Method and apparatus for recording and reproducing optical information, and recording medium
A technology for recording and reproducing devices and recording media, applied to optical recording media, recording/reproducing with optical methods, data recording, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
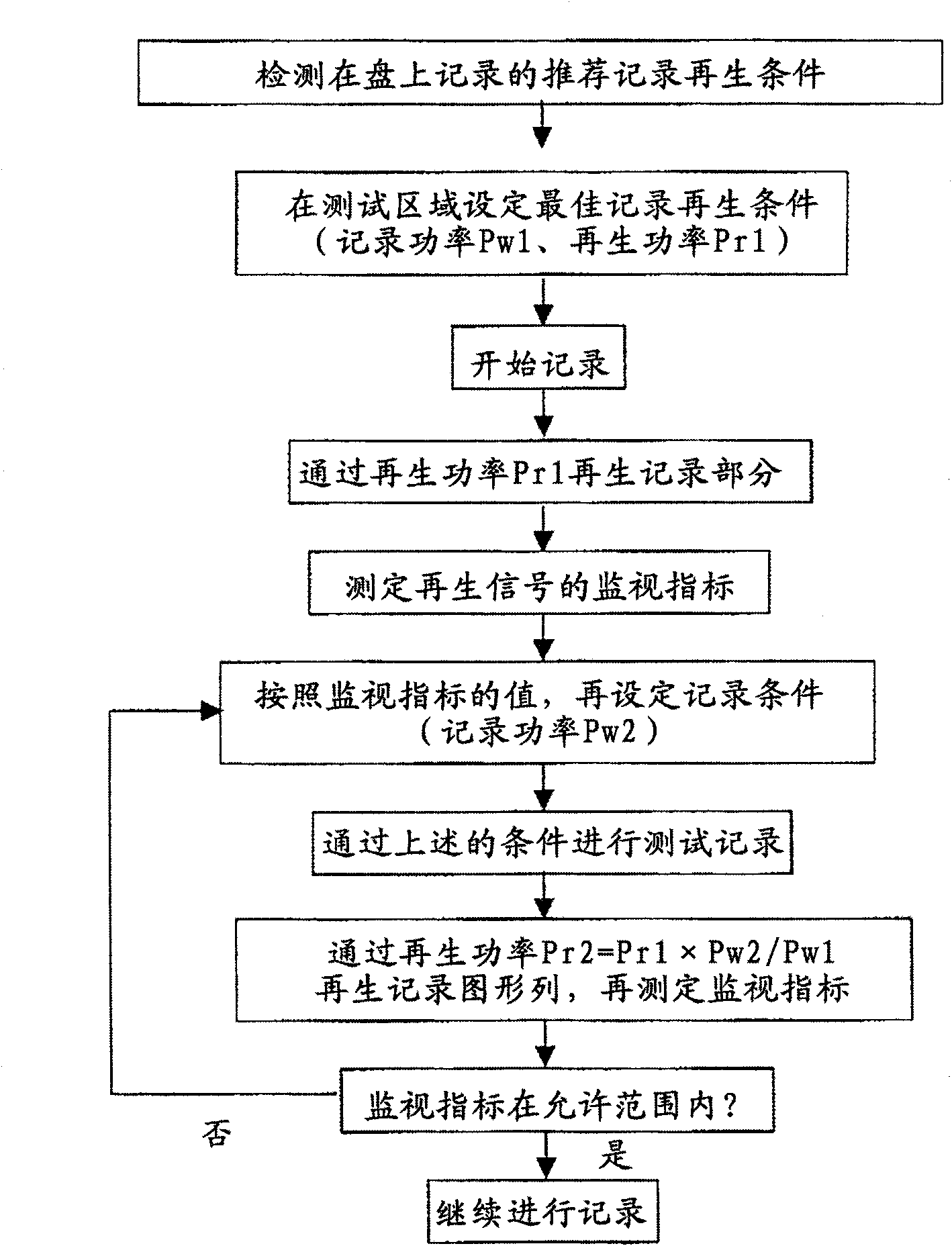
[0048] As a first aspect of the embodiment, a configuration example of an optical disk drive having a function of detecting an event such as a change in ambient temperature or a temperature change of laser light and performing adjustment of recording power and super-resolution reproduction power will be described.
[0049]FIG. 3(A) shows a configuration diagram of a driver. Laser light is emitted from a semiconductor laser 301 and passed through a lens 302 to become parallel light. The parallel light passes through the polarizing beam splitter 303 . At this time, the laser beam emitted from the semiconductor laser 301 is linearly polarized light, but the direction of the polarized beam splitter 303 is adjusted in advance so that the polarized light direction completely passes through the polarized beam splitter 303 . The laser light is converted into circularly polarized light by the λ / 4 plate 304 , passes through the reflector 305 and the objective lens 306 , and becomes a f...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Here, a case where the drive structure is substantially the same as that of the first embodiment, but that uneven data is provided on the disc will be described.
[0070] A write-once super-resolution disc is inserted into this drive. Here, the part up to the detection of the recommended recording and reproduction conditions is the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0071] Then, the optical head was moved to an area with a radius of 25.1 to 25.2 mm on the disk, where a data row consisting of 2T to 8T long unevenness was formed. The reproduction power is varied at intervals of 0.1 mW within ±20% of the recommended reproduction power, and the reproduction power at which the jitter of the uneven data is minimized is defined as the provisional super-resolution reproduction power Psr'. The value of Psr' at this time and the reproduced signal are recorded in the flash memory provided in the control system 312.
[0072] Then, the light spot is moved to the recording and...
Embodiment 3
[0081] A method for confirming the effects of this embodiment with an optical disc tester will be described.
[0082] Figure 4 A block diagram showing a disc tester. Functions and operations are almost the same as those of the optical disc drive shown in the first embodiment. The difference is that the reproduced signal and servo signal can be observed through the oscilloscope 416; the operation of the tester, the bias adjustment of the servo signal, the position of the optical head, the timing of laser irradiation, the waveform or power of laser irradiation, and other conditions can be controlled through the control computer 417. .
[0083] A write-once super-resolution disc 407 is mounted on this tester, and a spindle 415 is rotated to fix a light spot at a predetermined position on the disc by a servo system.
[0084] The disk used is a disk that has not yet been shipped as a product, and the recommended recording and reproduction conditions described in the first and s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com