Method for removing lead in cupper sulfate preparation process
A preparation process, copper sulfate technology, applied in copper sulfate and other directions, can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting feed, many processes, low removal rate, etc., and achieves deep lead removal. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
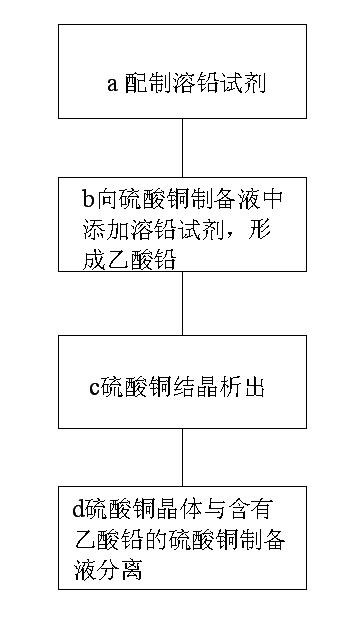
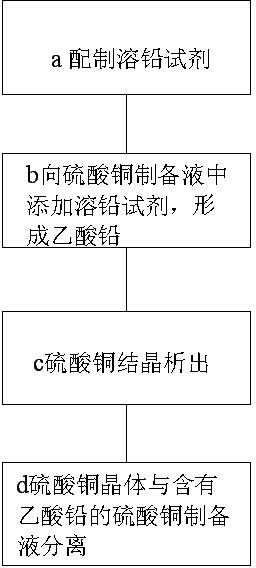
[0032] Pump 1500L of the same high-lead copper hydroxide slurry prepared from PCB etching waste liquid into two 2000L reactors A and B respectively for use.
[0033] While stirring, only add 1KG ammonium acetate into reactor A, then add sulfuric acid into reactors A and B to raise the temperature, cool and crystallize, separate and dehydrate to obtain copper sulfate products A and B. The results of lead detection in products are shown in Table 1.
[0034] project
[0035] Table 1
Embodiment 2
[0037] Pump 1500L of the same high-lead copper hydroxide slurry prepared from PCB etching waste liquid into two 2000L reactors A and B respectively for use.
[0038] While stirring, only add 5KG sodium acetate to reactor A, then add sulfuric acid to both reactors A and B to raise the temperature, cool and crystallize, separate and dehydrate to obtain A and B copper sulfate products. The results of the detection of lead in the product are shown in Table 2.
[0039] project
[0040] Table 2
Embodiment 3
[0042] Into two 2000L reactors A and B, respectively, pump 1800L of low-concentration copper sulfate solution containing excessive lead, prepared from copper ore or scrap copper, for use.
[0043] While stirring, only add 10KG copper acetate to reactor A, then heat, concentrate and crystallize the two reactors A and B respectively, and obtain A and B copper sulfate products after separation and dehydration. The results of the detection of lead in the product are shown in Table 3.
[0044] project
[0045] table 3
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com