Use of cardiotrophin- 1 for the treatment of metabolic diseases
A technology for cardiotrophin and metabolic diseases, applied in the field of cardiotrophin-1 for treating metabolic diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
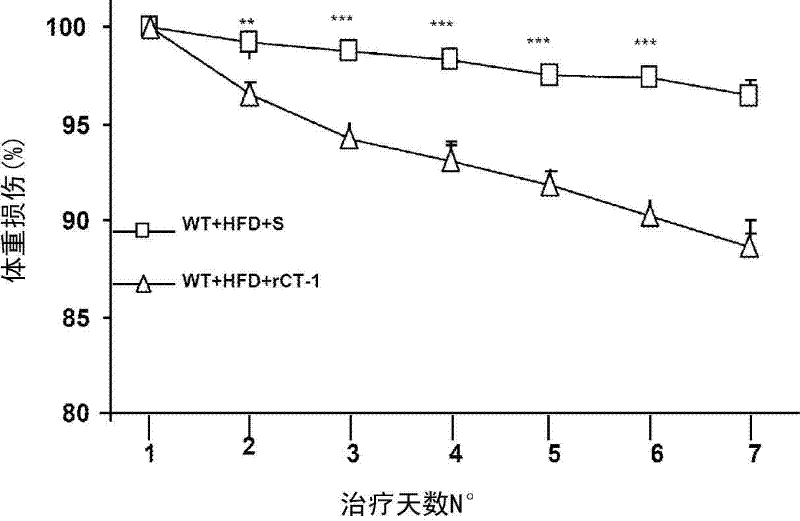
[0112] Effect of CT-1 on body weight
[0113] Obese mice were obtained by ingesting a high fat diet (HFD, 60% fat) for 3 months. Intravenous injection of rCT-1 (0.2 mg / kg / day) for 6 consecutive days resulted in a decrease in body weight ( figure 1 ). The doses used in this study did not induce febrile reactions (rectal temperature was measured daily during treatment).
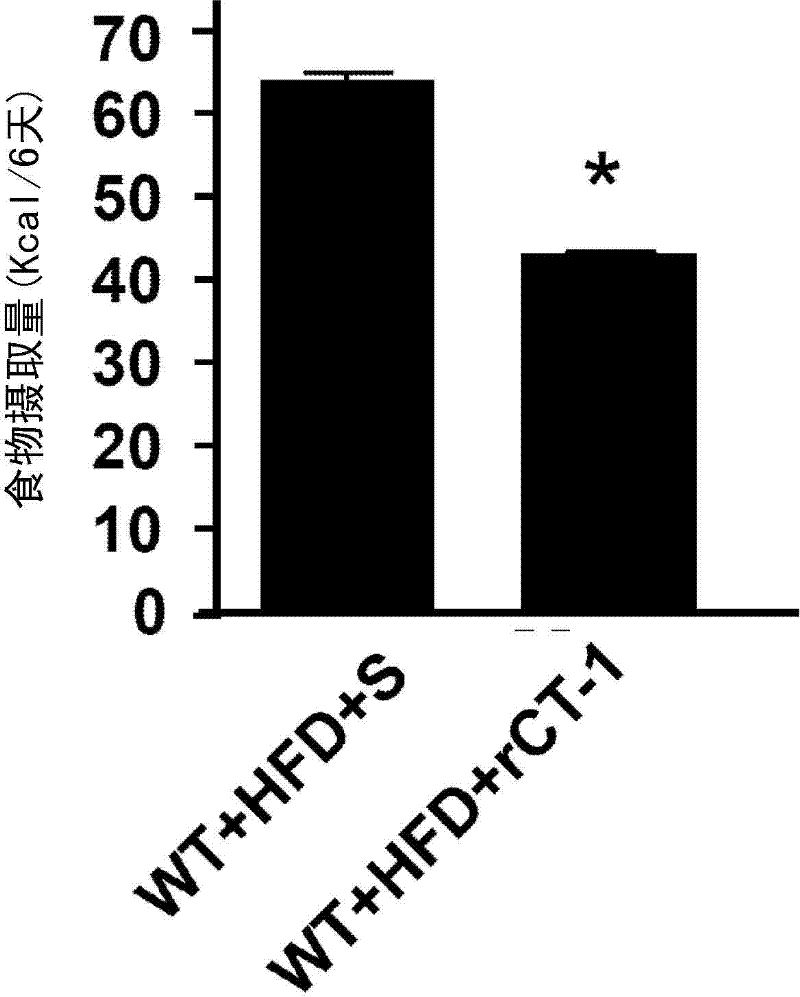
[0114] like figure 1 The obese mice fed with the indicated HFD and injected with the aforementioned 0.2 mg / kg / day dose of rCT-1 for 6 consecutive days observed a decrease in body weight, which was due to the appetite-suppressing effect of this cytokine ( figure 2 ). The graph shows the calorie intake over six days of treatment for the rCT-1 treated group and the corresponding control group treated intravenously with physiological serum.
