Method and device for preventing moisture condensation of roof of textile workshop
An anti-condensation and workshop technology, applied in roof insulation materials, heating methods, pipeline layout, etc., can solve problems such as high implementation costs, damage to the workshop production environment, and increased workshop construction costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
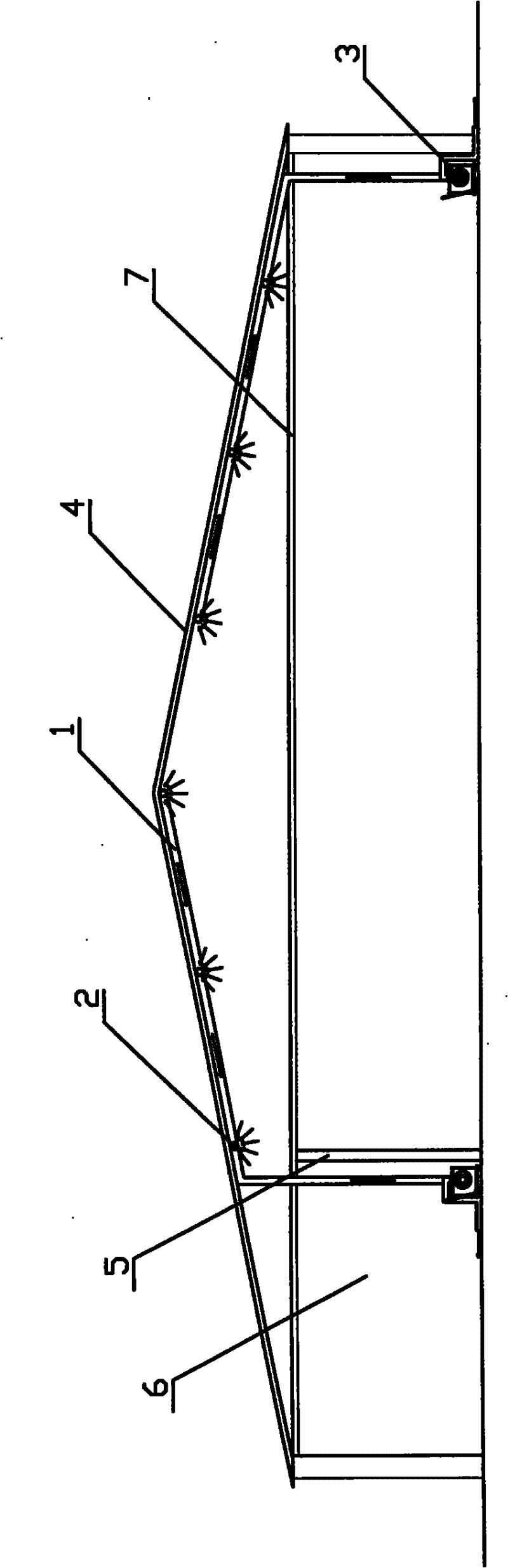
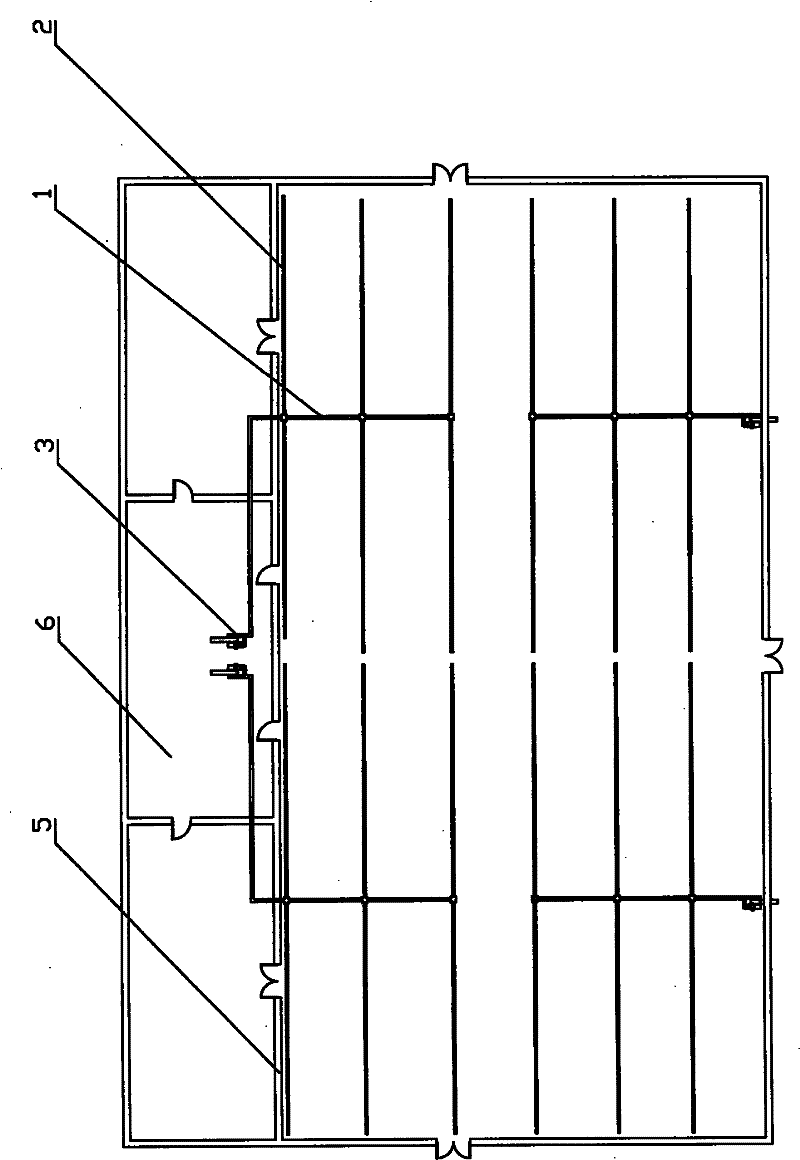
[0070] Embodiment one: the test textile factory of the present invention is a certain textile factory in the north of China, and the plant area is more than 1,000 square meters. The main body is a steel structure building, and the roof is a pointed roof such as figure 1 As shown, the outer surface is thin steel plate, the inner surface is W-C veneer, and the middle insulation material is Owens glass wool. The workshop is equipped with a suspended ceiling and an air-conditioning room. The temperature and humidity in the workshop are adjusted through the air-conditioning system. In winter, the temperature in the workshop is kept at about 25°C, and the relative humidity is 70%. In winter, the high-humidity water vapor in the workshop permeates and diffuses into the ceiling space through the gaps in the ceiling. There are gaps in the W-C veneer layer, and high-temperature and high-humidity water vapor enters the insulation through the gaps. In the material layer, it reaches saturat...
Embodiment 2
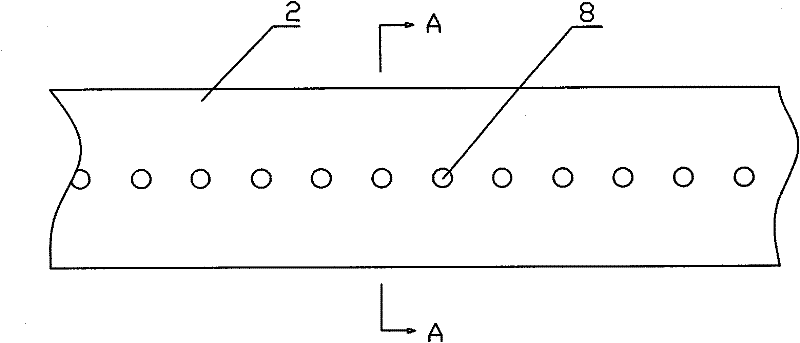
