Biological de-acidification method of fruit wine
A biological and acid-reducing technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve significant economic benefits, low cost, and strong operability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
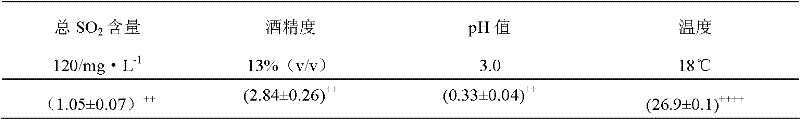
[0012] The raw fruit is processed by crushing, pitting, juicing, sugar adjustment, sulfur dioxide adjustment (range value 100-120mg / kg), adding yeast and other processes, and then carries out temperature-controlled alcoholic fermentation at 20-25°C. During the alcohol fermentation process, the specific gravity of the fermented mash is monitored, and when the specific gravity drops to 1.015-0.990 (20°C), the lactic acid bacteria that have been activated and expanded in advance are inserted. After inoculation of lactic acid bacteria, it is necessary to ensure that the content of lactic acid bacteria in the fermented mash is ≥10 8 Magnitude. When the sugar content of the fermented wine mash drops to the set value required for winemaking, the fermentation is stopped, and then the bottom of the tank can be removed, 50-70mg / L of sulfur dioxide is added, and filtration is carried out to remove yeast and lactic acid bacteria. After clarification, Cold treatment, deployment, filtratio...
example 1
[0014] Example 1: Biological acid reduction method for loquat wine
[0015] The method includes the following steps:
[0016] 1. Juicing: After fresh loquats are cored, crushed, and squeezed, add 120mg / L of sulfur dioxide (all within this range), and adjust the solid content to 18-22% (w / w) with sucrose (100g fruit juice Containing the sugar of 18-22g), the acid content of fruit juice reaches 0.6-0.7% (malic acid meter) this moment.
[0017] 2. Alcoholic fermentation: the adjusted loquat juice is inserted into the saccharomyces that have been expanded and cultivated in advance by 5% of the inoculum. Carry out temperature-controlled fermentation at 20-25° C. for 10-15 days.
[0018] 3. Lactic acid bacteria activation and expanded cultivation: Stir the lactic acid bacteria in the slant culture medium into the seed fermentation medium (tomato juice 100mL, yeast extract 7.4g, beef extract 10g, glucose 30g, magnesium sulfate 0.36g, sodium malate 20g, Tween 1g, tryptone 15g, ammo...
example 2
[0025] Example 2: Biological acid reduction method for southern thorn wine
[0026] The method includes the following steps:
[0027] 1. Pretreatment: After destemming and crushing fresh thorn grapes, add 110mg / L sulfur dioxide (all within this range), and adjust the solid content to 22% (w / w) with sucrose. At this time, the acid content of the juice The amount reaches 0.8-0.9% (malic acid).
[0028] 2. Alcoholic fermentation: the adjusted thorn grape juice (with skin) is inserted into the saccharomyces through expanding cultivation in advance by 5% inoculation amount. Temperature-controlled fermentation was carried out at 20-25°C for 1015 days.
[0029] 3. Activation of lactic acid bacteria: Stir up the lactic acid bacteria in the slant medium, inoculate them into 500 mL of thorn grape juice sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes, cultivate them at 25°C for 48 hours, and then inoculate them into 5L of the same sterilized fruit juice. Cultivate for 48 hours and set aside.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com