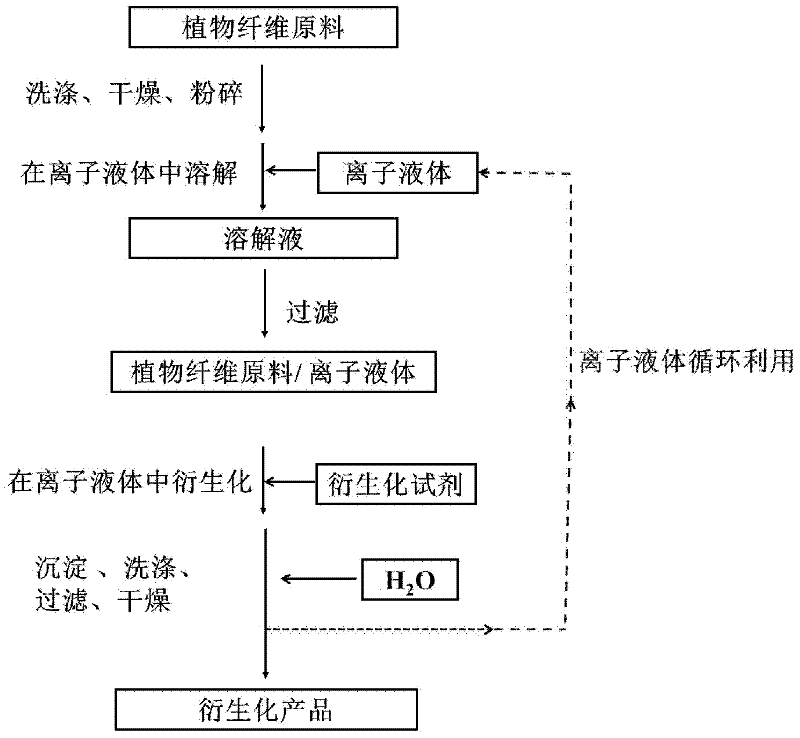
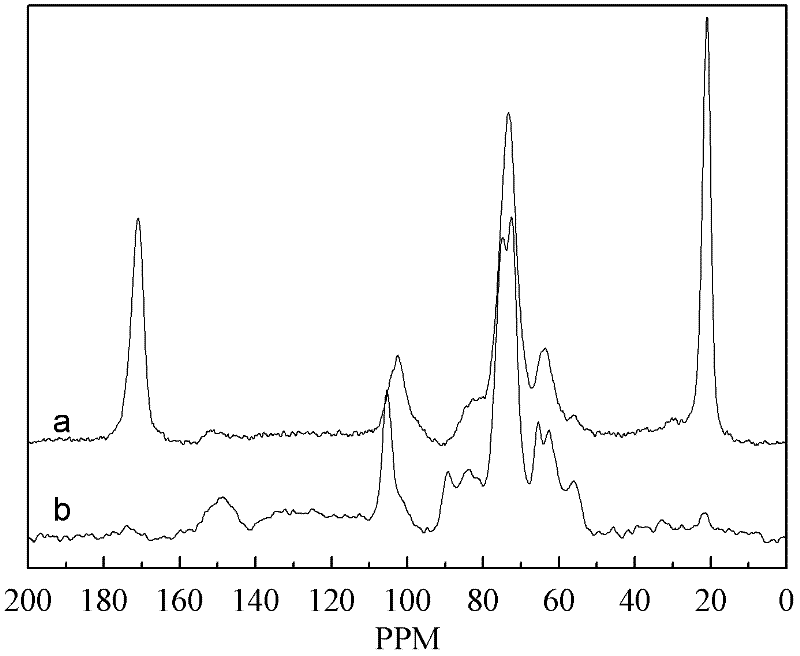
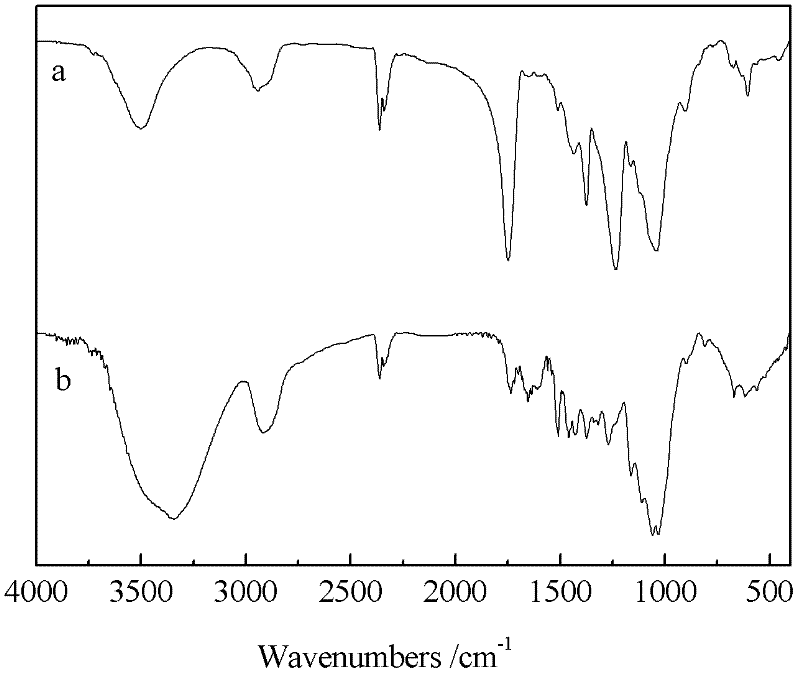
Method for homogeneously derivatizing plant fiber raw material by taking ionic liquid as medium
A plant fiber and ionic liquid technology, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve problems such as process complexity, environmental pollution, and difficulty in effective solvent recovery, and achieve the effects of simple process, easy dissolution and recovery, and strong industrial application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh about 0.5 g of pine sawdust and 50.0 g of ionic liquid 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (AmimCl), put them into a round-bottomed flask, heat to 110°C with microwave, and vigorously stir mechanically for 2 hours. After the dissolution, use a 300-mesh stainless steel filter to filter and separate.
[0040] Add 1.4 g of acetic anhydride to the filtrate, heat at 70° C. for 2 h, and add water to precipitate the product after the reaction is complete. Filtration, washing, and drying yielded a derivatized product with a WPG value of 156%.
Embodiment 2
[0042] Weigh about 0.5 g of pine sawdust and 50.0 g of ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EmimAc), put them into a round-bottomed flask, heat to 100°C with microwave, and vigorously stir mechanically for 2 hours. After the dissolution, use a 400-mesh stainless steel filter to filter and separate.
[0043] Add 0.7 g of acetic anhydride to the filtrate, heat at 70° C. for 3 h, and add water to precipitate the product after the reaction is complete. Filter, wash, and dry to obtain a derivatized product with a WPG value of 95%.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Weigh about 0.5 g of pine sawdust and 50.0 g of ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (BmimCl), put them into a round-bottomed flask, heat to 100°C with microwave, and vigorously stir mechanically for 3 hours. After the dissolution, use a 280-mesh stainless steel filter to filter and separate.
[0046] Add 2.3 g of acetic anhydride to the filtrate, heat at 80° C. for 24 h, and add water to precipitate the product after the reaction is completed. Filtration, washing and drying yielded a derivatized product with a WPG value of 149%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com