[0086] Embodiment 2: It is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be repeated. The difference is that the exhaust and dehumidification main pipe and the exhaust and dehumidification branch pipe have equal cross-sections, and each exhaust and dehumidification branch pipe is along the direction of the roof. There are two rows of approximately evenly distributed exhaust and dehumidification holes on each side wall. The distance between the exhaust and dehumidification holes is 150mm, and the distance between the exhaust and dehumidification pipe network and the lower surface of the factory roof is 5mm.
[0087] The method of this embodiment is that when the relative humidity value detected by the humidity sensor reaches 70%, the control circuit starts the exhaust and dehumidifier fan to extract the high-humidity air near the lower surface of the factory roof and send it to the air-conditioning room of the workshop, or directly discharge it outside , when...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Embodiment 3: It is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be repeated. The difference is that the exhaust and dehumidification branch pipes are connected obliquely to the main pipe, arranged at equal intervals in the oblique direction, and the exhaust and dehumidification branch pipes are connected with the main pipe. The cross-section of the main pipe is equal, the cross-sectional shape is elliptical, and the material is glass steel pipe. Each exhaust and dehumidification branch pipe has two rows of approximately uniformly distributed exhaust and dehumidification holes on both sides of the roof. The shape is elliptical, the distance between the exhaust and dehumidification holes is 50mm, and the distance between the exhaust and dehumidification pipe network and the lower surface of the factory roof is 5mm.
[0089] The method of this embodiment is that when the relative humidity value detected by the humidity sensor reaches 82%, the control c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com