Spiral coil structure of lamination chip component inner electrode
A technology of components and inner electrodes, applied in the field of spiral coil structure, can solve the problems of reducing DC resistance, inductance or impedance, and achieve the effects of stress elimination, weak diffusion, and small magnetic leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
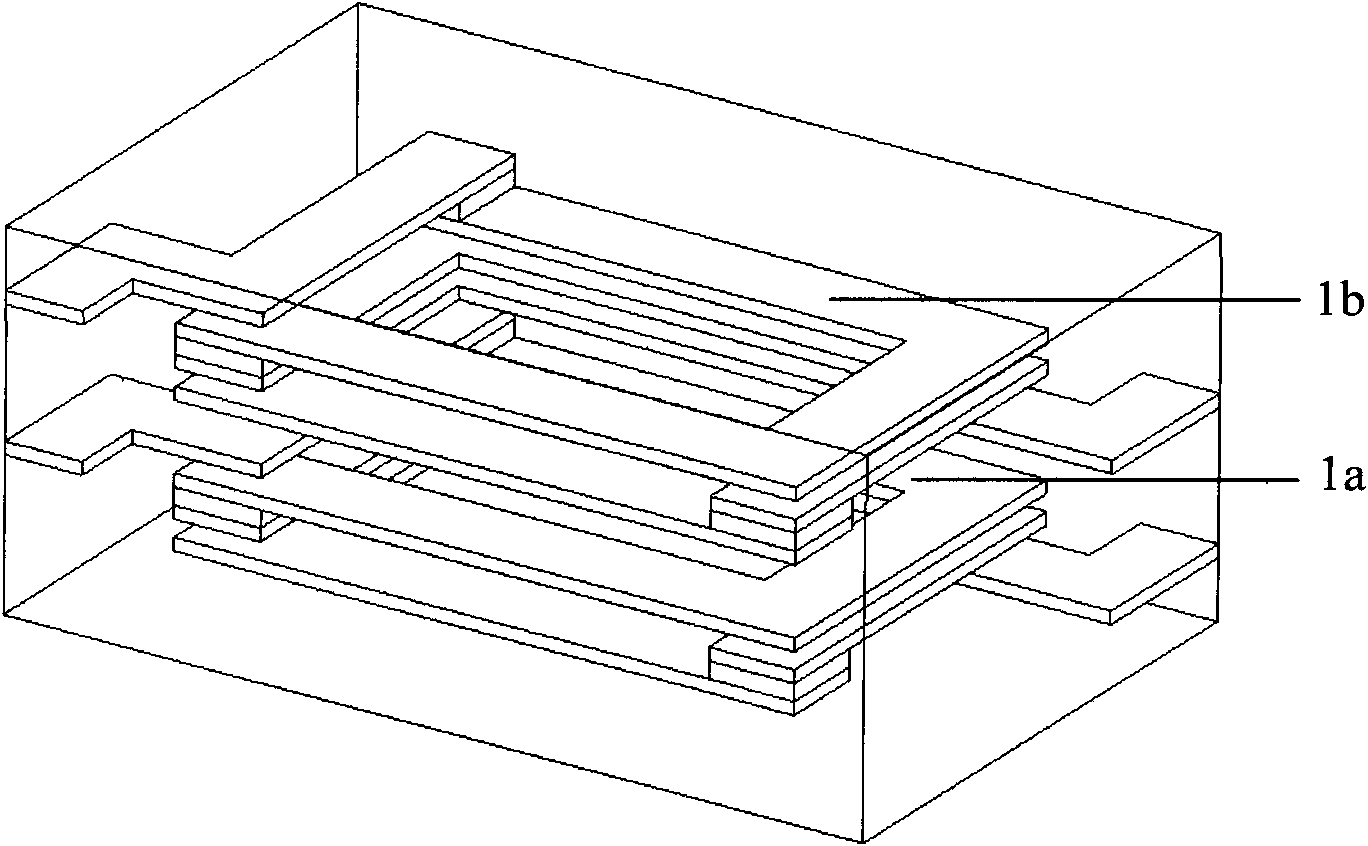
[0021] like figure 2 In the structure of the helical coil of the inner electrode of the laminated chip component shown, the helical coil 2 is divided into four sections by an upper lead-out 3 , a lower lead-out 4 and two electrodes 5 . The upper terminal 3, the lower terminal 4 and the two electrodes 5 are all connected in parallel by two electrodes of the same shape, and the DC resistance of each segment is reduced to 1 / 2 of each segment in the non-parallel state, so the total DC resistance of the helical coil The resistance is reduced to 1 / 2 of the non-parallel state. The upper lead-out 3 , the lower lead-out 4 and the parallel electrodes of the two electrodes 5 are completely or incompletely separated by electrically insulating thin-layer magnets (not shown in the figure). Both ends of the two coil-shaped electrodes 5 are connected by a conductive point 6, and one end of the upper lead-out terminal 3 and the lower lead-out end 4 is connected by the conductive point 6, and...
