Infrared spectrum interferometer and infrared spectrometer employing interferometer
A technology of infrared spectroscopy and interferometer, applied in spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromator, interference spectroscopy, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as translation sensitivity, and achieve the effect of enhancing the ability to resist environmental interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
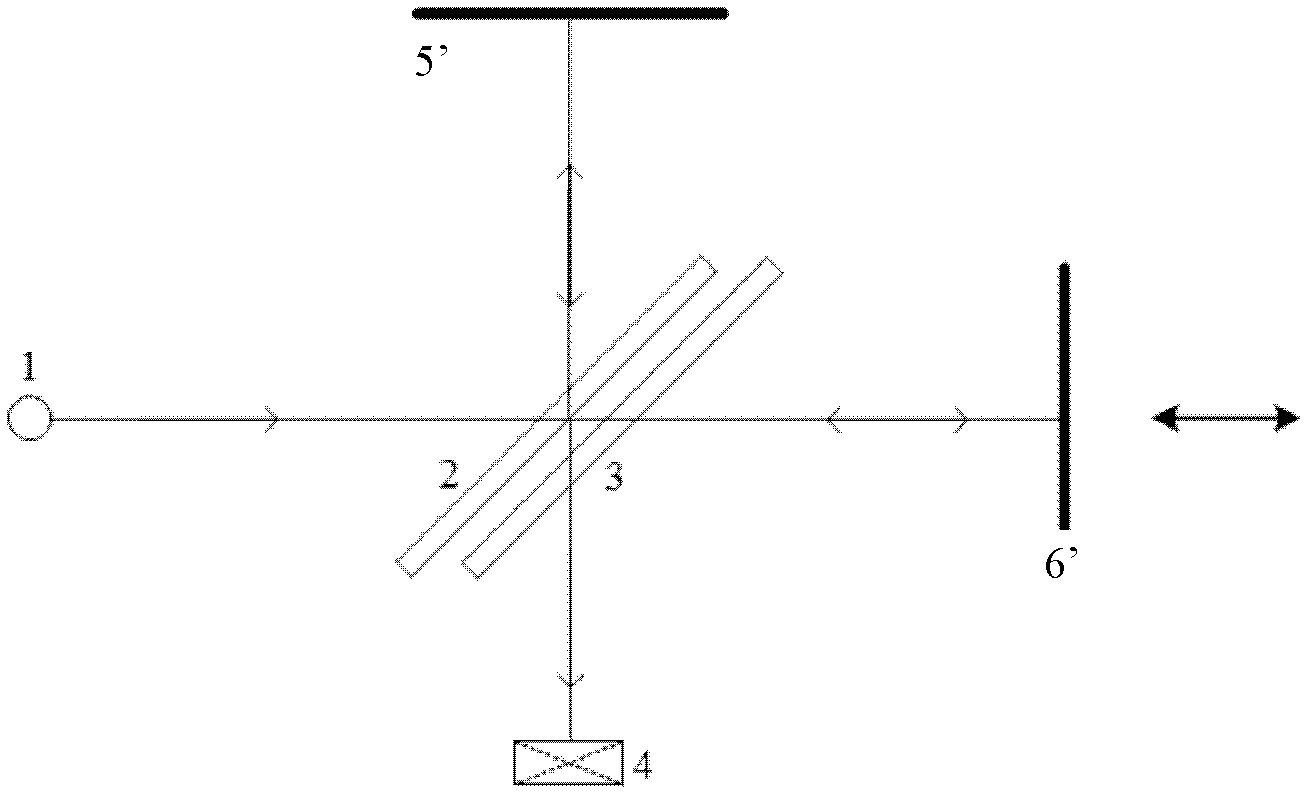
[0040] Such as image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of an optical path of the infrared spectral interferometer of the present invention, and at the same time image 3 It can also be a schematic structural view of the infrared spectrum interferometer of the present invention, which includes a light source 1 capable of emitting parallel rays, a beam splitter 2 arranged at an angle of 135 degrees with the parallel rays, and sequentially on the transmission light path of the beam splitter 2 A compensating mirror 3, a moving cube corner 8 that can move left and right along its own optical axis direction, a fixed first flat mirror 6 that can reflect the light emitted by the moving cube corner 8 back along the original optical path, are arranged on the side of the beam splitter 2 A fixed fixed cube mirror 7 and a fixed second plane mirror 5 that can reflect back the emitted light of the fixed cube mirror 7 along the original optical path are sequentially arranged on the reflected li...
