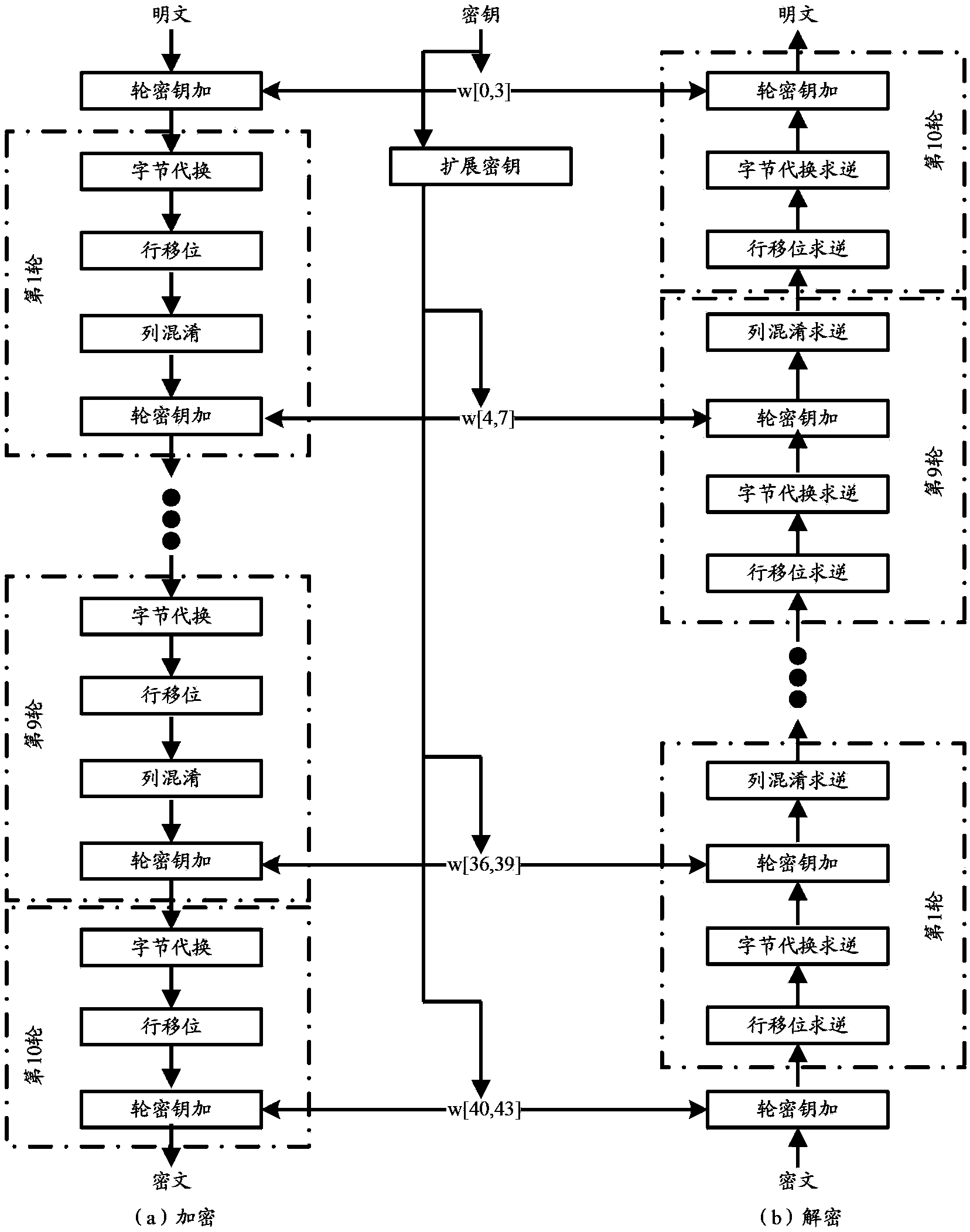
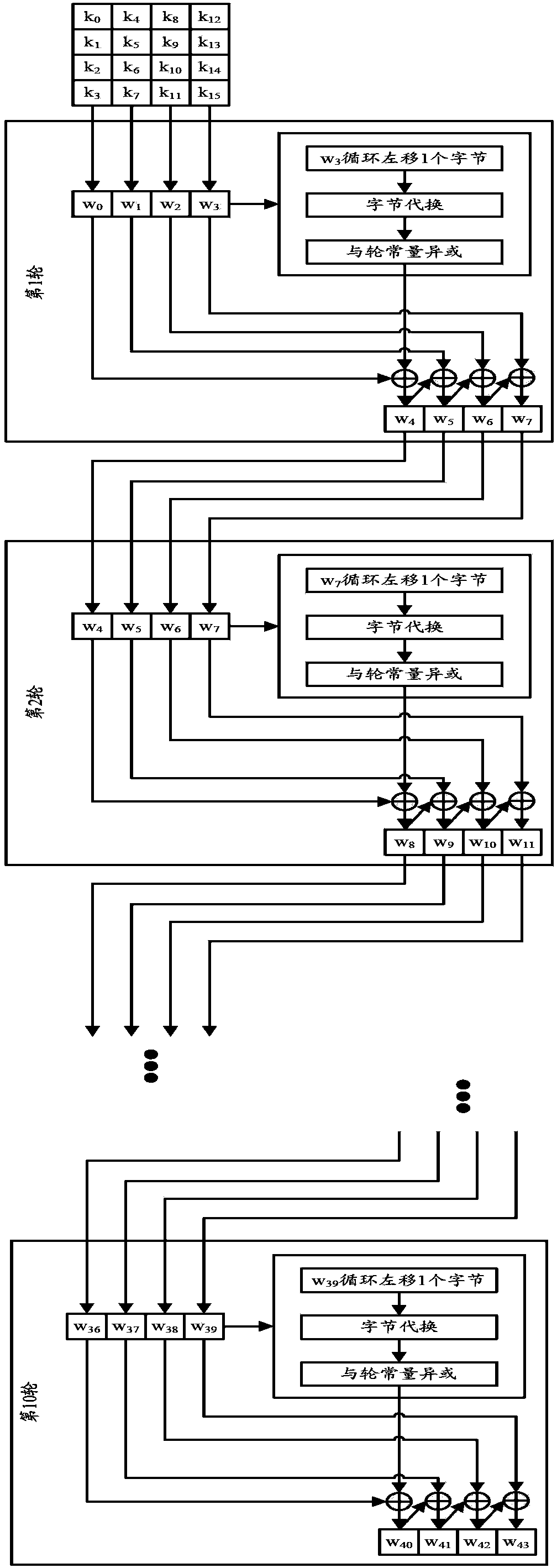
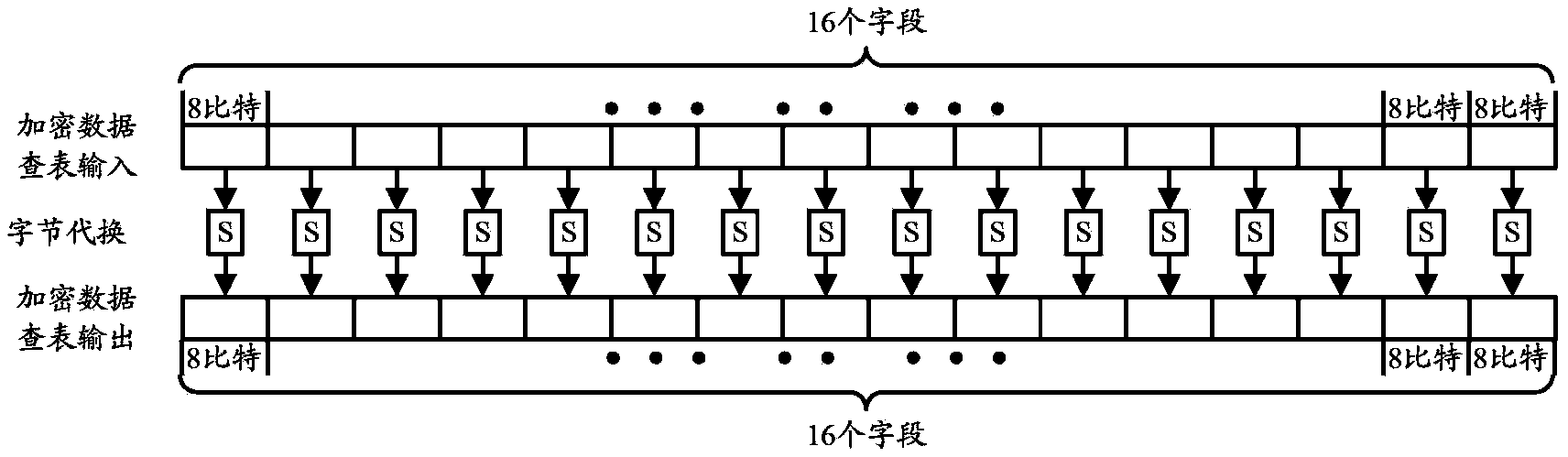
Method and table look-up device for encrypting and decrypting data by using symmetric cryptographic algorithm
A symmetric cryptographic algorithm, encryption and decryption technology, applied in the field of methods and table lookup devices, can solve problems such as occupying considerable hardware resources and unsatisfactory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0117] In this embodiment, an algorithm subunit uses a look-up table unit, as attached Figure 11 shown. Taking the standard symmetric encryption algorithm that requires the use of four S-boxes with 6-bit input and 4-bit output as an example, assuming that the total length of the input data of the algorithm subunit is 48 bits, the specific steps for implementing this application method are as follows:
[0118] (1) First determine that the S-box is an internal component of the symmetric encryption algorithm, and then determine that the type of S-box is 1, and the number of S-boxes is 4;
[0119] (2) Since the number of S boxes is greater than 1, S boxes can be reused;
