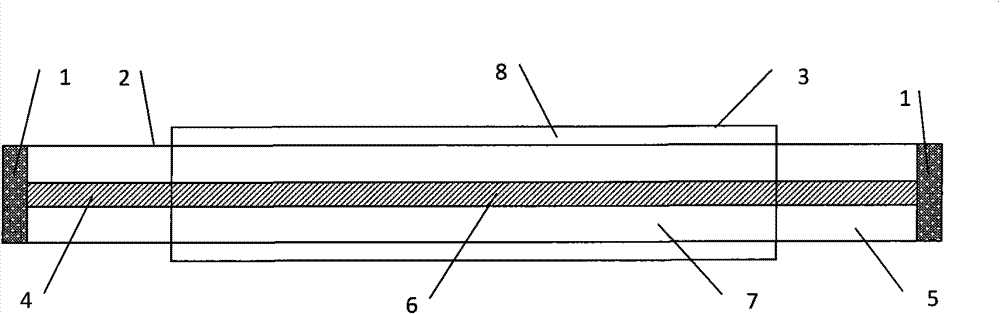
Fiber laser adopting end face coated cavity mirror
A fiber laser and coating cavity technology, applied in the direction of lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve problems affecting performance, grating ablation, and vulnerability to damage, and achieve long service life, not easy to aging, and anti-damage The effect of high threshold
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
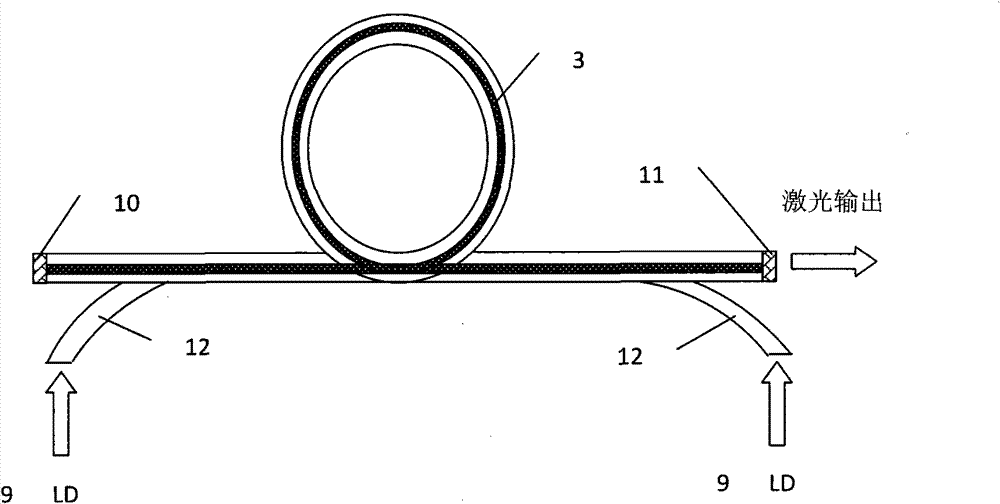
[0028] Such as figure 2 As shown, this example is an embodiment of a coated cavity mirror used in a side-pumped fiber laser. Semiconductor laser pumping source (9), optical coating layer (10), (11) and gain fiber (3) form basic Fabry-Perot resonant cavity, optical coating layer (10), (11) at fiber two ends as cavity mirror . The coated cavity mirrors (10), (11) are formed by coating a section of the gain fiber (3) with a thin film on the end face. The coated cavity mirror (10) at the left end is highly reflective to the fiber laser; the coated cavity mirror (11) as an output mirror is partially transparent to the fiber laser. The gain fiber (3) is formed by doping ytterbium ions with a flat top on the cross section. The pumping light is injected into the inner cladding of the gain fiber (3) from the side through the guide fiber (12), and the laser oscillation is excited in the gain fiber (3). In the laser, the laser light travels between two cavity mirrors multiple times ...
Embodiment 2
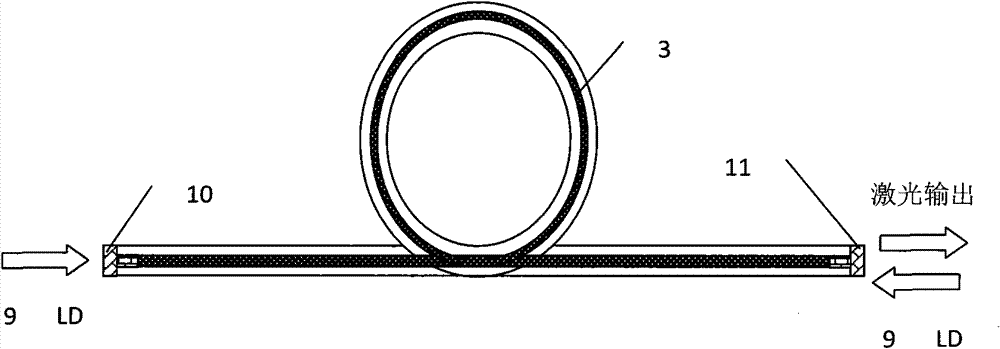
[0030] Such as image 3 As shown, this example is an embodiment of a coated cavity mirror used in an end-pumped fiber laser. The semiconductor laser pumping source (9), the coated cavity mirrors (10), (11) and the gain fiber (3) form a basic Fabry-Perot resonant cavity. The coated cavity mirrors (10) and (11) are respectively formed by coating optical thin films on the end surfaces of two small optical fibers. These two sections of small fibers are undoped fibers with the same parameters as the gain fiber (3). The coated cavity mirror (10) at the left end is antireflective to the pump wavelength and highly reflective to the laser wavelength; the coated cavity mirror (11) as an output mirror is antireflective to the pump wavelength and partially transparent to the laser wavelength. The gain fiber (3) is formed by gradual doping of germanium ions on the cross section. Pumping light is injected into the inner cladding of the gain fiber (3) from both end faces to excite laser o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com