Optoelectronic semiconductor device
A technology for optoelectronic semiconductors and optoelectronic devices, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor lasers, lasers, etc., can solve the problems of expensive and large wafer size, unavailability, high thermal expansion mismatch of GaN, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
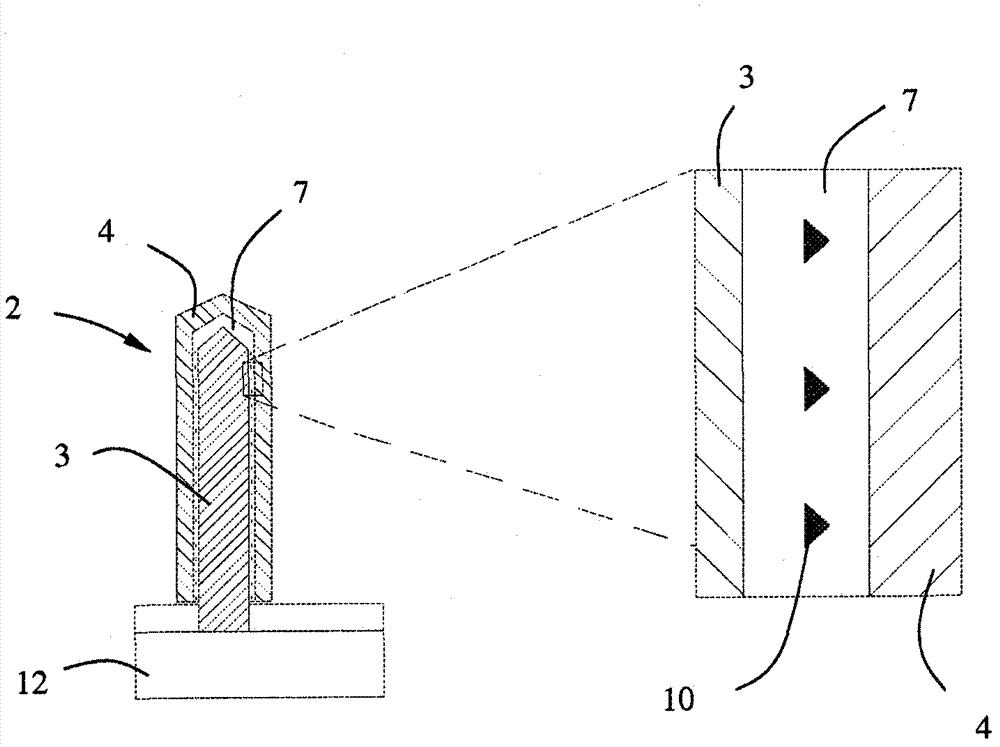
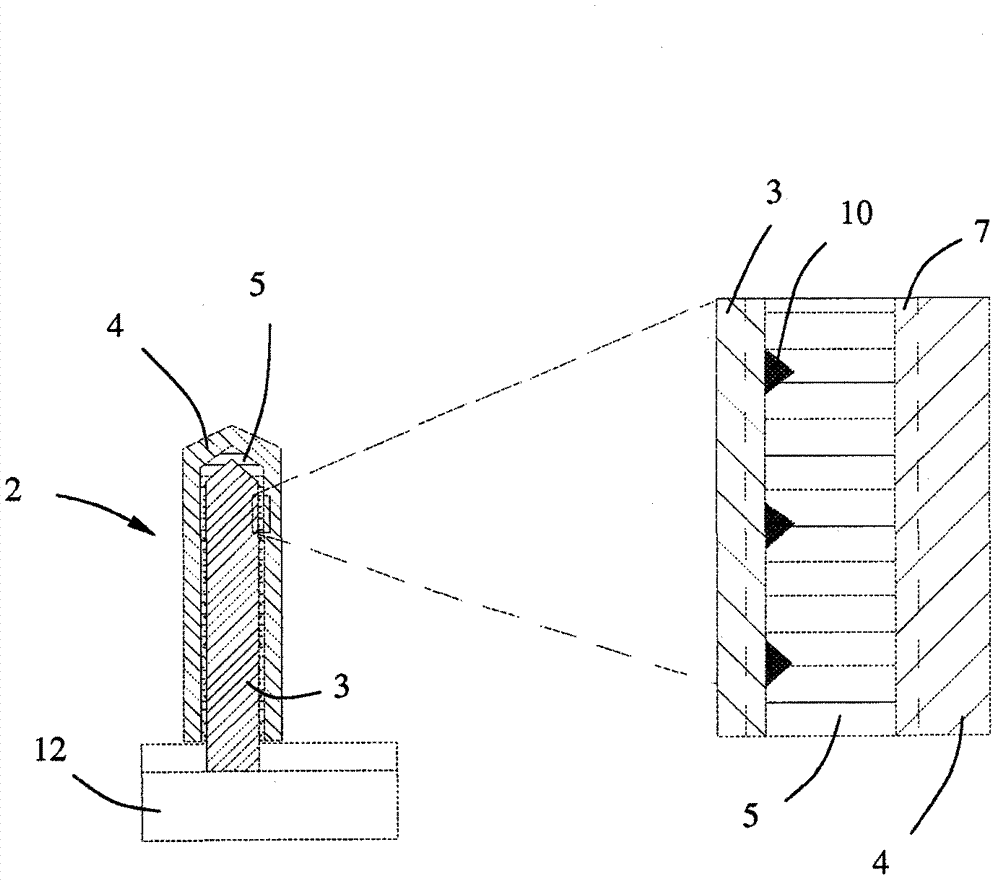
[0025] Nanowires are generally interpreted as nanostructures whose diameters are nanometer-sized. As the term "nanowire" implies, its lateral dimensions are on the order of nanometers and its longitudinal dimensions are unlimited. Such nanostructures are also commonly referred to as nanowhiskers, one-dimensional nanocomponents, nanorods, and the like. Although these terms imply an elongated shape, the nanowires may be tapered or stub-like, and since nanowires may have a variety of cross-sectional shapes, in this application the diameter is intended to mean effective diameter. Generally, nanowires are considered to have at least two dimensions, each no larger than 300 nm, but nanowires may have a diameter or width of up to about 1 um. The one-dimensional nature of the nanowires provides unique physical, optical and electronic properties. These properties can be used, for example, to form devices that exploit quantum mechanical effects or to form heterostructures of compositi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com