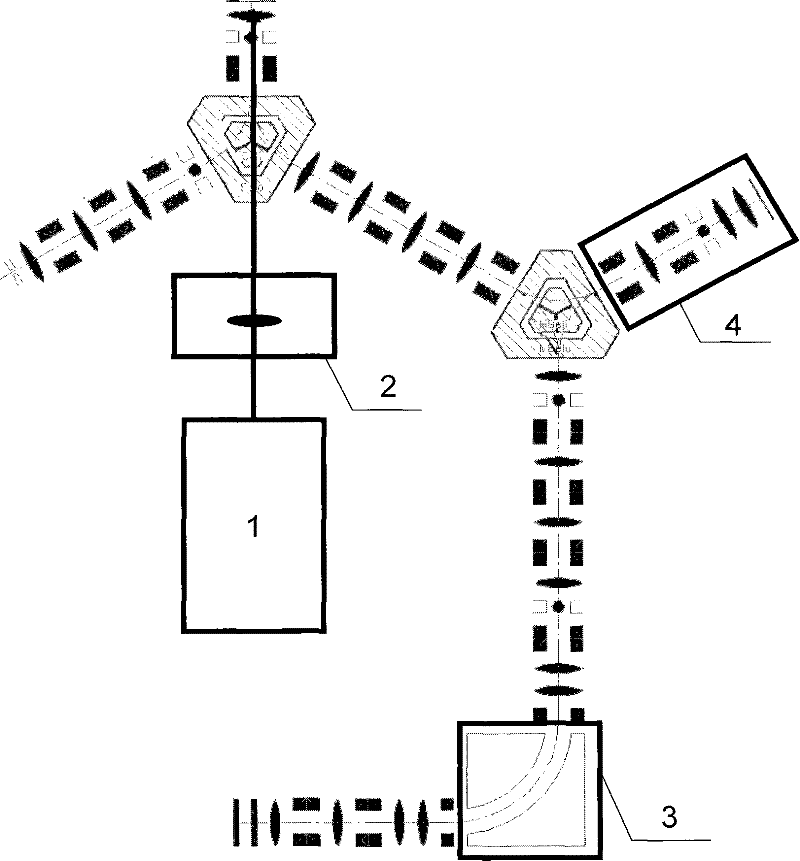
High-spatial-resolution photoemission electron microscope (PEEM) with ultraviolet or deep ultraviolet laser light source
An electron microscope and high spatial resolution technology, applied in the field of surface science research, can solve problems such as limited resources, poor applicability, and huge equipment, and achieve the effect of improving spatial resolution, high spatial resolution, and improving utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] A monolayer graphene structure is grown on the Ru(0001) single crystal surface. The graphene / Ru(0001) surface was studied by PEEM imaging using Hg lamp light source and deep ultraviolet laser (177nm) as excitation light source respectively. image 3 (a) and (b) are PEEM images recorded with Hg lamp light source and deep ultraviolet laser (177nm) as excitation light source, respectively. Image size is 10 microns. Only the graphene structure exhibits a higher gray scale when excited by the Hg lamp, and the photoelectron signal on the surface of the Ru substrate is weaker, appearing as a dark area, and its surface structure cannot be distinguished. A deep ultraviolet laser was used to excite the surface because its higher energy can simultaneously excite photoelectron emission from the graphene and Ru surface regions. Laser PEEM realizes the ability to distinguish the surface structure of the two structures at the same time. This implementation case shows that the deep ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A monolayer graphene structure is grown on the Ru(0001) single crystal surface. The PEEM imaging study of graphene / Ru(0001) surface was carried out with deep ultraviolet laser (177nm) as excitation light source. Figure 4 PEEM images excited by deep-UV laser without energy resolution (a) and with energy resolution (b). Image size is 10 microns. Using an energy analyzer can selectively pass photoelectrons with specific energies, which can further improve the contrast and resolution of PEEM images. This result shows that the energy-resolved PEEM image contrast is greatly improved (b), while the non-energy-resolved PEEM image has poor contrast in the graphene and Ru regions. This implementation example demonstrates that energy resolution can be achieved with an energy analyzer, further improving the quality of PEEM imaging.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The Si(001) with surface reconstruction is used as the sample, and the low-energy electron beam is used as the excitation source to form a LEEM image. Figure 5 Low-energy electron microscopy (LEEM) images excited by a low-energy electron beam with aberration correction (a) and without aberration correction (b). Image size is 0.6 microns. This result shows that the spatial resolution of LEEM with aberration correction function reaches 2.08nm, and the resolution without aberration correction function is 7.6nm. The reduction in spatial resolution caused by spherical and chromatic aberrations is reduced after the introduction of the aberration corrector. This implementation case illustrates the important role of the aberration corrector in improving the imaging quality, especially the spatial resolution, in the PEEM technique.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com