Method for constructing integrated submarine forest
A forest and substrate technology, applied in the field of integrated submarine forest construction, can solve the problems such as the failure of scientific, rational and orderly layout of marine resource utilization and protection, the lack of proper grasp of laws, and the imbalance of marine ecology. Insufficient plants, reduced shellfish mortality, and the effect of preventing the floating of sediment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] The construction method of the integrated seabed forest of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0051] (1) Selection and transformation of submarine forest substrate
[0052] There are 3 types of submarine forest substrates: (1) rocky substrate, (2) pebble substrate, (3) sandy mud substrate, and select different methods according to different substrates to select and transform submarine forests;
[0053] Pebble substrate: The pebble substrate is reef-built by throwing stones or artificial algae reefs;
[0054] The method of throwing the pebble substrate into the artificial algae reef is
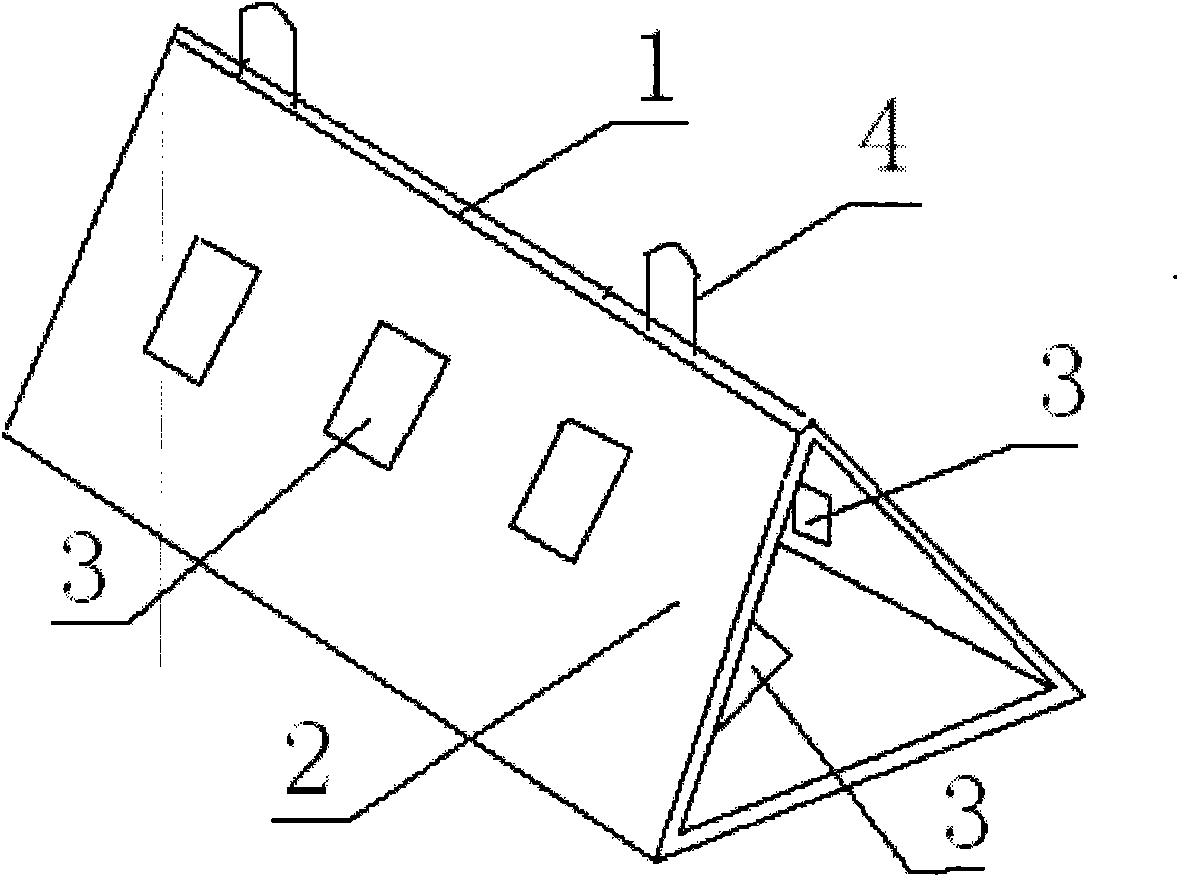
[0055] (1), construct the artificial algae reef, hoist the artificial algae reef onto the ship with a crane, and pull the marking line with anchors and ropes in the reef throwing area;
[0056] The artificial fishing reef adopts reinforced concrete members, including a hollow reef body 1 with openings at both ends, and holes 3 for allowing marine organisms to enter a...
