Cartilage complex of tissue engineering bone and method for preparing same
A tissue engineering bone and composite technology, applied in prosthetics, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of slow degradation of the underlying hydroxyapatite, complicated operation, and ineffective fixation of tissue engineered articular cartilage products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1 uses fresh bovine femoral condyle as raw material to prepare tissue engineered osteochondral scaffold
[0045] Purchasing fresh bovine femoral condyles from the market, removing the attached muscles and ligaments, sawing them into 2cm thick bone slices, washing the bone marrow with a high-pressure water gun and triple distilled water, cutting off the bone cortex, and dehydrating with absolute ethanol , degreased with ether, and air-dried. Then a trephine with a diameter of 1 cm was used to make a cancellous bone column with a diameter of 1 cm from the treated bovine femoral condyle. The lower 2 / 3 of the cancellous bone column was embedded in paraffin. The lower 2 / 3 part of the paraffin-embedded cancellous bone column was placed in 10% (w / v) EDTA solution for decalcification for 2 weeks, then the paraffin was removed with xylene and graded alcohol, and soaked in PBS buffer for more than 1 week. Then freeze-dry to obtain the tissue engineering osteochondral...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 HE staining to identify the decalcification effect of tissue engineered osteochondral scaffold
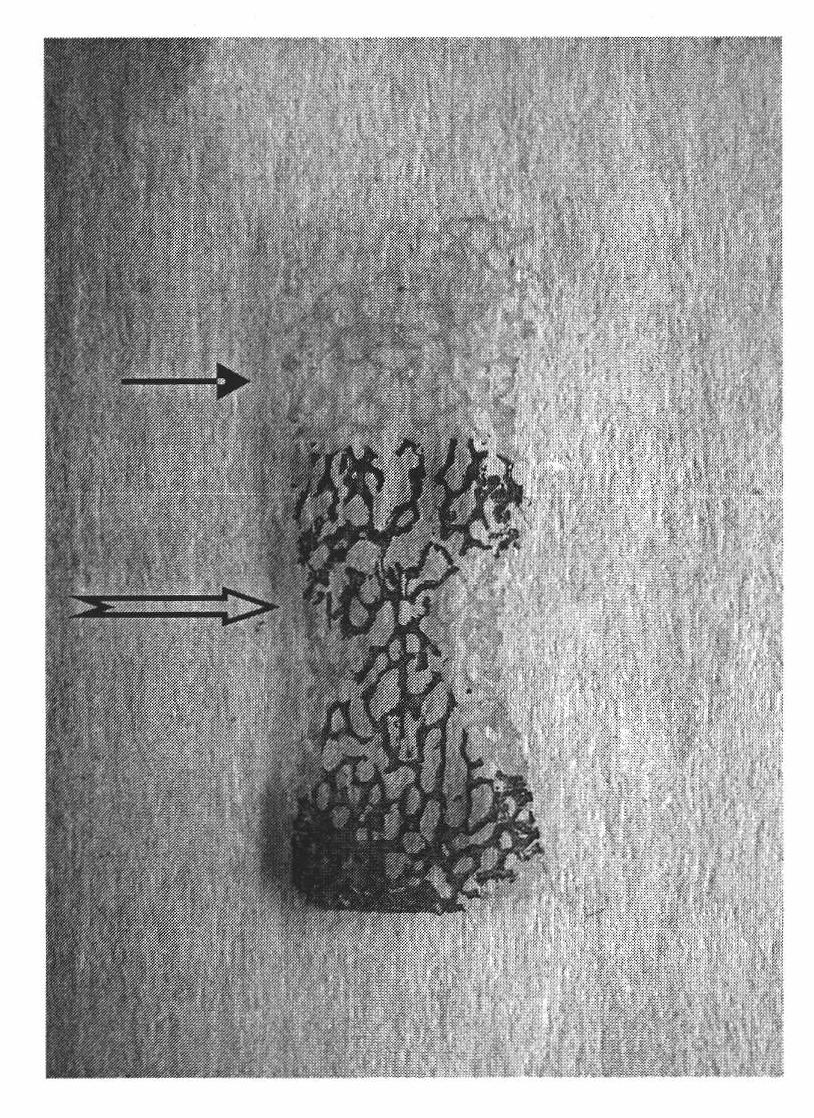
[0047] The tissue-engineered osteochondral scaffolds prepared in Example 1 were respectively resin-embedded, sectioned into hard tissues, stained with HE, and placed under a macroscopic microscope for photographing and observation, as shown in figure 1 shown. The results showed that the periphery of the upper layer of the stent (i.e. the upper 1 / 3 part of the stent) and the lower layer of the stent (i.e. the lower 2 / 3 paraffin-embedded part of the stent) was stained light red, and the lower layer of the stent (i.e. the lower 2 / 3 paraffin-embedded part of the stent) The central area of the embedding part) was stained purple-blue, and the interface between the upper and lower layers was very clear.
[0048] It can be seen that, through the layered decalcification treatment of the present invention, the upper layer (i.e. the upper 1 / 3 part) of the prepared tissue e...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 Sodium Alginate Gel as Secondary Scaffold to Construct Tissue Engineering Osteochondral Complex
[0050] Collect the second-generation rabbit chondrocytes cultured and expanded by conventional methods, and dilute them to 4×10 with 1.2% (v / w) sodium alginate solution. 7 / ml, get 0.5ml above-mentioned cell suspension and join in the hole of 48-well culture plate, the layered tissue engineered osteochondral scaffold prepared in embodiment 1 is inverted, allow the upper layer of the scaffold (that is, the completely decalcified part of the scaffold) and only the upper layer Immerse in the solution in the above-mentioned culture dish or culture plate, the lower layer of the support (i.e. only the decalcified part of the surface of the support) is exposed to the solution, and the liquid surface is 5mm away from the decalcification interface of the support (i.e. the interface between the upper and lower layers of the support), Add 0.1ml 2% (w / v) CaCl 2 Solution, put...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com