Promoter BgIosP587, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for promoters and monocotyledonous plants, which is applied in the field of promoters and can solve problems such as limited regulatory effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1P587
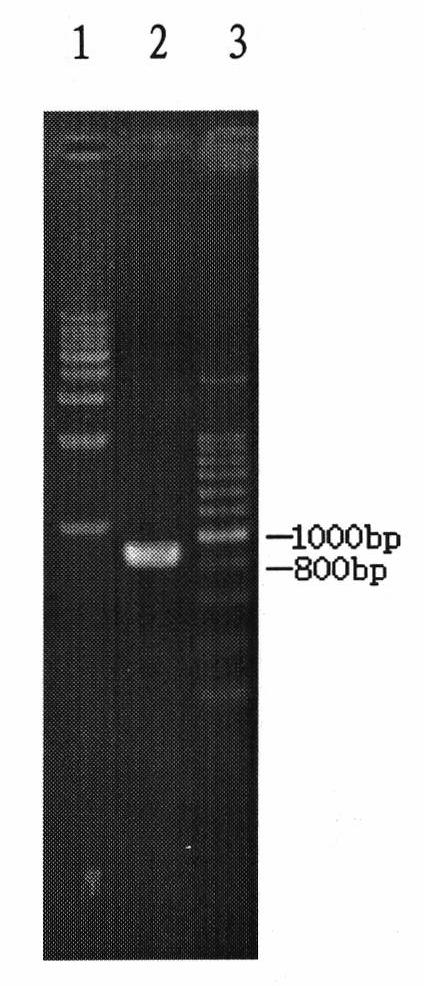
[0059] The PCR amplification of embodiment 1P587 promoter fragment and the construction of pMD18-T+P587 recombinant vector
[0060] PCR amplification
[0061] Using a plant genomic DNA extraction kit (TIANGEN new plant genomic DNA extraction kit, catalog number: DP320-02) to extract rice Nipponbare (preserved in Wuhan University Preservation Center, Luojia Mountain, Wuchang, Wuhan City, Hubei Province on December 18, 2009, namely China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preservation number is CCTCC-P200910) Genomic DNA, according to the sequence of the promoter in the rice Nipponbare gDNA, a pair of PCR-specific amplification primers (upstream primer F1, upstream primer F1, Add restriction enzyme site EcoR I and protection base, downstream primer R1, add restriction enzyme site Sbf I and protection base). Using the rice Nipponbare gDNA extracted above as a template, high-fidelity Ex Taq TM (TaKaRa, DRR100B) polymerase for PCR amplification. As shown in Table 1....
Embodiment 2p8
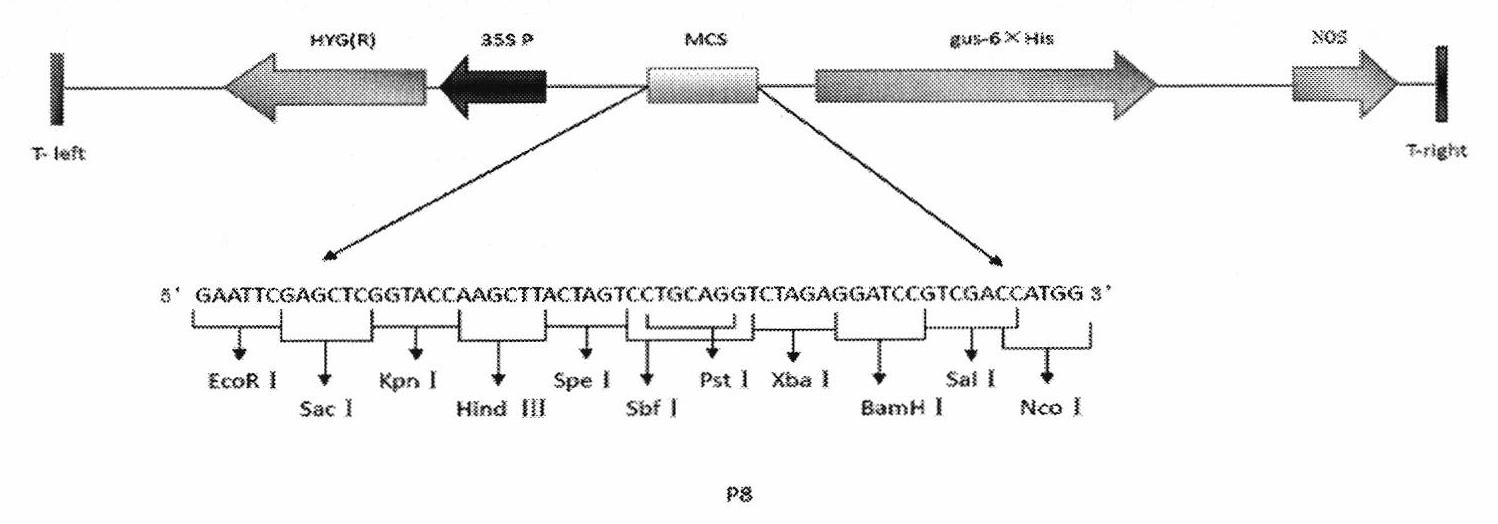
[0082] Construction of embodiment 2p8+P587 recombinant vector
[0083] According to the operating manual of the TIANGEN ordinary plasmid small extraction kit (catalogue number: DP103-03), extract the cloning vector with the P587 promoter sequence of the present invention from the Escherichia coli DH5α-P587 transformed with the promoter P587 constructed in Example 1 pMD18-T+P587; after purification, digest with the corresponding restriction enzymes EcoR I (NEB) and Sbf I (NEB), recover the corresponding promoter insert, and use the same restriction endonucleases as the p8 plasmid The large vector fragments recovered after digestion with Dicer enzyme were ligated.
[0084] Transform the resulting ligation product p8+P587 recombinant vector into competent cells DH5α prepared according to the calcium chloride method shown in the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" (third edition, Science Press), and culture it upside down at 37°C for 16-24 hours. After the colonies grow out, sin...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Example 3 Preparation of recombinant Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105-P587 cells
[0111] The p8+P587 recombinant vector constructed as described in Example 2 and the p8 plasmid as a control were respectively transformed into the root cancer prepared by the calcium chloride method described in the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" (third edition, Science Press). Competent cells of Agrobacterium EHA105 (preserved on December 24, 2009 at the Wuhan University Collection Center, Luojia Mountain, Wuchang, Wuhan City, Hubei Province, that is, the China Type Culture Collection Center (CCTCC), the preservation number is CCTCC M 209315), and the specific method as follows:
[0112] The Agrobacterium tumefaciens competent cells EHA105 were taken out from the ultra-low temperature refrigerator and thawed on ice. After thawing, add 5 μl of p8+P587 recombinant vector and p8 plasmid and p8 empty vector as a control, mix gently, ice bath for 10 minutes, freeze in liquid nitrogen f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com