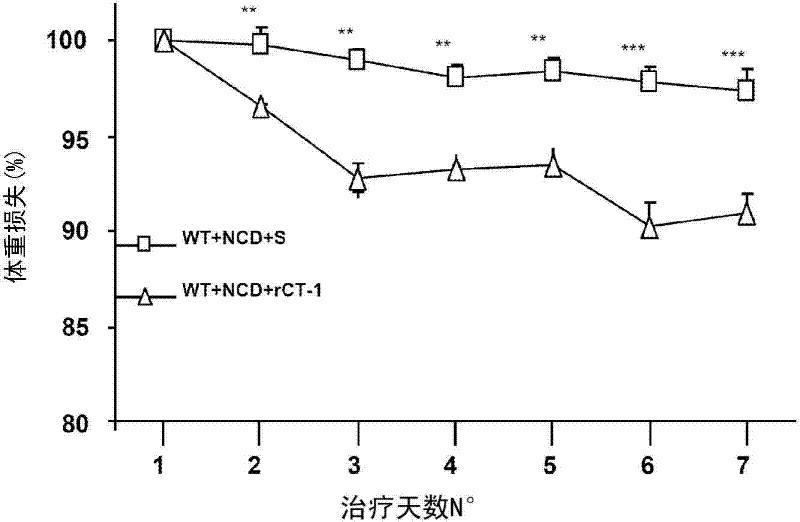
[0115] Similarly, continuous 6-day intravenous injection of rCT-1 (0.2 mg / kg / day) also caused weight loss ( image 3 ). The doses administered in this experiment did n...
Embodiment 2
[0118] CT-1 blood sugar lowering effect
[0119] To determine whether acute intravenous injection of a single dose of rCT-1 (10 μg) into C57BL / 6 mice (3 months old) would reduce baseline blood glucose levels, blood glucose levels were measured after 1 hr treatment with rCT-1 and saline serum. like Figure 5 As shown in A, rCT-1 significantly lowered the blood glucose level. Mechanisms of blood glucose lowering are not due to elevated blood insulin levels (eg, Figure 5 B), because the insulin levels of animals treated with rCT-1 and saline serum were not significantly different. Results are expressed as mean ± SE. n=5 animals per group, *p Figure 5 C shows a representative Western).
[0120] Acute administration of a single dose (10 μg) of rCT-1 suppressed blood glucose elevation after a high glucose diet. In order to study the effect of rCT-1 on postprandial blood glucose, mice (C57BL / 6, 3 months old) were used to carry out the following experiments: the mice were given ...
Embodiment 3
[0131] Different effects of CT-1 and CNTF
[0132] Figure 16 Shown are the results of experiments performed in rat adipocyte primary cultures to determine the ability of rCT-1 and CNTF to regulate adipocyte leptin secretion. Figure 16 A shows that rCT-1 treatment (72 hours) is able to suppress both basal and insulin-stimulated secretion of leptin (1.6 nM). However, these effects were not observed at the same concentration of CNTF ( Figure 16 B).
[0133] Figure 17Shown are the results of experiments performed in primary cultures of rat adipocytes to determine the ability of CT-1 and CNTF to regulate lipolysis in the presence or absence of insulin. The figure shows that CT-1 is able to induce the release of glycerol (measured by lipolysis) and inhibits the antilipolytic activity of insulin, whereas CNTF is not. These data suggest that CT-1 is able to mobilize fat and, as previously shown, increase beta oxidation in muscle, suggesting that this cytokine can reduce fat a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com