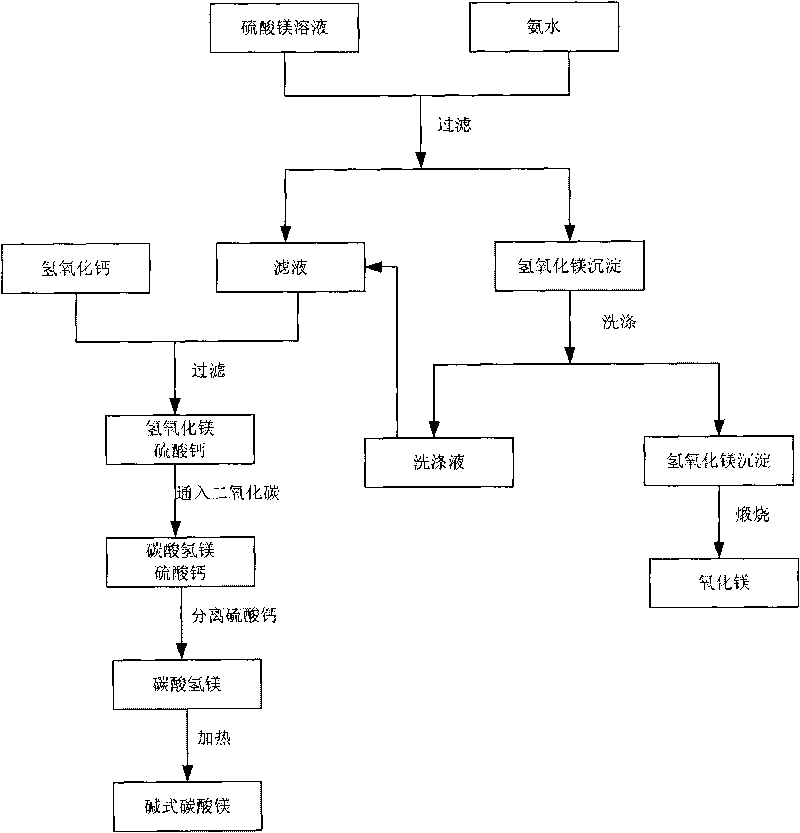
Technology for recovering magnesium from magnesium sulfate solution
A magnesium sulfate solution technology, applied in the field of magnesium recovery, can solve the problems of energy consumption, high production costs, and environmental pollution again, and achieve the effect of reducing processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0052] Table 1 magnesium sulfate solution composition table (g / l)
[0053] Mg
SO 4 2-
Al
Ni
co
mn
Fe
26-40
103-160
0.023
0.004
0.0016
0.0024
0.002
[0054] Ammonia: 10-25% ammonia
[0055] Get the magnesium sulfate solution 500ml of table 1.
[0056] Ammonia is the theoretical amount
[0057] Reaction temperature: room temperature~60℃
[0058] Addition method: ammonia water is added to magnesium sulfate solution
[0059] Reaction time: 0.5 hours to 2 hours
[0060] Filtration time: 1 minute to 5 minutes
[0061] The yield of magnesium hydroxide is 35-50%
[0062] Magnesium hydroxide purity ≥ 98%
example 2
[0064] Get the magnesium sulfate solution 500ml of table 1
[0065] Ammonia is 1-2 times the theoretical amount
[0066] Reaction temperature: room temperature~60℃
[0067] Addition method: ammonia water is added to magnesium sulfate solution
[0068] The amount of magnesium hydroxide seed crystals added is 0.5 to 3 times the theoretical amount
[0069] Reaction time: 0.5 hours to 2 hours
[0070] Filtration time: 0.5 minutes to 5 minutes
[0071] Magnesium hydroxide yield: 40-60%
[0072] Magnesium hydroxide purity ≥ 99%
example 3
[0074] Take the filtrate and lotion of Example 1 ~ 500ml
[0075] Add pre-prepared gypsum seeds
[0076] The excess of 1.05 lime slurry is used at a concentration of 5% to 20% by weight.
[0077] Causticizing time: 1 hour to 2 hours
[0078] Causticizing temperature: 45℃~105℃
[0079] Pickling gypsum and magnesium hydroxide,
[0080] PH2~5.5 Filtration output gypsum purity ≥ 95%, Mg ≤ 0.5-1%
[0081] The output temperature is 75-85°C, the specific gravity is 1.37-1.38 magnesium sulfate dissolves
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com