specific Embodiment approach 2
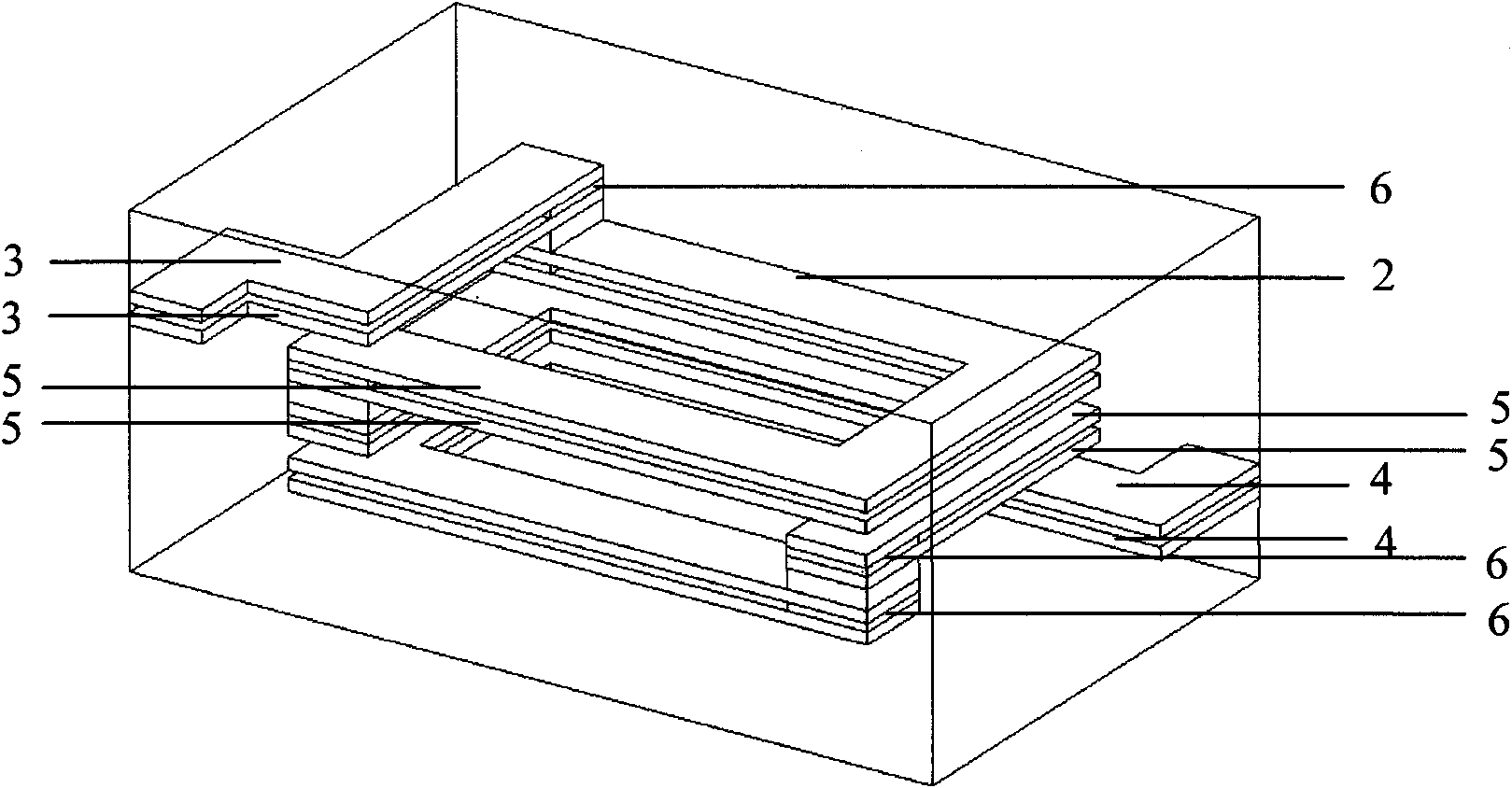
[0022] like image 3 In the structure of the helical coil of the inner electrode of the laminated chip component shown, the helical coil 2 is divided into four sections by an upper lead-out 3 , a lower lead-out 4 and two electrodes 5 . The lower terminal 4 and an electrode 5 are connected in parallel by two strands of electrodes with the same shape, and the DC resistance of the parallel segment is 1 / 2 of that of each segment in the non-parallel state, so the total DC resistance of the helical coil is greatly reduced. The parallel lower leads 4 and the parallel electrodes 5 are completely or partially separated by electrically insulating thin-layer magnets (not shown in the figure). Two ends of the parallel electrode 5 are connected by a conductive point 6, and one end of the parallel lower lead-out terminal 4 is connected by the conductive point 6, and the other end is connected by a common external terminal electrode (not shown in the figure). It can make the laminated chip ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