Embodiment 2
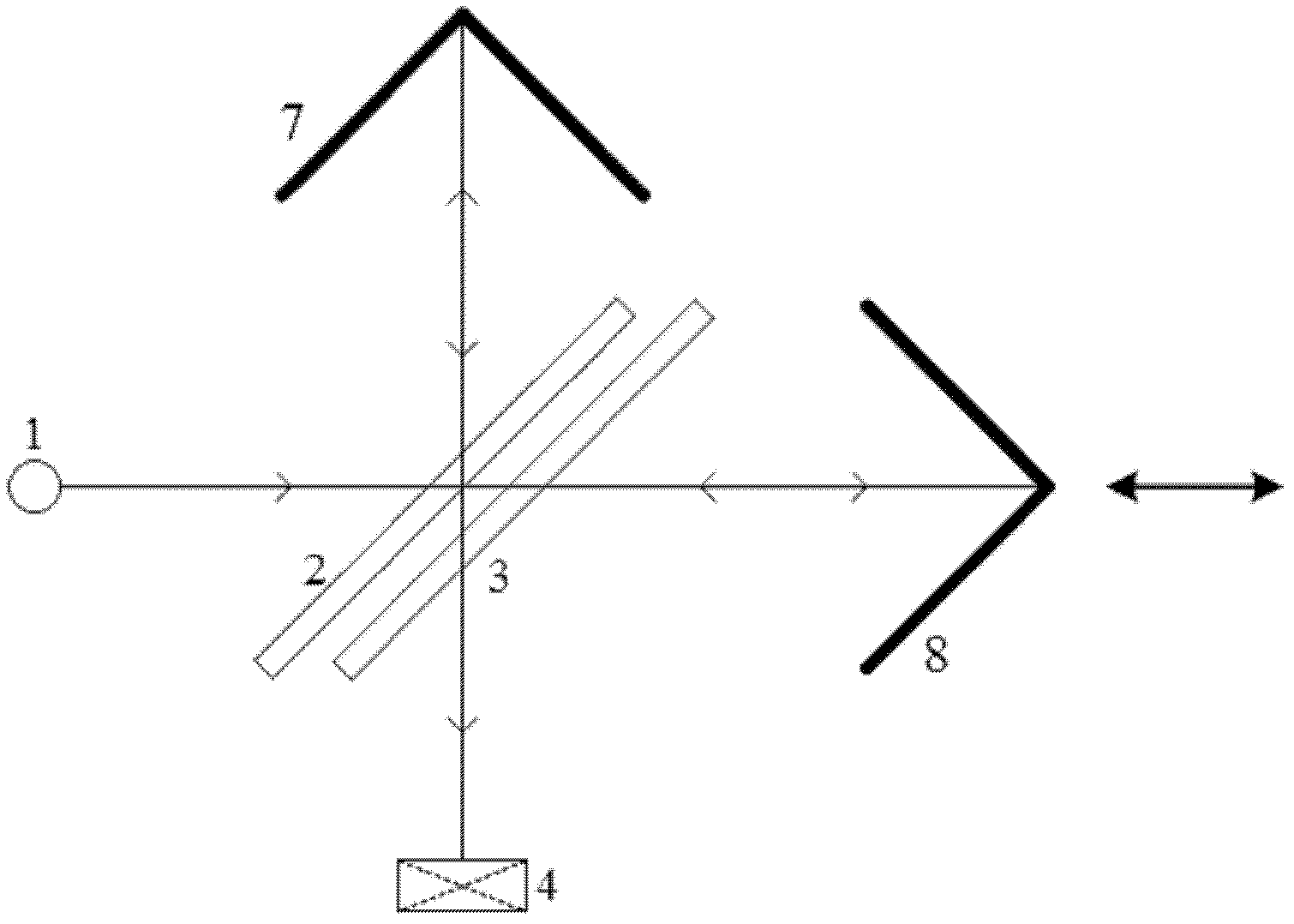
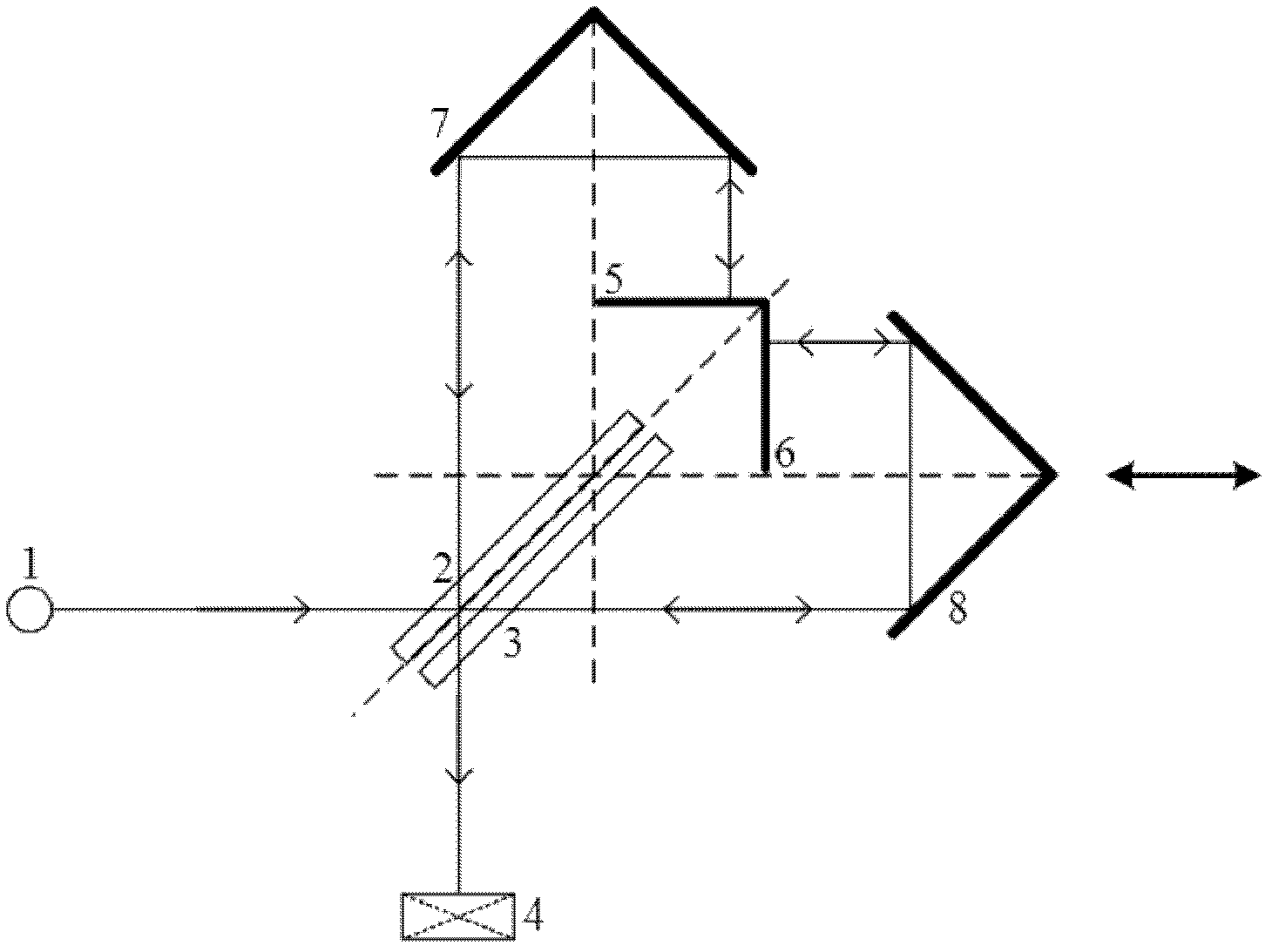
[0048] Figure 4 It is another optical path schematic diagram of the infrared spectrum interferometer of the present invention; at the same time Figure 4 It can also be another structural schematic diagram of the infrared spectrum interferometer of the present invention. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the angle between the first plane mirror 6 and the second plane mirror 5 is 60 degrees, and at this time, the beam splitter 2 is set at an angle of 120 degrees to the incident parallel light. The optical axis of the fixed cube corner mirror 7 is perpendicular to the second plane mirror 5 and passes through the edge of the second plane mirror 5 , and the optical axis of the movable cube cube mirror 8 is perpendicular to the first plane mirror 6 and passes through the edge of the first plane mirror 6 .
[0049] The structure with an included angle of 60 degrees is conducive to the utilization of the beam splitter 2. It can be calculated that in th...
Embodiment 3
[0051] In the infrared spectrum interferometer in embodiment 1, the slight position change and angle offset of the moving cube-corner 8 and the fixed cube-corner 7 will not affect the degree of interference of the interferometer. Compared with the prior art, the infrared spectrum has been greatly improved. The stability of the spectral interferometer. However, the surface of the beam splitter 2 coated with the beam splitting film must be strictly parallel to the angle bisector of the angle between the second plane mirror 5 and the first plane mirror 6, and the error should generally be within 1-5 arc seconds, and the relative position change is very important. The influence of the degree of interference is still considerable. For this reason, this embodiment proposes an optical monomer structure, so that the relative positions of the first plane mirror 6, the second plane mirror 5 and the beam splitter mirror 2 are fixed, so that the infrared spectrum interferometer can comple...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com