Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
一种免疫球蛋白、蛋白质的技术,应用在对免疫球蛋白具有亲和性的蛋白质和免疫球蛋白结合性亲和配体领域,能够解决没有导入等问题,达到高耐碱性、充分抗体酸解离特性的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0138] Example 1: Preparation of DNA encoding wild-type C domain (C-wild type)
[0139]Using the expression vector pNK3262NX encoding wild-type protein A as a template, the oligonucleotide primers of sequence number 19-20 were used for PCR to amplify the DNA fragment (177bp) encoding C-wild type (sequence number 5). The pNK3262NX used as a template is a protein A expression vector in which a part of pNK3262 has been modified, which encodes wild-type protein A from which a part of the cell wall binding domain X and the like have been removed (International Publication No. WO 06 / 004067). The nucleotide sequence encoding C-wild type obtained in this Example is shown in SEQ ID NO: 21. In addition, the oligonucleotide primers shown in SEQ ID NO: 19-20 were designed such that the DNA amplified using them had restriction enzyme recognition sites of BamHI and EcoRI on the outside of the gene encoding C-wild type point, and has a Cys residue on the C-terminal side (after Lys-58) of ...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Example 2: Preparation of DNA encoding wild type B domain (B-wild type)
[0143] Such as figure 1 As shown, the amino acid sequence of B-wild type (SEQ ID NO: 4) is a sequence obtained by introducing mutations of T23N, V40Q, K42A, E43N, and I44L into C-wild type. Therefore, the DNA encoding the B-wild type was prepared by introducing mutations T23N, V40Q, K42A, E43N, and I44L into the DNA encoding the C-wild type (SEQ ID NO: 21). Using the C-wild-type expression plasmid obtained in Example 1 as a template, and using the oligonucleotide primers shown in SEQ ID NO: 22-23, such a plasmid was obtained, which contained the encoding method and introduced into the C-wild-type by the QuickChange method. The gene for the amino acid sequence of the T23N mutation. In addition, using the obtained plasmid as a template, using the oligonucleotide primers shown in SEQ ID NO: 24-25, to obtain such a GST fusion type B-wild type expression plasmid, which contains V40Q, K42A introduc...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Example 3: Introduction of mutations into Gly-29
[0147] Using the C-wild-type expression plasmid obtained in Example 1 and the B-wild-type expression plasmid obtained in Example 2 as templates, using the primers of sequence numbers 27-52 shown in Table 1, various coding variants were obtained using the QuickChange method. Gene.
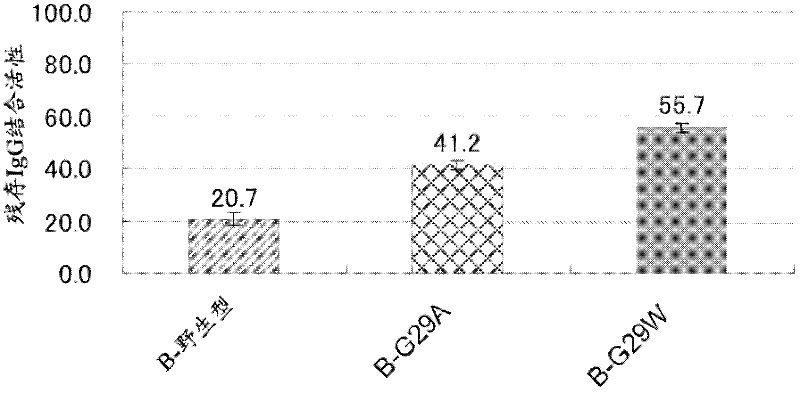
[0148] Using the C-wild-type expression plasmid as a template, replace Gly-29 in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 5 with Val, Leu, Ile, Tyr, Phe, Thr, Trp, Ser, Asp, Glu, Arg, His or Met, Various expression plasmids encoding the C domain variant (C-G29X) described in any one of SEQ ID NO:6-18 were obtained. Similarly, using the B-wild-type expression plasmid as a template, replace Gly-29 in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 4 with Val, Arg, Asp or Trp to obtain the B structure described in any one of the coding sequence numbers 53-56 Various expression plasmids for the domain variant (B-G29X).
[0149] Transformation of Escheric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com