Method for quickly detecting pathogenic bacteria in blood based on machine code recognition technology
A technology of identification technology and detection method, which is applied in the field of rapid detection of blood pathogens based on machine code recognition technology, can solve problems such as inability to be clear at a glance, and achieve fast detection speed, high sensitivity, and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below. It should be understood that the preferred embodiments are only for illustrating the present invention, but not for limiting the protection scope of the present invention.
[0034] The blood pathogen rapid detection method based on the machine code recognition technology of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
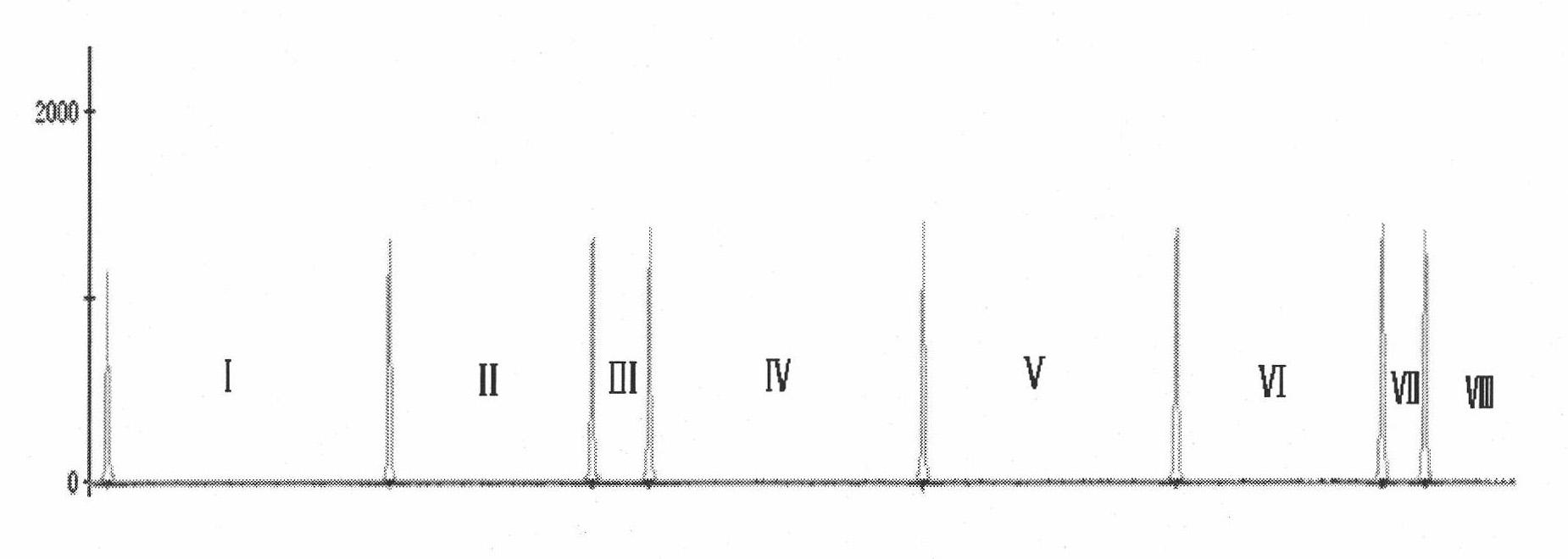
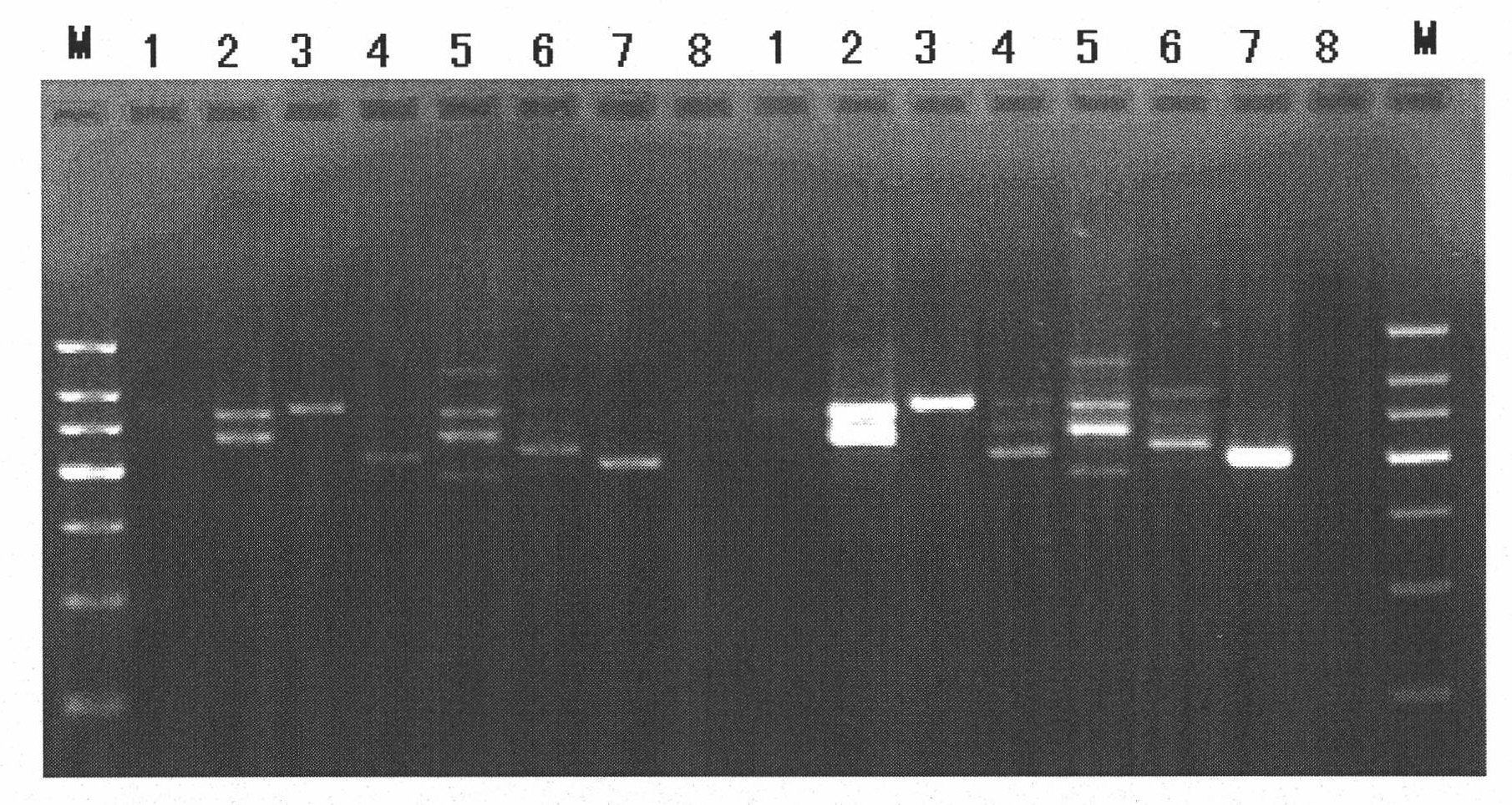
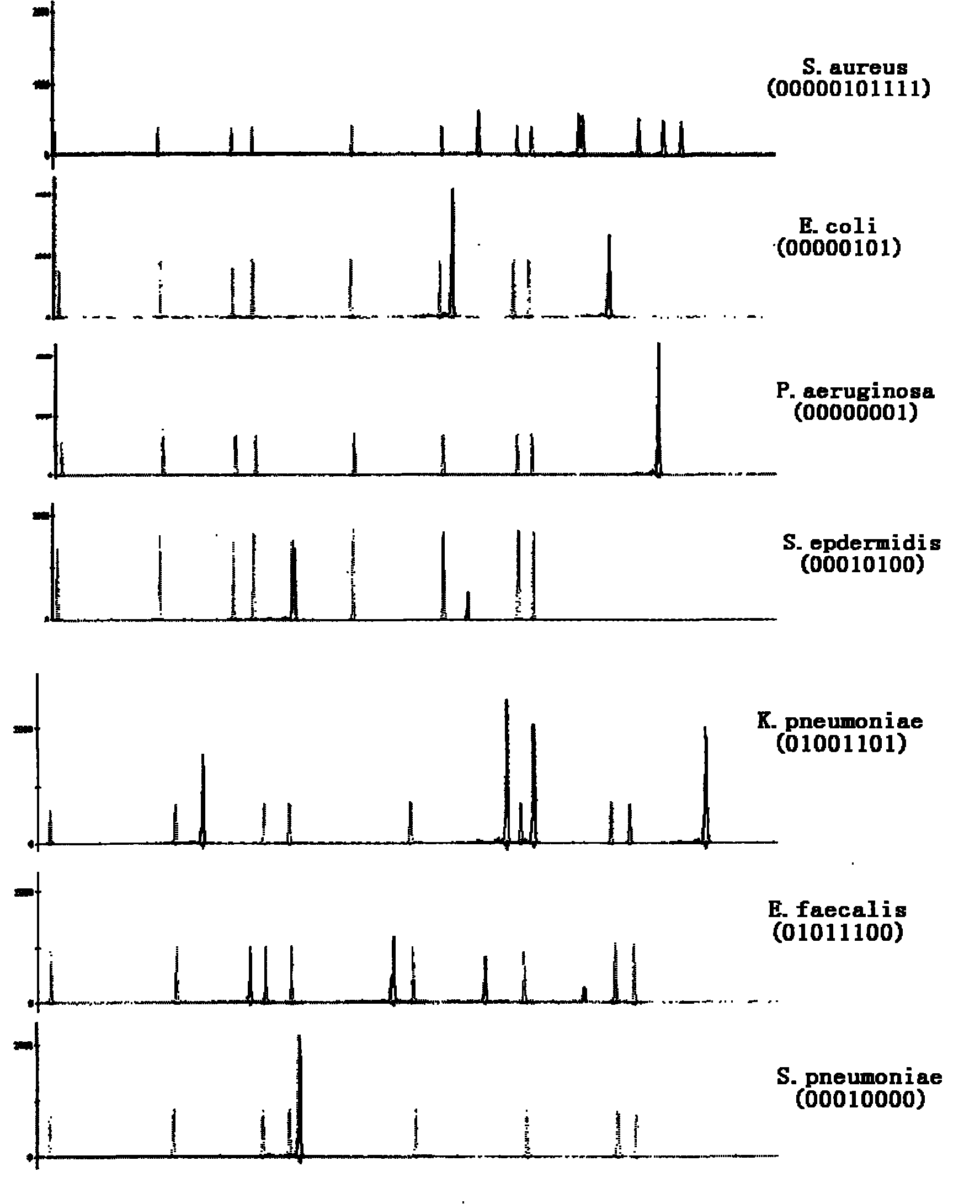
[0035] (1) Design general primers for Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus pneumoniae, the operation is as follows: query the seven species respectively The sequences of the 16S rDNA and 23S rDNA of the pathogenic bacteria were compared using ClustalX 1.81 software to find the conserved regions of the seven pathogenic bacteria, and then the universal primers were designed and fluorescently labeled using Primer Premier 5.0. The sequences of the univ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com