Process for separating acetone, butanol and ethanol in situ by coupling biomass fermentation and pervaporation
A biomass fermentation and pervaporation technology, which is applied in the field of in-situ separation of acetone, butanol and ethanol by coupling pervaporation and biomass fermentation, can solve the problem that the product is difficult to achieve high purity requirements, affects the total solvent yield of ABE, and weakens enzyme activity. and other problems to achieve the effect of reducing the probability of bacterial contamination, shortening the production cycle, and eliminating the inhibitory effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
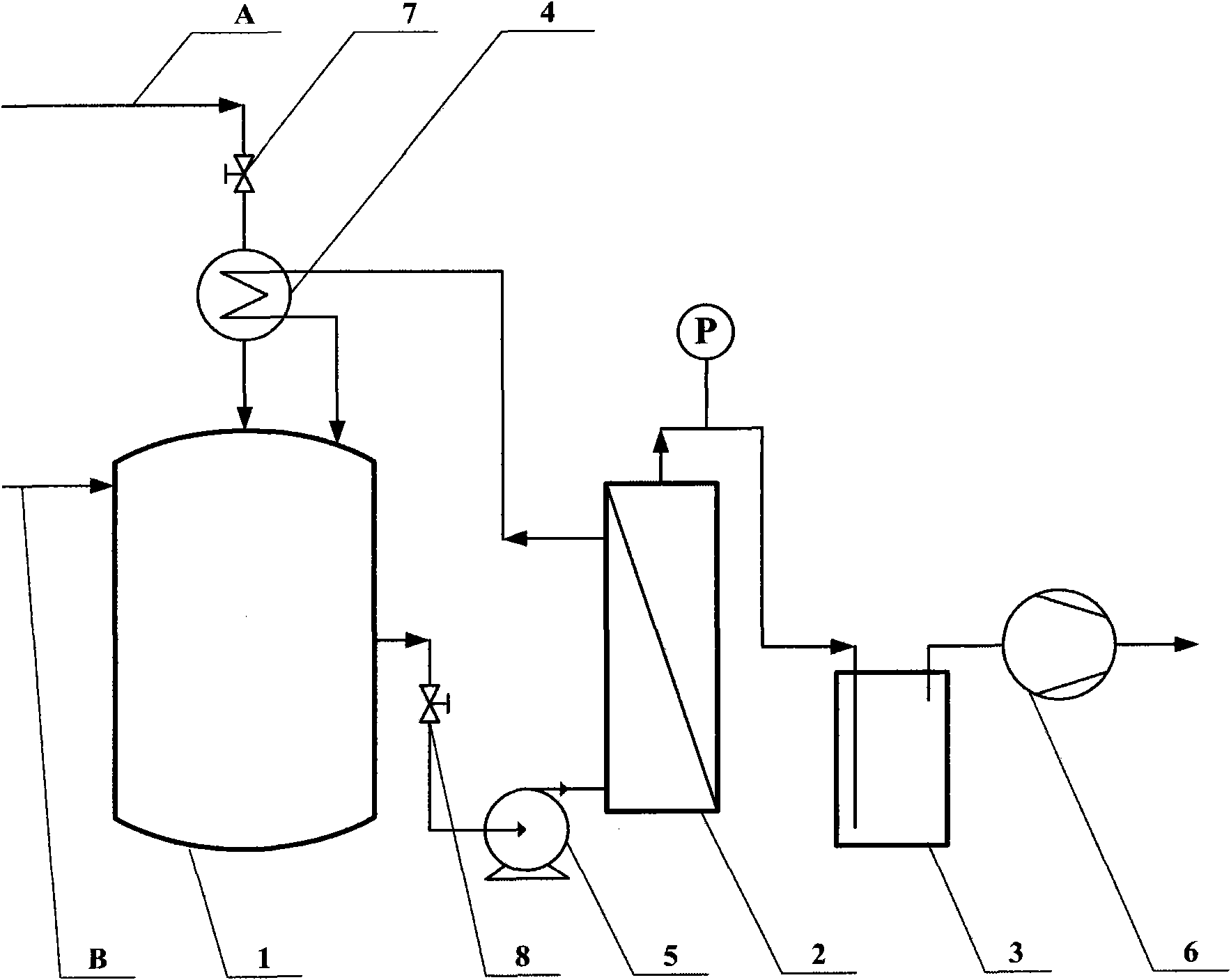
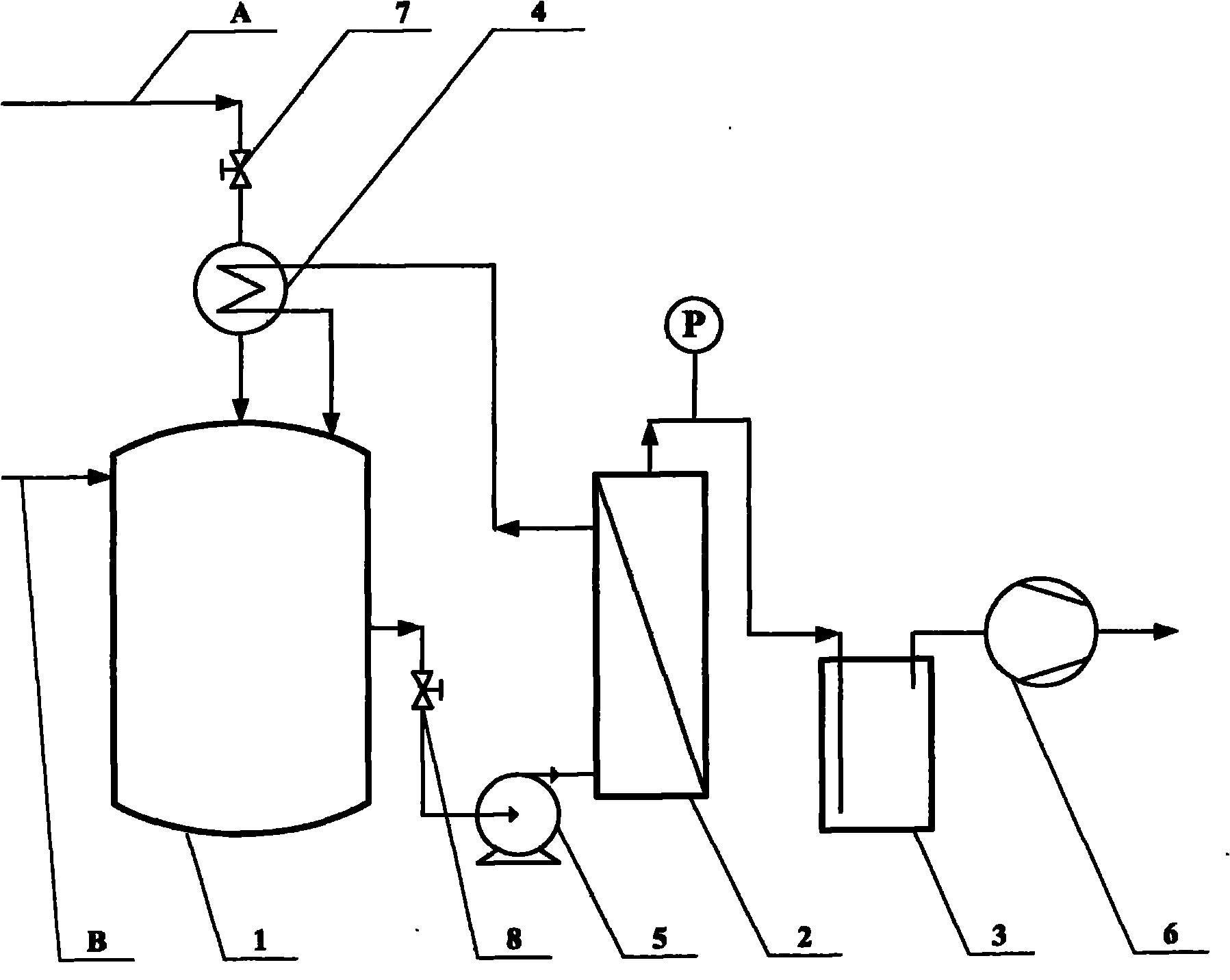
[0020] use figure 1 The process flow chart of scheme one shown.
[0021] The corn stalk sugar solution obtained after a series of pretreatments was used as a fermentation substrate to prepare a medium, and the medium composition was: total sugar concentration 60g / L, corn steep liquor 2g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g / L, FeSO 4 0.01g / L. Open the feed valve 7, inject the sterilized medium into the high-temperature sterilized fermenter 1, inoculate Clostridium beijerinckii, carry out ABE fermentation at 37°C for 36 hours, and detect the quality of the total ABE solvent in the fermenter The concentration reaches 1.0%. Now open the discharge valve 8, the feed pump 5 and the vacuum pump 6, and the fermented liquid enters the pervaporation membrane separator 2 with a feed rate of 6L / h, and the vacuum on the permeate side is maintained at 3 mm Hg, and the pervaporation The separator is made of a unit pervaporation membrane separator, and the pervaporation membrane adopted ...
