Segment parallel coding method of feedforward convolutional code
A coding method and convolutional code technology, applied in the direction of using convolutional code error correction/error detection, data representation error detection/correction, etc., can solve the problem that the number cannot be large, unavailable, and the throughput of convolutional encoders can be improved and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing power consumption, reducing usage, and improving encoding throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
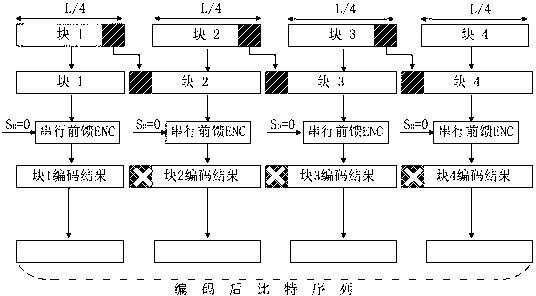
[0026] This embodiment corresponds to technical solution 1, and the corresponding structure diagram is image 3 .
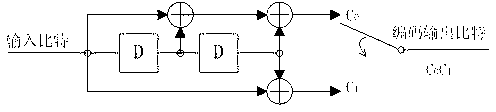
[0027] Selection of the corresponding serial feedforward convolutional encoder in this embodiment figure 1 The packet with a bit length of L is divided into 4 smaller blocks, which are called blocks 1–4 in this article. Block 1 contains L / 4 bits, and other blocks contain L / 4+2 bits. Two bits overlap between block 1 and block 2, block 2 and block 3, and block 3 and block 4.
[0028] Configure the initial state of each serial feedforward convolutional encoder before encoding: the initial state of the serial feedforward convolutional encoder of block 1 is known, and the serial feedforward convolutional encoders of block 2, 3, and 4 are known. The initial state of is set to all 0s.
[0029] Each block is independently coded in parallel by a serial feedforward convolutional encoder.
[0030] The first two input bits of blocks 2, 3, and 4 are the same as the last two input bi...
Embodiment 2
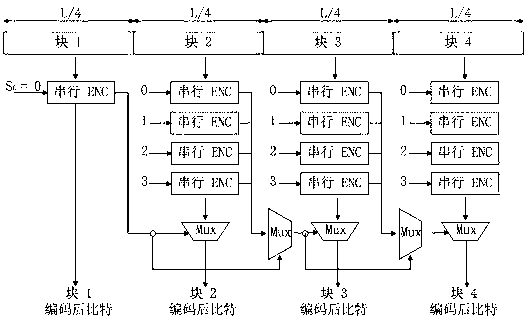
[0032] This embodiment corresponds to technical solution 2, and the corresponding structure diagram is Figure 4 .
[0033] In this embodiment, a packet with a bit length of L is divided into 4 smaller blocks, called blocks 1-4, and each block contains L / 4 bits. Selection of the corresponding serial feedforward convolutional encoder in this embodiment figure 1 Structure.
[0034] Each block is independently coded in parallel by a serial feedforward convolutional encoder. Configure the initial state of each serial feedforward convolutional encoder before encoding: the initial state of the serial feedforward convolutional encoder of block 1 is known, and the serial feedforward convolutional encoders of block 2, 3, and 4 are known. The initial state of is set to all 0s.
[0035] The serial feedforward convolutional encoders of each block work independently and in parallel, and the encoding is completed in L / 4 clock cycles. In the input of the serial feedforward convolutional encoder ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com