Molecular markers of rice stripe virus disease-resistant major gene locus qSTV11
A molecular marker and major gene technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve the problems of environmental pollution, economic loss, field loss, etc., and achieve the effect of not being affected by the environment, clear location, and convenient identification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The detailed description of the present invention is as follows:
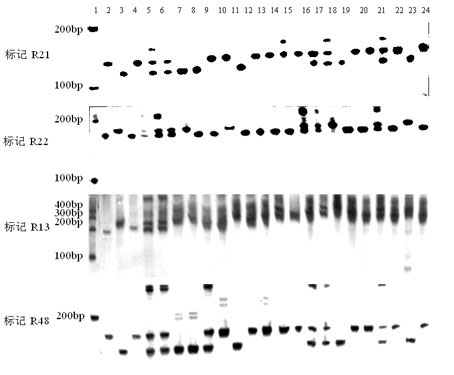
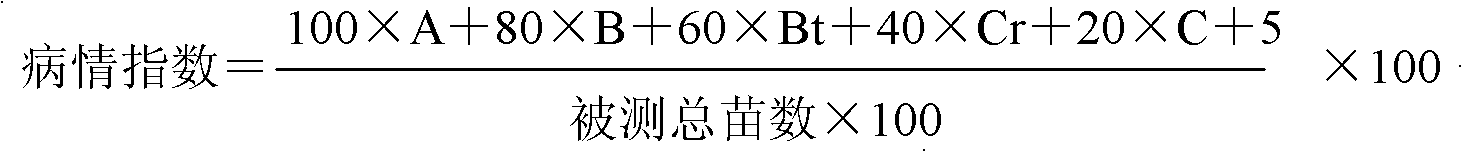
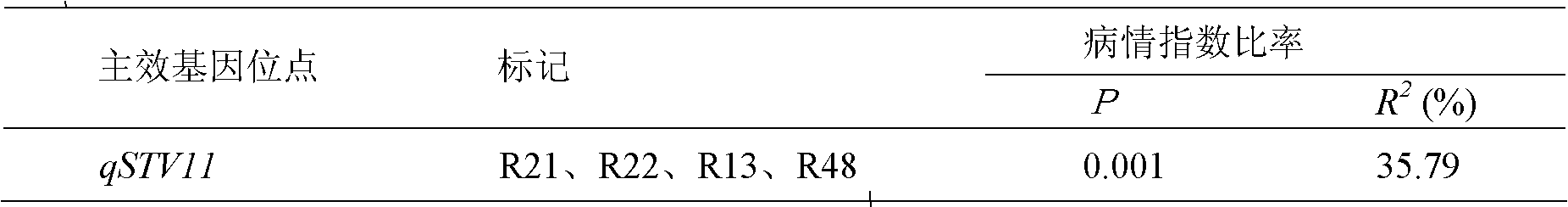
[0033] Studies have shown that there is a major gene locus that controls the stable expression of stripe leaf blight resistance at the same position on rice chromosome 11. Maeda H et al. (Maeda H, Nemoto H, Yagi T, Fukuta Y. QTL analysis for rice stripe disease resistance using recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from crossing between Milyang and Akihikari. In: China Association of Agricultural Science Societies, China National Rice Research Institute, China National Hybrid Rice Research and Development Center, China Foundation Society for Agricultural Science and Education (eds). Prospects of rice genetics and breeding for the 21st century-Paper collection of international rice genetics and breeding symposium. Beijing: China Agriculture Technology Press, 1999, 53~57.) Using the recombinant inbred line population of Miryang 23 / Qiuguang, it was detected that there was a QTL for resistance to stripe le...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com