Embodiment 2
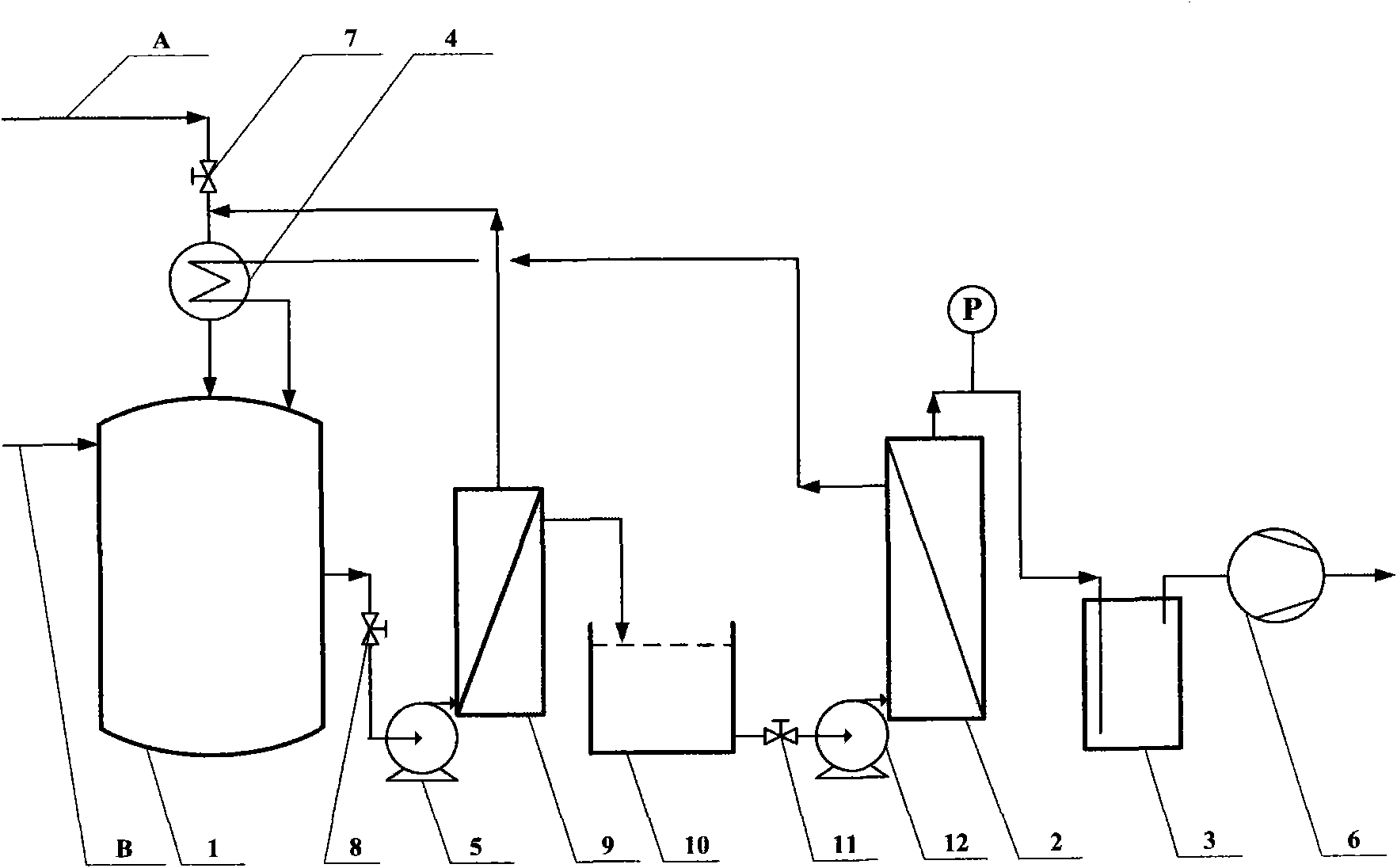
[0024] use figure 2 The process flow chart of scheme two shown.
[0025] Corn flour was used as a fermentation substrate to prepare a medium, and the medium composition was as follows: the concentration of corn flour was 60g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g / L. Open the feed valve 7, inject the sterilized culture medium into the high-temperature sterilized fermenter 1, inoculate Clostridium acetobutylicum at the same time, carry out ABE fermentation at 35°C for 24 hours, and detect the quality of the total ABE solvent in the fermenter The concentration reaches 0.5%. Now open the discharge valve 8, the feed pump 5, the fermented liquid with high solid content in the fermenter is passed into the aluminum alloy with an average pore diameter of 0.5 μm. 2 o 3The microfiltration membrane separator of the microfiltration membrane, the intercepted feed liquid first enters the preheater 4 to exchange heat with the fresh corn flour medium, and then returns to the fermenter 1, ...
Embodiment 3
[0028] use figure 1 The process flow chart of scheme one shown.
[0029] Glucose is used as a fermentation substrate to prepare a medium, and the medium composition is: the total sugar concentration is 70g / L, yeast powder is 1g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.5g / L, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.01g / L, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O0.01g / L. Open the feed valve 7, inject the sterilized culture medium into the high-temperature sterilized fermenter 1, inoculate Clostridium acetobutylicum, carry out ABE fermentation at 36°C for 48 hours, and detect the quality of the total ABE solvent in the fermenter The concentration reaches 1.2%. Now open the control valve 8, the feed pump 5 and the vacuum pump 6, the fermented liquid enters the pervaporation separator 2 with a feed rate of 6L / h, the vacuum on the permeate side is maintained at 2 mm Hg, and the pervaporation separator It is composed of a unit pervaporation membrane separator, and the pervaporation membrane used in the pervaporation membrane separa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com