Material-in-air conveying theory principle and technical scheme of conveying material by fluid
A technology of fluid conveying and technical solutions, applied in the field of fluid jet conveying materials, can solve the problems of weakening conveying capacity, affecting the service life of pipeline equipment, and failing to reach the design index of the pneumatic continuous conveying project. Small, the effect of reducing the probability of pipe blockage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
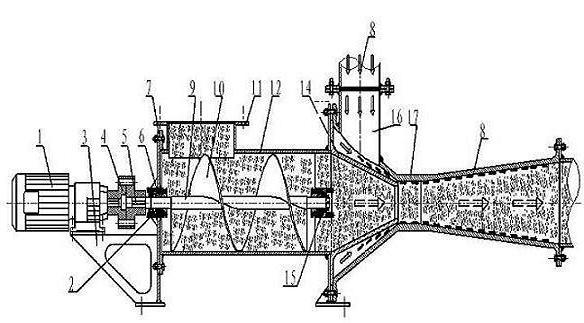
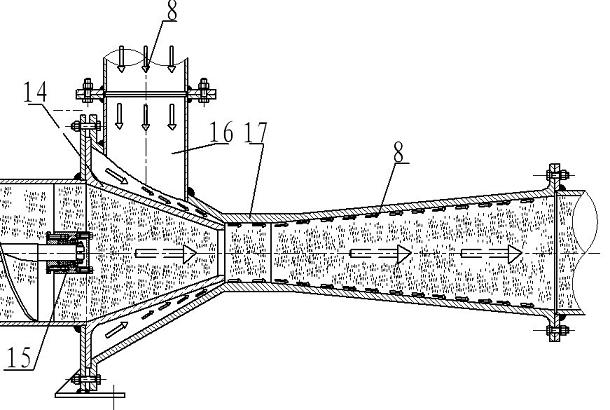
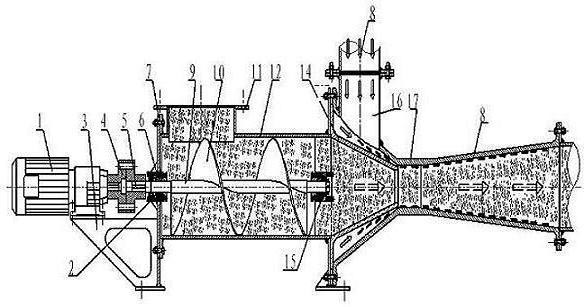
[0030] According to attached figure 1 , 2 As shown, start the power unit (1) and feed gas into the air inlet ⒃ at the same time, and add materials from the feed inlet ⑾. When the power part ⑴ starts, the output shaft of the power part is rigidly connected with the coupling ⑷, and the coupling ⑷ is rigidly connected with the screw pump shaft ⑼ through the key ⑸, thereby driving the rotation of the screw pump shaft ⑼, in which the screw pump shaft ⑼ is supported by the left end bearing Frame ⑼, the right end bearing support frame ⒂ cooperate; the screw pump shaft ⑼ is rigidly connected with the screw blade ⑽, so that the screw pump shaft ⑼ and the screw blade ⑽ rotate together. When the screw blade ⑽ rotates, it provides the speed of the axial movement of the material, and converts the circular motion of the screw blade ⑽ into the axial motion of the material. The screw blade ⑽ is respectively connected to the left end bearing support frame ⑵ and the right end bearing support f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com