[0120] (3) Select S-box multiplexing, and confirm that the number of S-boxes used is 3, then the maximum length of the input data of the table lookup unit is 18 bits;
[0121] (4) Divide the maximum length of the input data of the table lookup unit into three data units of 6 bits, determine that the first data...
Embodiment 2
[0127] This embodiment describes the application mode in which two or more algorithmic subunits share a table lookup unit, as shown in the attached Figure 12 shown. Taking the standard symmetric encryption algorithm that requires eight 8-bit input and 8-bit output S-boxes as an example, it has two algorithm subunits, and the total length of input data for each algorithm subunit is 32bits. The specific steps for implementing this application method are as follows:
[0128] (1) First determine that the S-box is an internal component of the symmetric encryption algorithm, and then determine that the type of S-box is 1, and the number of S-boxes is 8;
[0129] (2) Since the number of S boxes is greater than 1, S boxes can be reused;
[0130] (3) Select S-box multiplexing, and confirm that the number of S-boxes used is 2, then the maximum length of the input data of the table lookup unit is 16 bits;
[0131] (4) Divide the maximum length of the input data of the table lookup uni...
Embodiment 3
[0136] This embodiment describes the application mode in which two or more algorithmic subunits independently use a table lookup unit, as shown in the attached Figure 13 shown. Taking the standard symmetric encryption algorithm that requires eight 8-bit input and 8-bit output S boxes as an example, it has two algorithm subunits, and the total length of input data for each algorithm subunit is 32bits. The specific steps for implementing this application method are as follows:
[0137] (1) First determine that the S-box is an internal component of the symmetric encryption algorithm, and then determine that the type of S-box is 1, and the number of S-boxes is 8;
[0138] (2) Since the number of S boxes is greater than 1, S boxes can be reused;
[0139] (3) Choose to reuse the S box;
[0140] (4) Determine the table lookup unit used by the first algorithm subunit, the specific steps are as follows:
[0141] a. Make sure that the number of S boxes used is 2, then the maximum le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com