Embodiment 2
[0071] The construction method of the integrated seabed forest of the present embodiment, and the difference of embodiment 1:
[0072] (1) Selection and transformation of submarine forest substrate
[0073] For rocky substrates:
[0074] Most of the bottom of the rocky reef does not need to be transformed, but the artificial transplantation of large algae is carried out on the rocky reef without algae growth;
[0075] (2) Multiplication of large marine plants
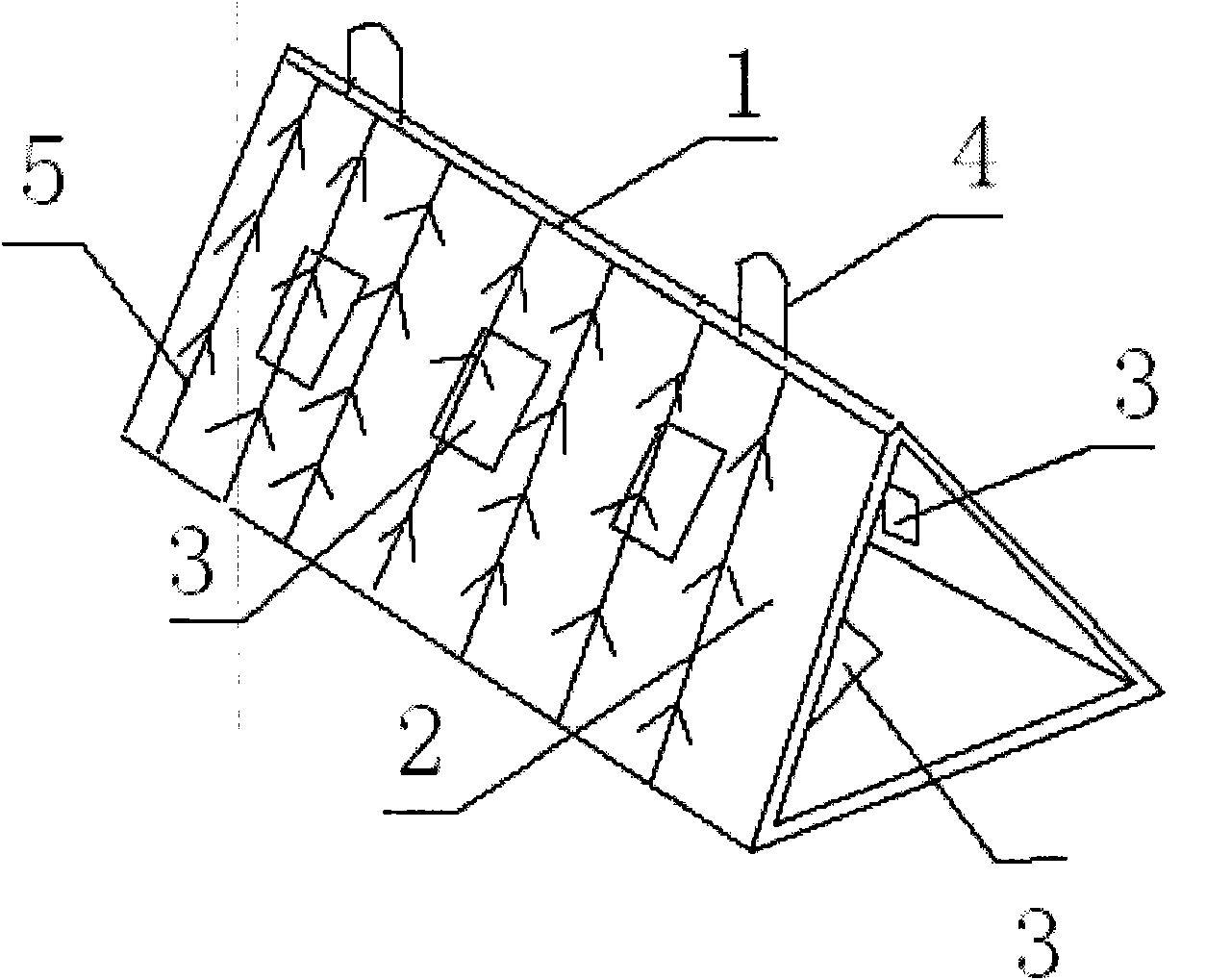
[0076] Transplant large algae such as kelp and wakame to the algae-free rocky bottom.
Embodiment 3
[0078] The construction method of the integrated seabed forest of the present embodiment, and the difference of embodiment 1:
[0079] (1) Selection and transformation of submarine forest substrate
[0080] For sandy mud substrate:
[0081] A. Carry out reef building by throwing stones, throwing reinforced concrete members to build reefs, and shipwrecks to build reefs;
[0082] B, carry out the artificial transplantation cultivation of eel algae.
[0083] (2) Multiplication of large marine plants
[0084] For pebble geology and sandy mud bottom, after reef building, adopt methods such as bundling kelp seedling pickers to transplant algae;
[0085] Carry out artificial planting and transplantation of eelgrass on the sandy mud substrate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com