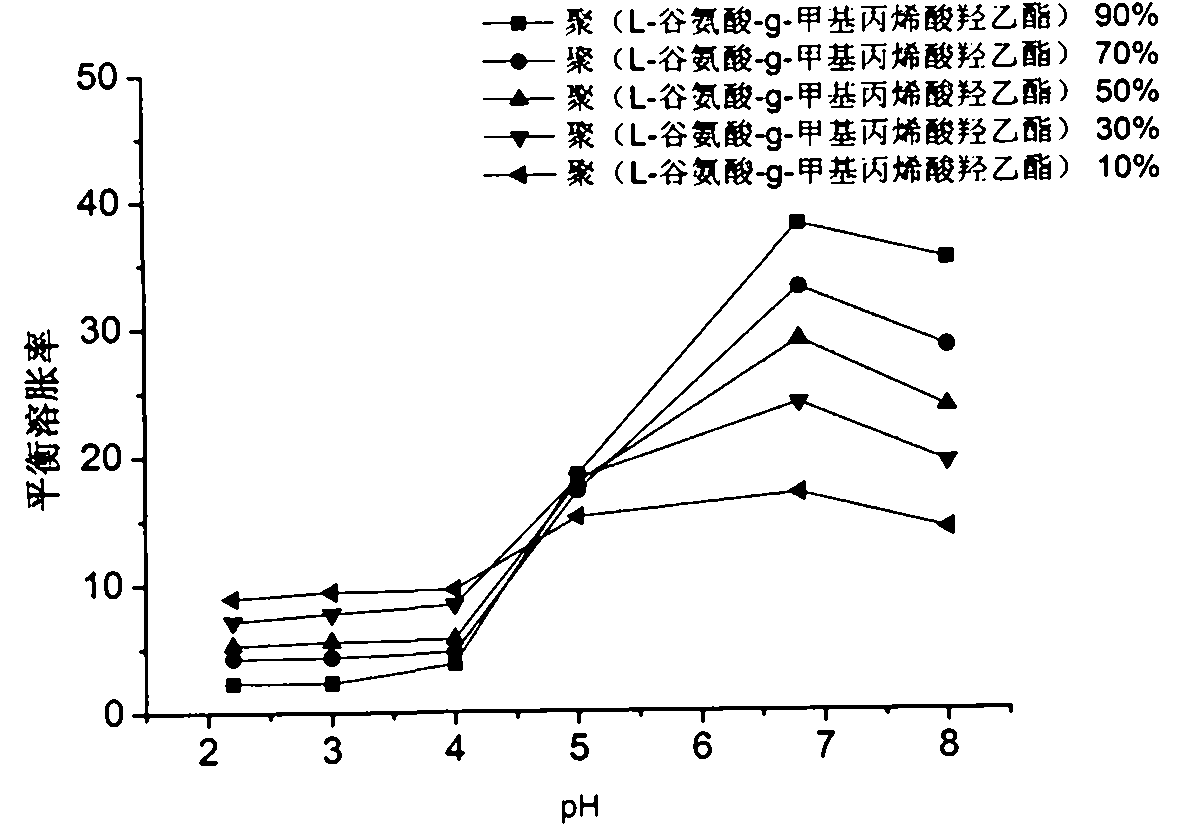
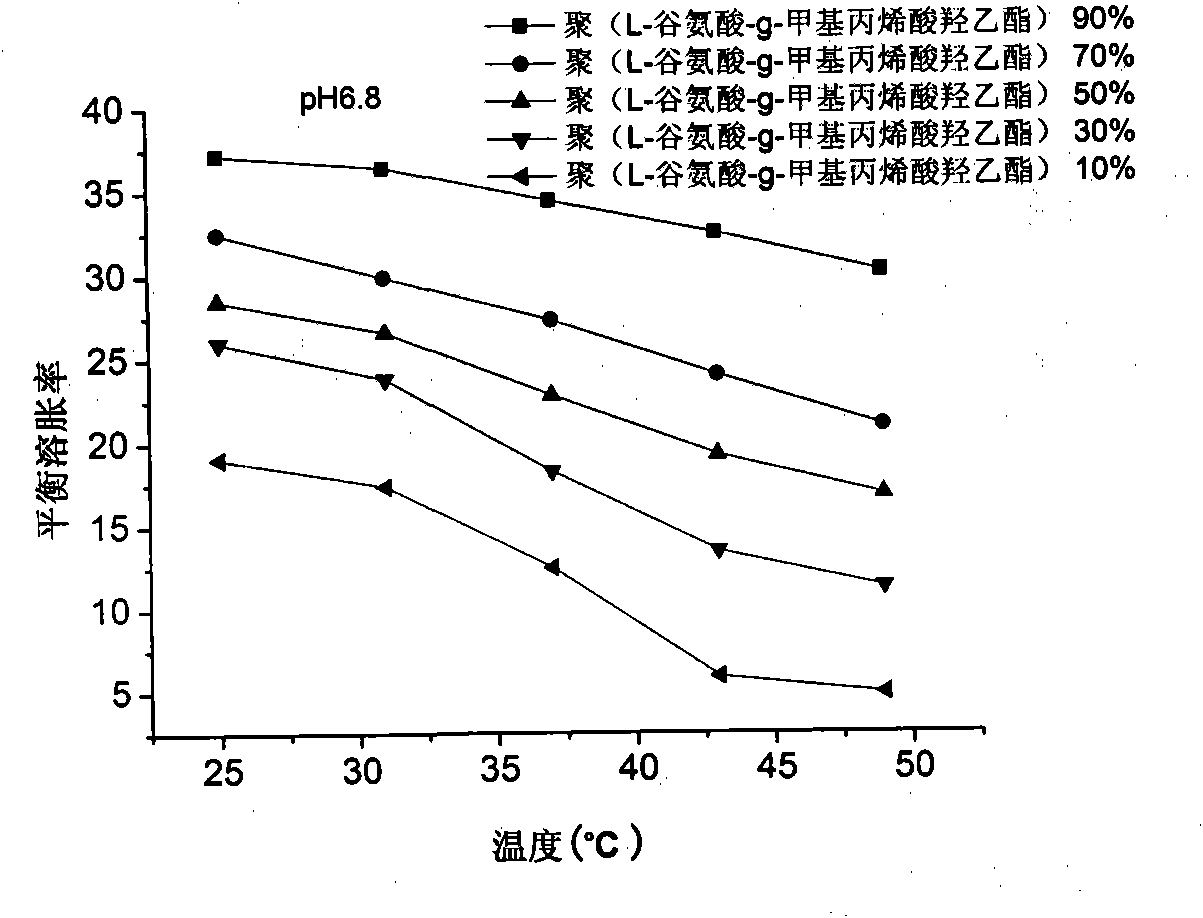
Poly (L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxy-ethyl methacrylate) and hydroxy propyl cellulose-g-acrylic acid copolymer hydrogel and preparation method thereof
A technology of hydroxyethyl methacrylate and hydroxypropyl cellulose, which can be used in medical preparations, medical science, prostheses and other directions of non-active ingredients, and can solve the problems of non-biodegradation of hydrogels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: the preparation of poly(L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
[0024] Mix 1.3g poly(L-glutamic acid) (viscosity average molecular weight: 88000) with 0.013g hydroxyethyl methacrylate monomer, dissolve it in 30mL dimethyl sulfoxide, dissolve all the solids, and define it as a solution a.
[0025]Then, 0.02 g of N, N'-cyclohexylcarbodiimide and 0.012 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dissolved in 0.16 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, which was defined as solution b. The above solution b was poured into the solution a, reacted at room temperature for 72 hours, and filtered off the generated precipitate. The filtrate was settled with 300 mL ether, filtered, washed three times with ether, and dried under vacuum at room temperature for 24 hours to obtain poly(L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxyethyl methacrylate).
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: the preparation of poly(L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
