Protecting component
A technology for protecting components and components, applied in electrical components, emergency protection devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in cost reduction, unsatisfactory, and difficult to achieve compactness, and achieve the effect of easy assembly and manufacturing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
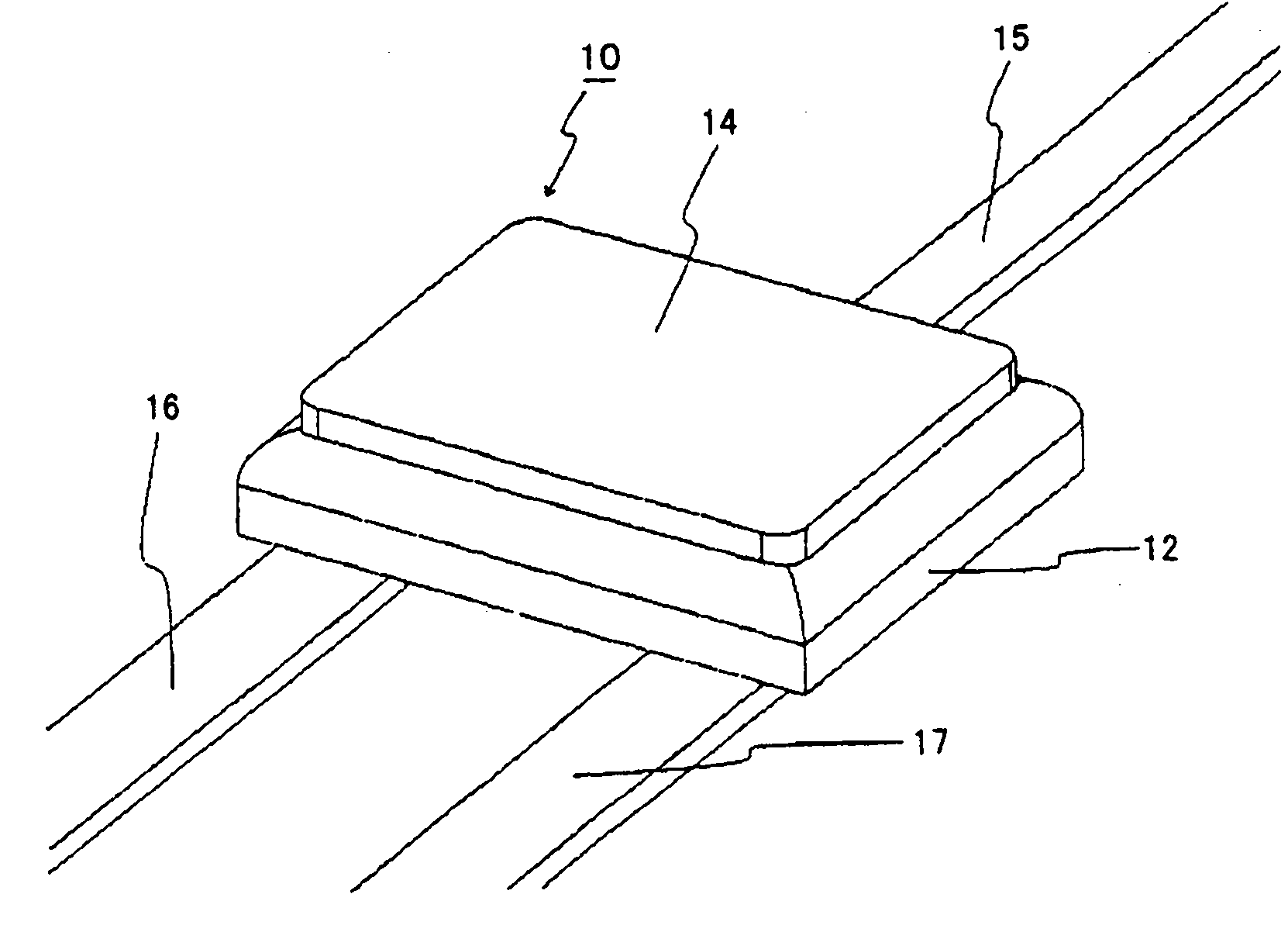
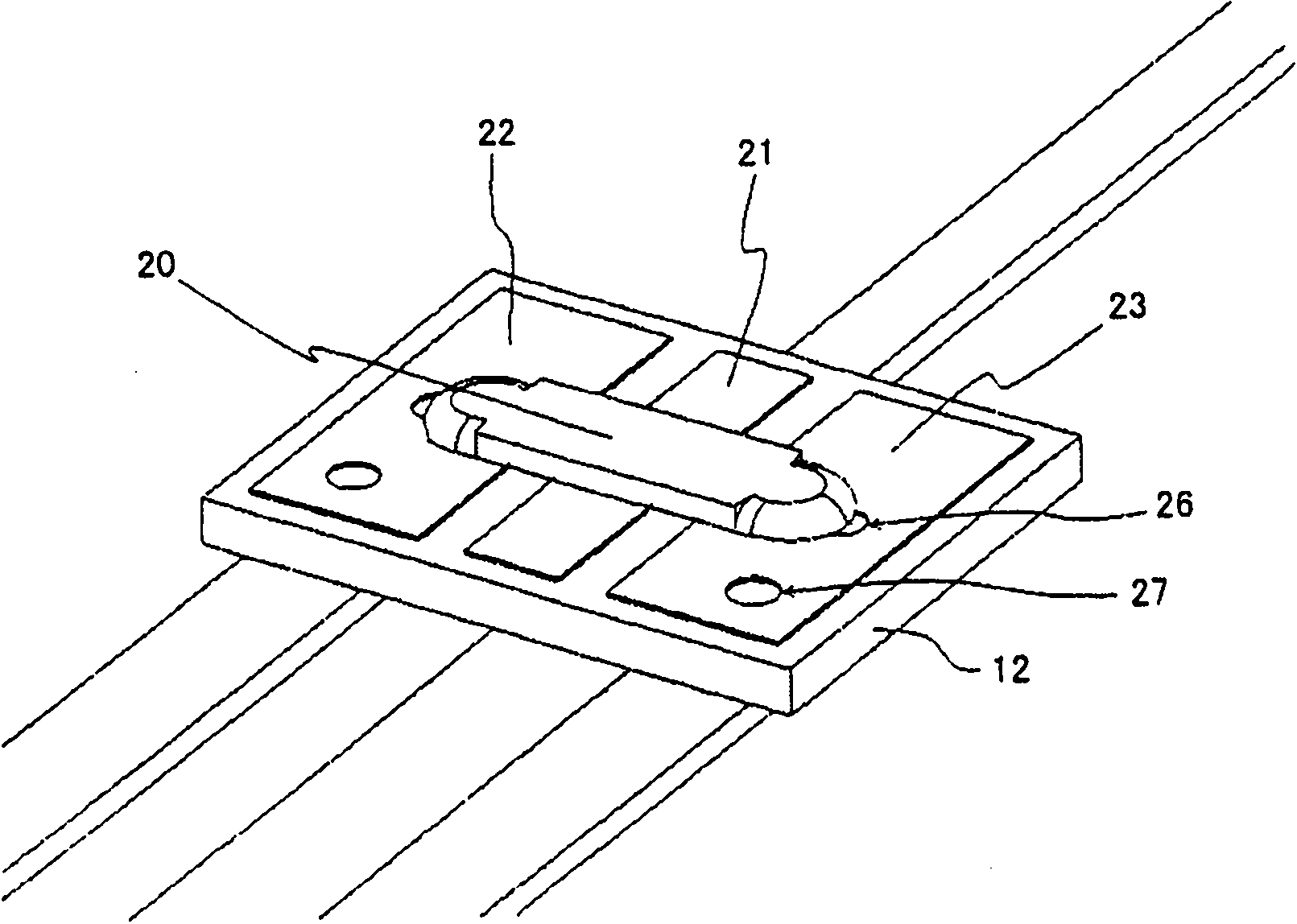
[0043] Hereinafter, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. The axial lead type protection element 10 of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown in a perspective view on its surface side, it includes: a ceramic chip body 12; A fuse element, a resistance heating element in the through hole, etc.; and lead-out leads 15-17, and these lead-out leads 15-17 are connected to the pattern electrodes on the back side. Here, patterned electrodes are formed on both surfaces of the ceramic chip body 12, a fusible alloy fuse element is installed on the surface side, lead wires for leading out are installed on the back side, and a resistance heating element is installed in the through hole of the chip body. . figure 2 It is a perspective view showing the state before the housing cover 14 of the package is mounted. On the pattern electrodes 21 to 23 provided on the ceramic chip body 12, a fusible alloy fuse element 20 wh...
