Method for screening antibodies
A purposeful and systematic technology, applied in the field of antibody screening, can solve problems such as growth differences, difficulty in displaying molecular weight proteins, loss of library diversity, etc., and achieve the effect of huge disease diagnosis and treatment, and promotion of disease diagnosis and treatment
Active Publication Date: 2011-01-19
INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
View PDF2 Cites 3 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
However, due to the limited display efficiency of phage display technology, not all sequences can be well expressed in phage
Moreover, during the process of phage amplification, due to the different nature of the insert fragments, there may be differences in growth, which may result in loss of library diversity.
In addition, phage display systems have difficulty displaying larger molecular weight proteins, so they cannot successfully display complete IgG antibody molecules
However, yeast display technology is difficult to construct a large enough antibody library due to the impact of transformation efficiency
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
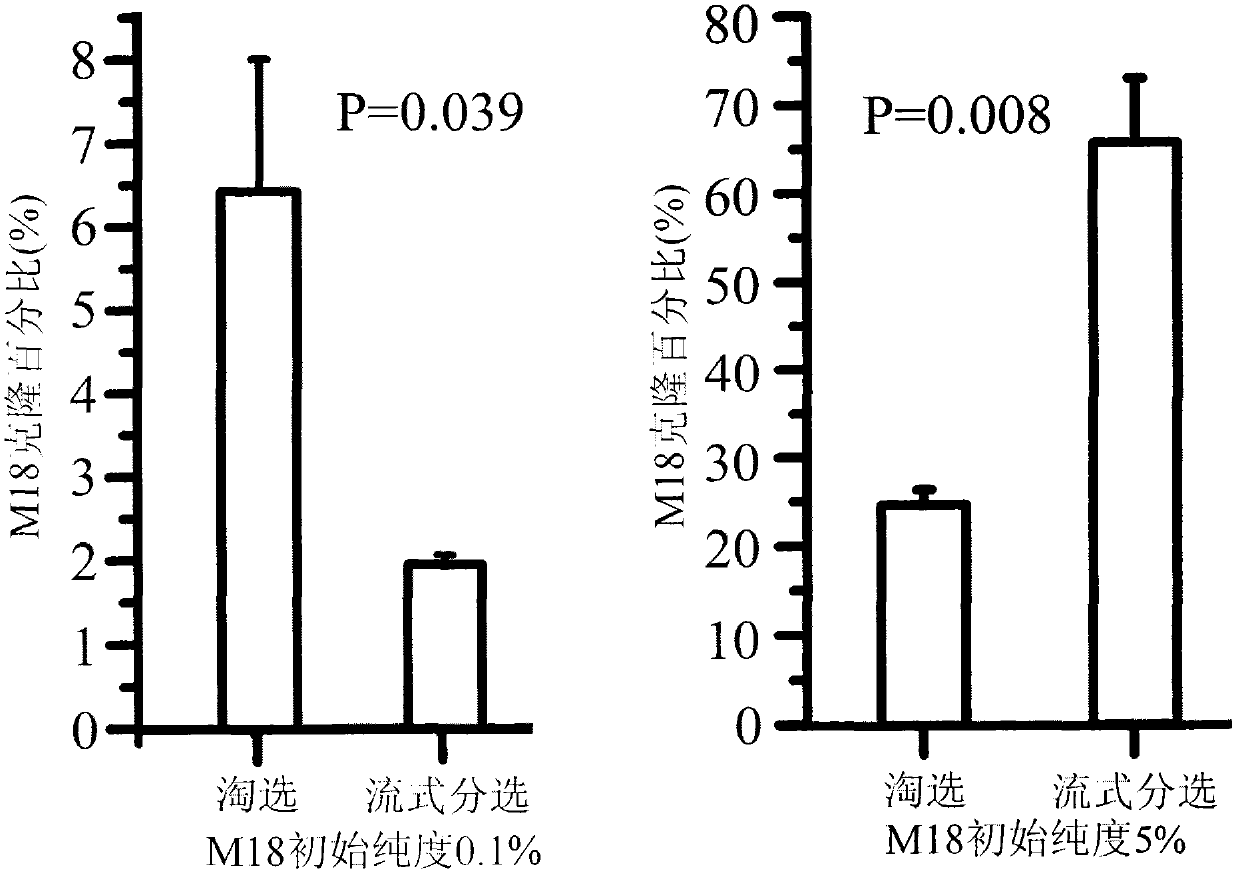
The invention discloses a method for screening antibodies, which comprises the following steps of: 1) displaying a target protein on the cell membrane surface of an in vitro eukaryocyte to obtain eukaryocyte of which the surface is provided with the target protein; and 2) respectively displaying each protein to be screened in a protein library on the surface of bacteria protoplast to obtain a bacteria rotoplast library of which the surface is provided with proteins to be screened. The invention provides a screening method for screening the antibodies for specifically identifying human cell surface antigens by taking complete human cells as the antigens through the APEx display technology. An APEx bacteria display system has an antibody library (more than or equal to 109) equivalent to that of a phage display system, and has the capacity of displaying complete IgG antibodies. The established method is favorable for screening more antibodies for identifying cell surface molecular markers, and has great promotion function for disease diagnosis and treatment.
Description
technical field The invention relates to a method for screening antibodies. Background technique High-throughput antibody screening by means of protein display technology has become one of the main methods for antibody production. Phage display technology, ribosome display technology and yeast display technology have been widely used in the screening of new antibodies and the improvement of antibody affinity. The displayed antibodies can bind to the target antigen and be quickly screened from the complex antibody library. Commonly used antigens for antibody screening are known soluble purified antigens. However, the molecular markers of many diseases are located on the surface of the cell membrane and have complex post-translational modifications, such as glycosylation (Ohtsubo K, Marth JD: Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell 2006, 126(5): 855- 867.). Glycosylation loss will affect protein folding efficiency and stability (Shental-Bechor D, L...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C07K16/00G01N33/53
Inventor 杭海英邱俊康
Owner INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com