Novel method for breeding kelp seedlings with gametophyte cloning method
A technology of gametophytes and new methods, applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, horticulture, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient high-quality macroalgae seedlings and cannot meet the needs of breeding, and achieve low cultivation costs, protection of germplasm resources, The effect of improving quality and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
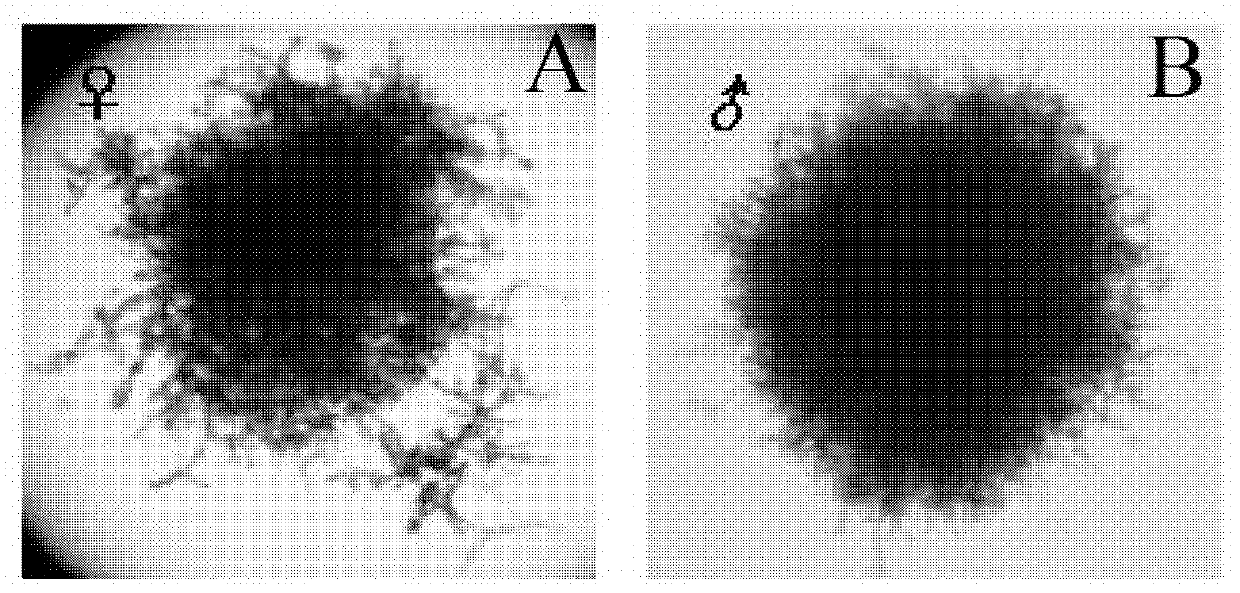
[0027] This experiment was conducted from June 2011 to November 2011. The macroalgae species is Macrocystis Pyrifera, and the male and female gametophytes will be cloned and reproduced in June.