Embodiment 2
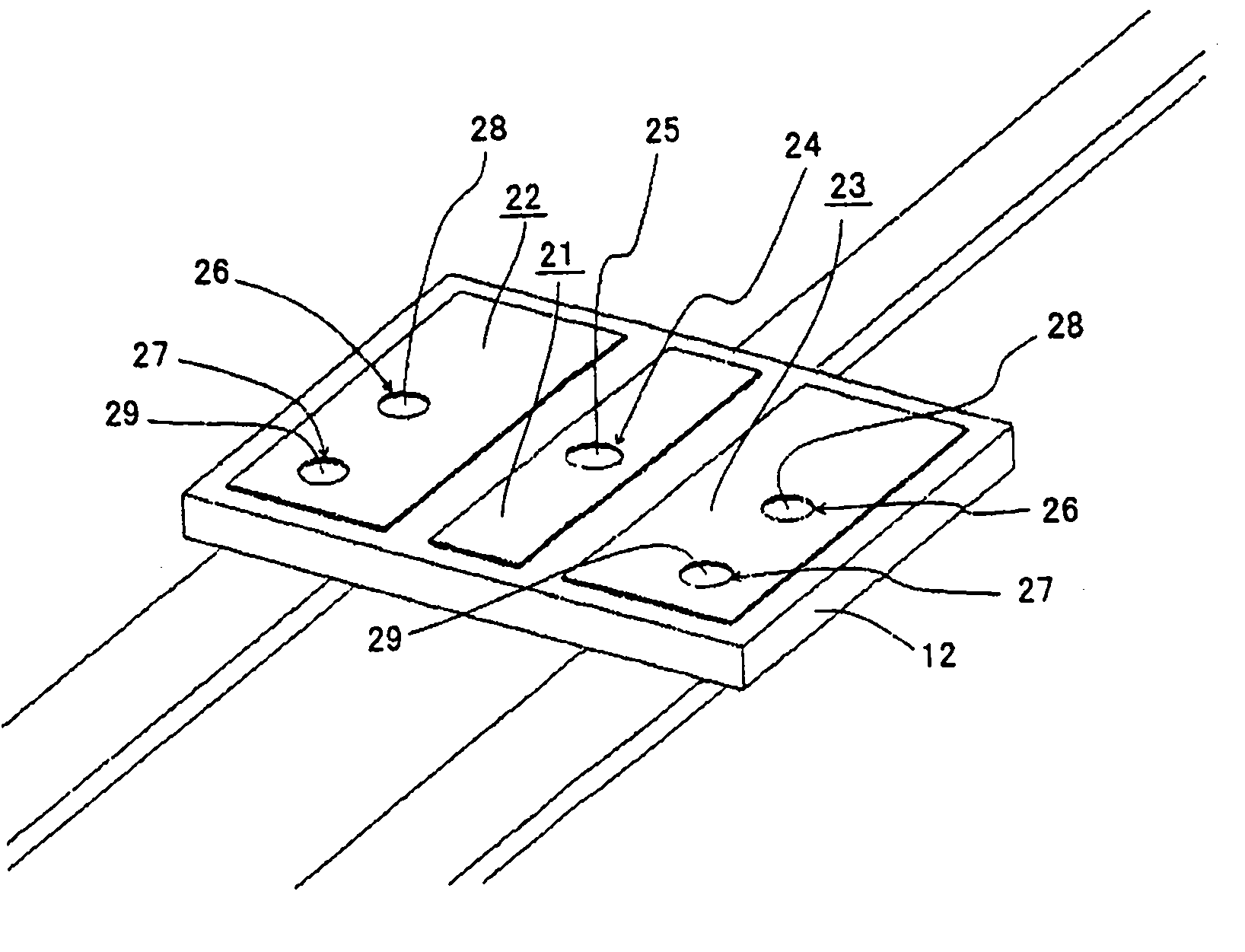
[0046] Other embodiments of the present invention are Figure 4 The chip-type protective element 30 shown in the perspective view of FIG. Figure 4 A perspective view showing the surface side with the protective cover removed, the protective element 30 is formed by mounting a fusible alloy fuse element 35 on the surface of a ceramic chip body 32, and is a structure that can be handled as a surface mount type chip component. The above-mentioned chip-type protective element 30 has a first pattern electrode 41 formed in the center on both surfaces of the ceramic chip body 32, and a second pattern electrode 42, 43 is formed on the end face side, and the pattern electrode on the back side is installed on the printed circuit board in this way. Soldering is performed between the printed substrate and the pattern electrodes on the substrate. Figure 5 It is a perspective view showing the state before the protective cover and the fusible alloy fuse element are attached. Figure 5 The...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The mounting structure of the protection element of the present invention can be applied to an overcharge protection circuit of a rechargeable battery. Mounted with the ceramic cover facing down between active components such as MOSFETs mounted on the main printed circuit board. The protective element that seals one surface of the ceramic chip body with the package of the ceramic lid as described above can be mounted close to the heat-sensitive portion of the active element. In addition, mounting a protection element by utilizing the gap space between circuit components is advantageous for miniaturization and thinning, and can be applied to compact mobile information communication equipment using such a protection circuit. In addition, when two or more resistance heating elements are used, they are arranged in parallel in the through hole of the ceramic chip body, thereby achieving uniform heat transfer to the fusible alloy fuse element and improving accuracy. Moreover...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com