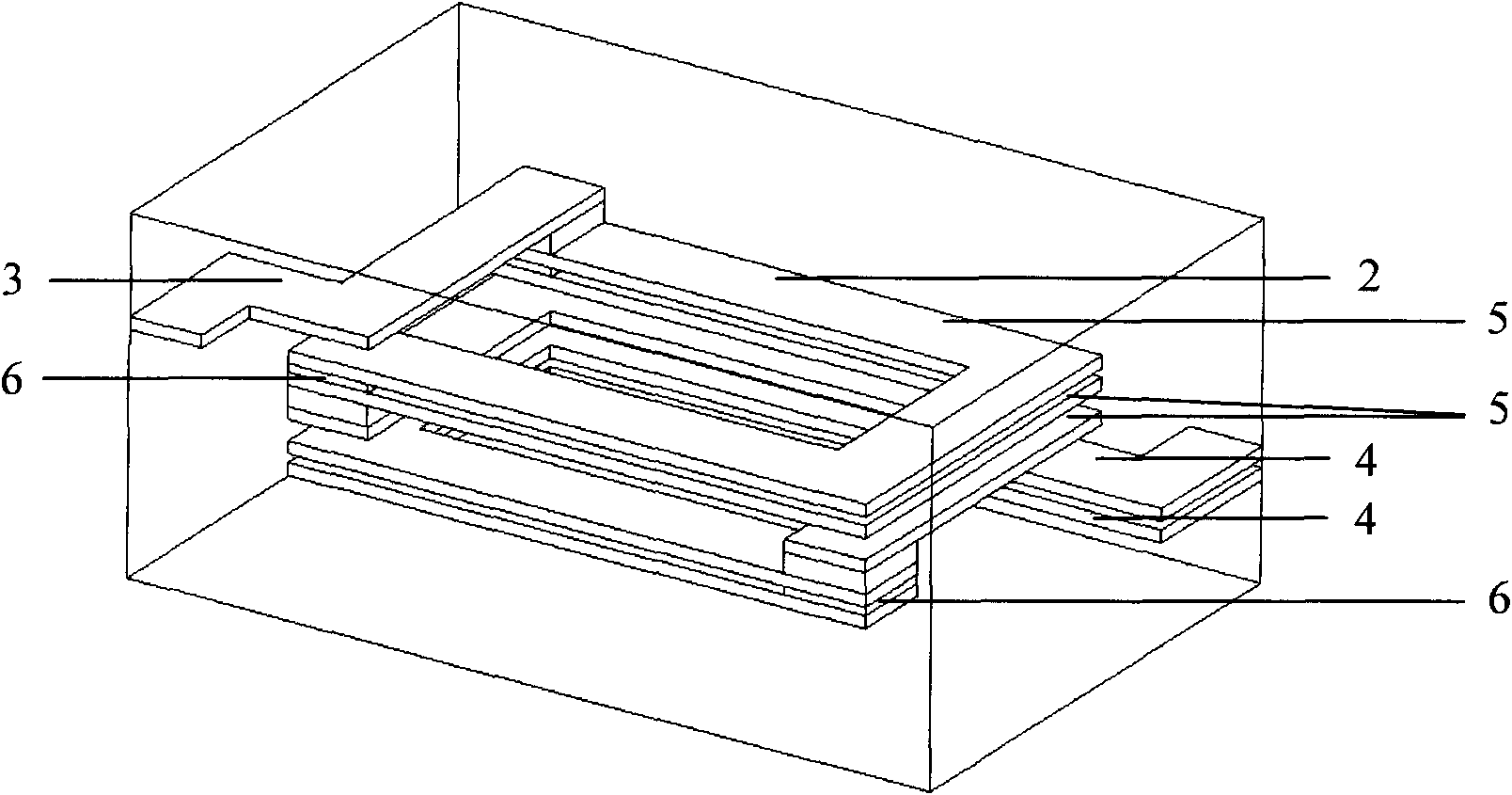
[0023] like Figure 4 In the shown structure of the helical coil of the internal electrode of the laminated chip component, the helical coil 2 is divided into two sections by the upper lead-out end 3 and the lower lead-out end 4 . The upper terminal 3 and the lower terminal 4 are connected in parallel by three terminal electrodes with the same shape, so the total DC resistance of the helical coil is reduced to 1 / 3 of that of the non-parallel state. One end of the upper lead-out terminal 3 and the lower lead-out end 4 is connected by a conductive point 6, and the other end is connected by a common external terminal electrode (not shown in the figure). It can make the laminated chip components maintain high inductance or impedance while greatly reducing the DC resistance, and will not cause short circuit of the laminated chip components and magnet cracking.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com