A method for isolation and identification of sea cucumber pathogenic bacteria
An identification method, a technology of pathogenic bacteria, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems that restrict the sustainable and stable development of the industry, economic losses, etc., and achieve the effects of rapid separation and identification of bacteria, early diagnosis, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1, separation and purification of dominant bacteria in the lesion
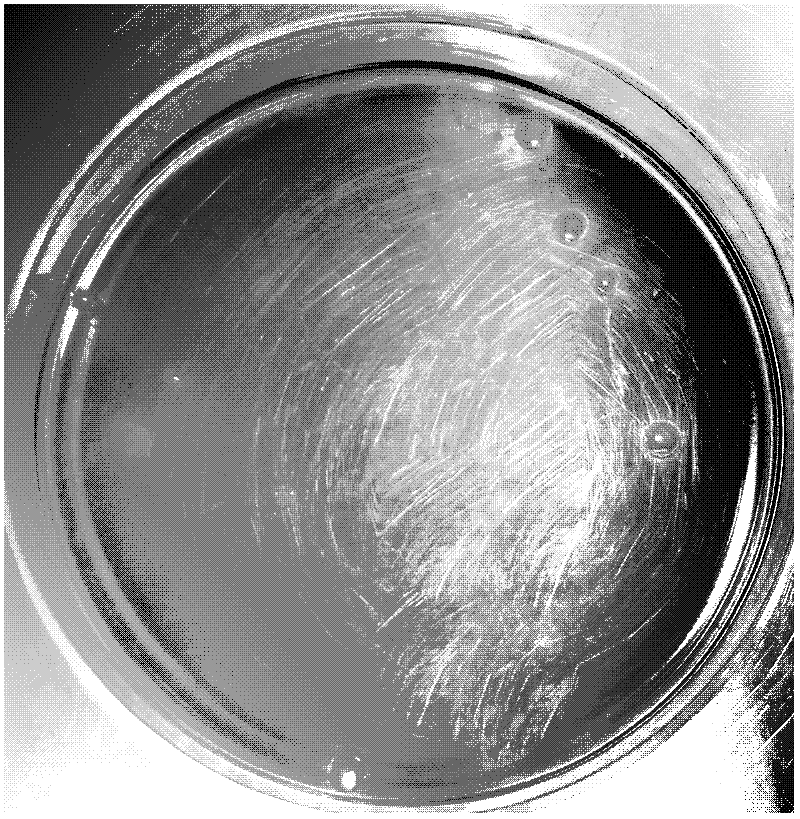
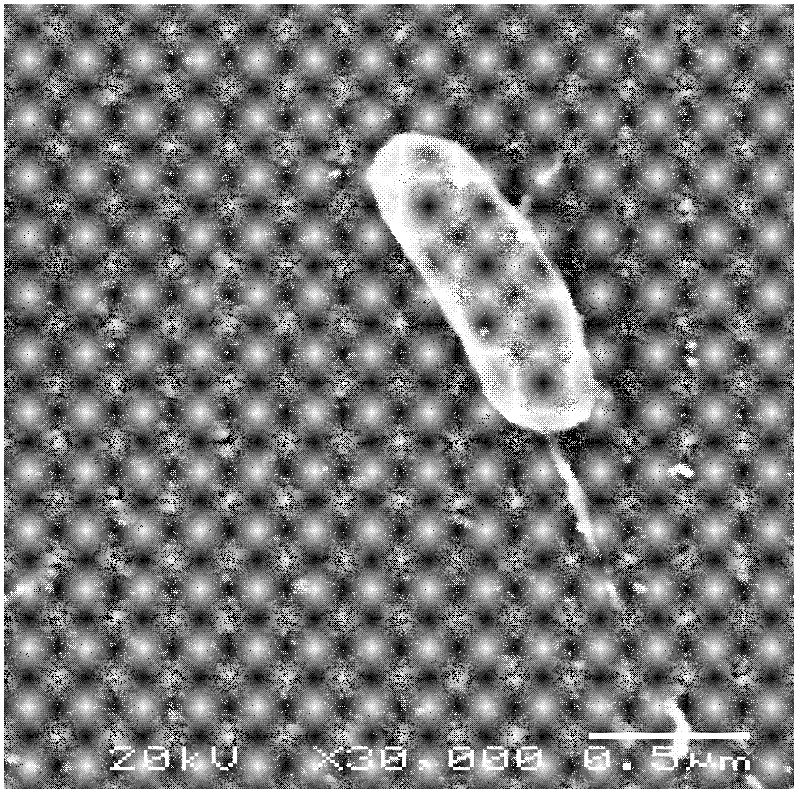
[0018] Take samples of sea cucumbers suffering from rotting skin syndrome (see figure 1 ) in the ultra-clean workbench, cut out 1cm × 1cm × 1cm tissue pieces, put them in a 5mL sterile centrifuge tube, and use sterilized ophthalmic scissors to homogenize to make a bacterial suspension. Streak on solid agar medium, culture in 24-28°C incubator for 48-72 hours, separate the colonies grown on the petri dish again by specific TCBS plate streak separation method, and culture in 24-28°C incubator Observe after 48-72, select a single colony according to the colony shape, color and bacterial culture characteristics, and then store the pure culture of the bacteria.
[0019] Results: The colony was in the shape of fried egg, flat, about 3-5mm in diameter, with raised surface, corn yellow, opaque, odorless, not easy to stir up the bacteria, and the colony was smooth and sticky. (See figure 1 )
Embodiment 2
[0020] Embodiment 2, strain preservation
[0021] Inoculate the single colony of the pure pathogenic bacteria prepared by the above method on the plate directly on the 2216E solid slope, place it in an incubator at 28°C for 24 hours, and then store it in a refrigerator at 4°C;
[0022] Long-term storage: culture the bacteria in 2216E liquid medium for about 5 to 6 hours, and the concentration of bacteria reaches the logarithmic growth phase OD 600 When = 0.2, add glycerin, adjust the volume concentration of glycerin to about 30-50%, and store in a -80°C refrigerator.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Embodiment 3, artificial inoculation infection experiment of pathogenic bacteria
[0024] (1) Preparation before the experiment
[0025] The plastic basin with a volume of about 8000mL was cleaned with detergent and then wiped and disinfected with 75% alcohol. After the alcohol evaporated, it was rinsed three times with filter-sterilized PBS. Inject 5000mL of seawater into each basin, and ventilate with the inflation valve. The temperature of the seawater is maintained at 18-25°C.
[0026] (2) Pretreatment of sea cucumber
[0027] The sea cucumbers retrieved from the farm were domesticated for 7 days in a laboratory environment with filter-sterilized seawater, and healthy individuals of similar size were selected, washed twice with sterilized PBS, and 10 were placed in each pot.
[0028] (3) Preparation of bacterial suspension
[0029] The isolated dominant strains were plated, cultured at 28°C for 48 hours, and the colonies were washed with filter-sterilized PBS to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com