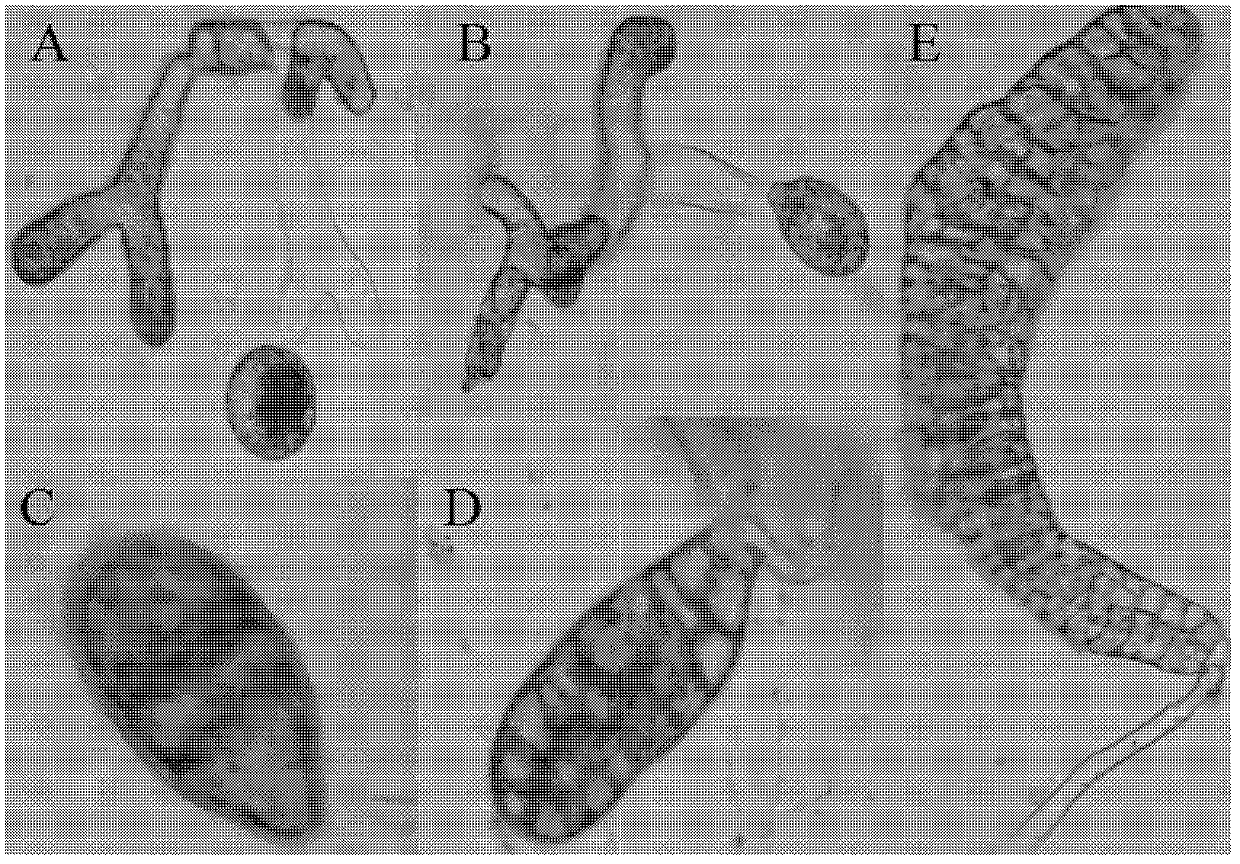
[0028] (1) Cloning and expansion When the zoospores of macroalgae develop to the gametophyte stage, under an inverted microscope (the microscope is Nikon Ti-U, the magnification is 100 times), a female cell and a male cell are separated by capillary separation technology Separate from male and female gametophytes, put the separated cells into 100ml sterile seawater with nutrient salt for culture, keep the temperature and culture temperature at 8℃ during operation, and the light intensity is 20-40μE m -2 s -1 , The nutrient salt is in sterilized seawater: KNO 3 1.2×10 -4 mol / L, KH 2 PO 4 1.2×10 -5 mol / L. Male and female cells develop into male and female gametophytes and continue to multiply. The environmental conditions during the propagation process are: the temperature is kept at 10℃,...
Embodiment 2
[0032] This experiment was conducted from July 2011 to December 2011. The macroalgae species is Macrocystis Pyrifera, and the cloning of male and female gametophytes began in July.
[0033] (1) Cloning and propagation When the zoospores of macroalgae develop to the gametophyte stage, they are separated from a female cell and a male cell under an inverted microscope (the microscope is Nikon Ti-U, the magnification is 100 times). Separate the male and female gametophytes. Put the separated cells into 100ml sterile seawater with nutrient added and culture them separately. During operation, the temperature and culture temperature are kept at 7℃, and the light intensity is 20-40μEm. -2 s -1 , The nutrient salt is in sterilized seawater: KNO 3 1.5×10 -4 mol / L, KH 2 PO 4 1.5×10 -5 mol / L. Male and female cells develop into male and female gametophytes and continue to multiply. The environmental conditions during the propagation process are as follows: the temperature is maintained at 15...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com