Method for detecting polymorphism of flora of prawn culture water body
A technology for aquaculture water and polymorphism, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA preparation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
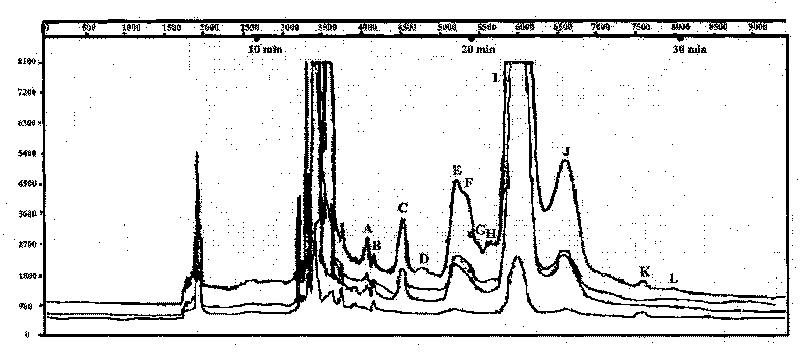
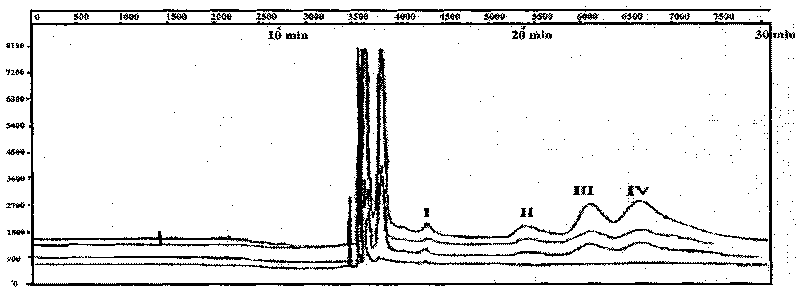
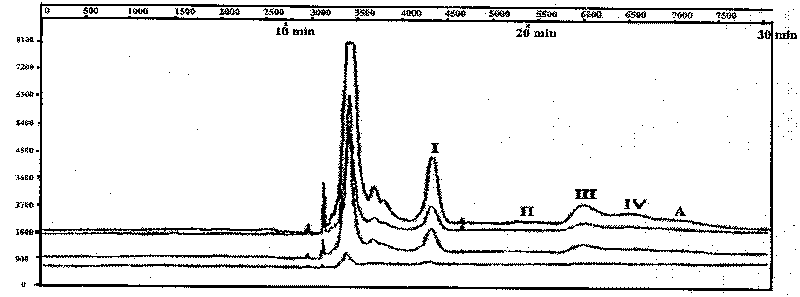
[0042] The aquaculture industry is an important pillar industry in my country's coastal areas, and the prawn aquaculture industry plays an important role in it. The area of prawn aquaculture in my country reaches 2.4 million mu. However, due to the frequent occurrence of diseases, the output of shrimp farming in my country has been lower than the bottom in recent years. More and more scholars believe that the root cause of shrimp diseases is the deterioration of the farming ecological environment, and the vicious circle between the polluted environment and the farming organisms has led to the disease. continuous outbreak. However, only a part of the traditional method of isolating strains can be cultured, and when analyzing microbial diversity, it cannot accurately reflect the composition and diversity of the mixed flora. In this experiment, the shrimp breeding farm in Dongsheng Town, Zhongshan City, Guangdong Province was taken as the research object. T-RFLP combined with FI...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Use the shrimp culture water environment of Example 1 to carry out the flora detection and analysis at different time points, sampling once every two weeks from April to May (April 1st, April 16th, May 1st, May 16th). Collect 4 x 2000ml of water samples within 30cm of the surface at multiple points, bring them back to the laboratory for vacuum filtration, and store the filtrate at -20°C. The steps and process conditions for detecting the polymorphism of the shrimp aquaculture water are as follows:
[0077] (1) Extraction of microbial total DNA in water body samples of shrimp breeding farms:
[0078] a. Transfer the filtrate to a 100ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 13000rpm for 10min, suck off the supernatant, resuspend the precipitate with sterile water, and transfer to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube;
[0079] b. Add 567 μl TE, pipette repeatedly to resuspend it, add 40 μl 10% SDS and 5 μl 20mg / ml proteinase K, mix well, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour;
[0080] c. Add 100 μ...
Embodiment 3
[0112] With embodiment 1 shrimp breeding water environment, T-RFLP combined with FISH technology directly detects the vertical (depth 40cm and 150cm) distribution changes of shrimp pond water microbial flora, on June 5, 2009 respectively in the surface layer (40cm) and deep layer (150cm) Random multi-point sampling once 2×2000ml, take it back to the laboratory for vacuum filtration, and store the filtrate at -20°C. The steps and process conditions for detecting the polymorphism of the shrimp culture water body flora are as follows:
[0113] (1) Extraction of microbial total DNA in the water body sample of the shrimp breeding farm;
[0114] a. Transfer the filtrate to a 100ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 8min, suck off the supernatant, resuspend the precipitate with sterile water, and transfer to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube;
[0115] b. Add 567 μl TE, pipette repeatedly to resuspend it, add 35 μl 10% SDS and 4 μl 20mg / ml proteinase K, mix well, and incubate at 37°C f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com