Bacillus coagulans and application thereof in mixed fermentation to produce L-lactic acid
A technology of Bacillus coagulans and mixed fermentation, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, bacteria, and microorganism-based methods, can solve the problems of low conversion rate and low optical purity of fermentation products, achieve high conversion rate of sugar and acid, shorten fermentation time, significant Effects of social significance and economic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] This example illustrates the method of performing low-energy nitrogen ion implantation mutagenesis screening on the original strain of Bacillus coagulans.
[0042] The specific steps for the first step of low-energy nitrogen ion implantation mutagenesis screening are as follows:
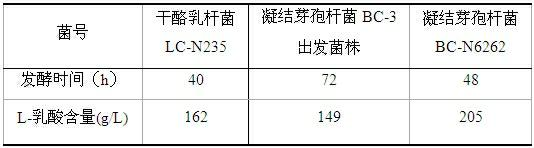
[0043] (a) Preparation of single spore suspension: take the original starting strain of Bacillus coagulans BC-3 cultured at 40~45°C for 2~3 days and add 10 mL of sterile water to the fresh slant, scrape and wash the spores and pour them on the glass beads with certain amount Shake well in a 250mL conical flask for 20min (250rpm), break up the spore chains, filter through three layers of degreasing gauze, count the filtrate with a hemocytometer, and adjust the spore concentration by 10 6 individual / ml.
[0044] (b) Low-energy nitrogen ion implantation mutagenesis: take 0.1 mL of the spore suspension in step (a) and evenly spread it on a sterile plate, and perform low-energy nitrogen ion implan...
Embodiment 2
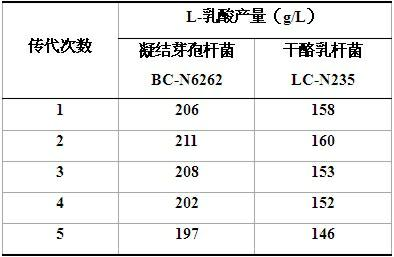
[0059] This example illustrates the genetic stability of high-yield strains Bacillus coagulans BC-N6262 and Lactobacillus casei LC-N235. The results of the subculture fermentation test are shown in Table 2:
[0060] Table 2
[0061]
[0062] From the experimental results, it can be seen that after 5 consecutive passages, the mutant strain Bacillus coagulans BC-N6262 has a relatively stable L-lactic acid production and good passage stability. In addition, the stability of Lactobacillus casei LC-N235 is also ideal. Both can be used as production strains for further research and development.
Embodiment 3
[0064] This example illustrates the production of L-lactic acid by mixed fermentation of Bacillus coagulans BC-N6242 and Lactobacillus casei LC-N235.
[0065] The medium formula described in this embodiment (% is mass percent):
[0066] Plate basic medium: glucose 5.0%, peptone 1.0%, beef extract 0.3%, yeast extract 0.3%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.05%, heavy calcium carbonate 3.0%, agar 1.2%, the rest is water, pH 7.0.
[0067] Slant medium: glucose 0.5%, peptone 1.0%, beef extract 0.3%, yeast extract 0.3%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.05%, heavy calcium carbonate 0.3%, agar 1.2%, the rest is water, pH 7.0.
[0068] Seed medium: glucose 6.0%, peptone 1.0%, yeast extract 1.0%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.05%, heavy calcium carbonate 3.0%, the rest is water, pH 7.0.
[0069] Fermentation medium: glucose 15%, peptone 0.05%, yeast extract 1.5%, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.05%, heavy calcium carbonate 7.5%, the rest is water, pH 7.0.
[0070] Inoculate the sc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com