Method for extracting selenium from selenium-contained material
A process method and technology of process steps, applied in the direction of elemental selenium/tellurium, etc., can solve the problems of high copper content, low qualified rate of electrolytic silver powder, incomplete selenium precipitation, etc., and achieve shortening of technological process, reduction of production cost, and improvement of qualified rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
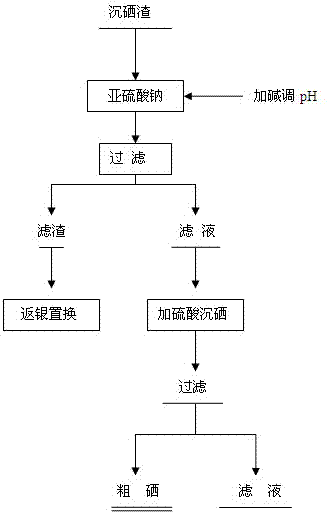
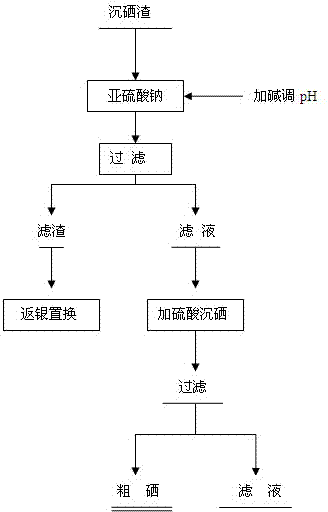
[0020] (1) First, add the dried selenium residue containing silver, copper, lead, and tellurium impurities into the reactor, add water to make slurry, turn on the stirring, and then slowly add sodium sulfite to control the liquid-solid ratio of the solution to 10:1, and the concentration of sodium sulfite 1mol / l, then add liquid alkali to adjust the pH value of the solution to 10;
[0021] (2) Stir and heat up, control the reaction temperature at 95°C, react for 1 hour, filter after the reaction is complete, and further recover selenium from the filtrate, so that selenium can be dissolved in alkaline sodium sulfite solution to form sodium selenosulfate which is easily soluble in water, while silver , copper and other impurities remain in the solution in solid form;
[0022] (3) Add sodium selenosulfate filtrate into the reaction kettle, add sulfuric acid reagent, adjust the final pH value of the solution to 4, start to heat up, turn on the stirring, and adjust the temperature ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] (1) First, add the dried selenium slag containing silver, copper, lead, and tellurium impurities into the reaction kettle, add water to make slurry, turn on the stirring, and then slowly add sodium sulfite to control the liquid-solid ratio of the solution to 20:1 and the concentration of sodium sulfite 2mol / l, then add liquid alkali to adjust the pH value of the solution to 12;
[0026] (2) Stir and heat up, control the reaction temperature at 90°C, react for 2 hours, filter after the reaction is complete, and further recover selenium from the filtrate, so that selenium can be dissolved in alkaline sodium sulfite solution to form sodium selenosulfate which is easily soluble in water, while silver , copper and other impurities remain in the solution in solid form;
[0027] (3) Add sodium selenosulfate filtrate into the reaction kettle, add sulfuric acid reagent, adjust the final pH value of the solution to 5, start to heat up, turn on the stirring, and adjust the tempera...
Embodiment 3
[0030] (1) First, add the dried selenium slag into the container, add water to slurry, turn on the stirring, and then slowly add sodium sulfite, control the liquid-solid ratio of the final solution to 20:1, and the concentration of sodium sulfite to 2mol / l, then add liquid alkali to adjust the solution The pH value is 12;
[0031] (2) Control the reaction temperature at 90°C and react for 2 hours. After the reaction is complete, filter and wash to remove impurity elements in the solution;
[0032] (3) Add sulfuric acid to the filtrate to adjust the pH value to 4, stir and heat up, adjust the temperature to 75°C, react for 2 hours, filter and wash the solution to obtain crude selenium with a purity of not less than 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com