[0027] Mix 1.3g poly(L-glutamic acid) (viscosity average molecular weight: 88000) with 0.656g hydroxyethyl methacrylate monomer, dissolve it in 30mL dimethyl sulfoxide, dissolve all the solids, and define it as a solution a. Then, 1.04 g of N, N'-cyclohexylcarbodiimide and 0.615 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dissolved in 8.25 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, which was defined as solution b. The above solution b was poured into the solution a, reacted at room temperature for 72 hours, and filtered off the generated precipitate. The filtrate was settled with 300 mL ether, filtered, washed three times with ether, and dried under vacuum at room temperature for 24 hours to obtain poly(L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxyethyl methacrylate).
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3: the preparation of poly(L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)
[0029] Mix 1.3g poly(L-glutamic acid) (viscosity-average molecular weight: 88000) with 0.13g hydroxyethyl methacrylate monomer, dissolve it in 30mL dimethyl sulfoxide, dissolve all the solids, and define it as a solution a. Then, 0.2 g of N, N'-cyclohexylcarbodiimide and 0.12 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dissolved in 1.6 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, which was defined as solution b. The above solution b was poured into the solution a, reacted at room temperature for 72 hours, and filtered off the generated precipitate. The filtrate was settled with 300 mL ether, filtered, washed three times with ether, and dried under vacuum at room temperature for 24 hours to obtain poly(L-glutamic acid-g-hydroxyethyl methacrylate).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com