Method for rapid in-situ remediation soil polluted by heavy metals
An in-situ remediation and heavy metal technology, applied in the field of in-situ remediation of contaminated soil, can solve the problems of complex, secondary pollution operation, high cost, etc., and achieve the effects of convenient material collection, reduced absorption and accumulation, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] The test site was selected in Hubei, near the Daye Nonferrous Metal Smelter. The total cadmium content in the soil was 4.55mg / kg, and the total copper content was 289.9mg / kg. The dried rice straw (with a water content of 5%) is crushed mechanically to make its length equal to or less than 2 cm, and used as a restoration material for repairing cadmium-contaminated soil. The heavy metal fixation effect of repair materials was verified by field experiments.
[0014] Rice straw was applied to the surface layer (0-20cm) of the polluted soil at an application rate of 0, 5.2, 7.7, 10.3, 15.4, 23.2 tons / ha, and soil samples were taken for analysis after three months (ie 90 days). See Table 1 for the soil pH, organic matter and available phosphorus content after remediation.
[0015] Table 1 Test of soil pH, organic matter and available phosphorus content after restoration by the present invention
[0016]
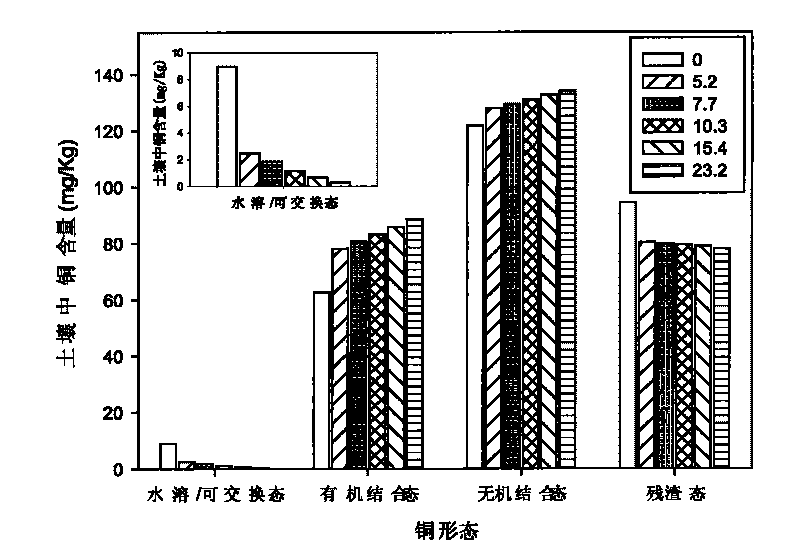
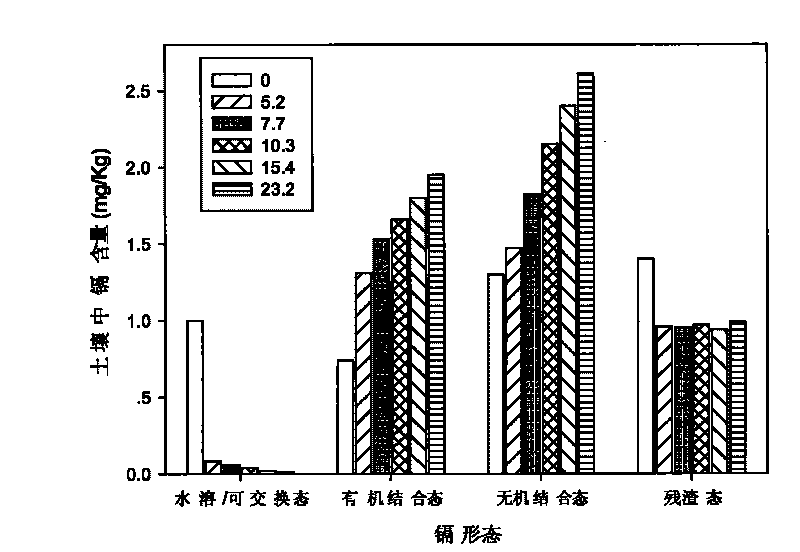
[0017] Sposito continuous extraction method was used (Sposito G, L...
Embodiment 2
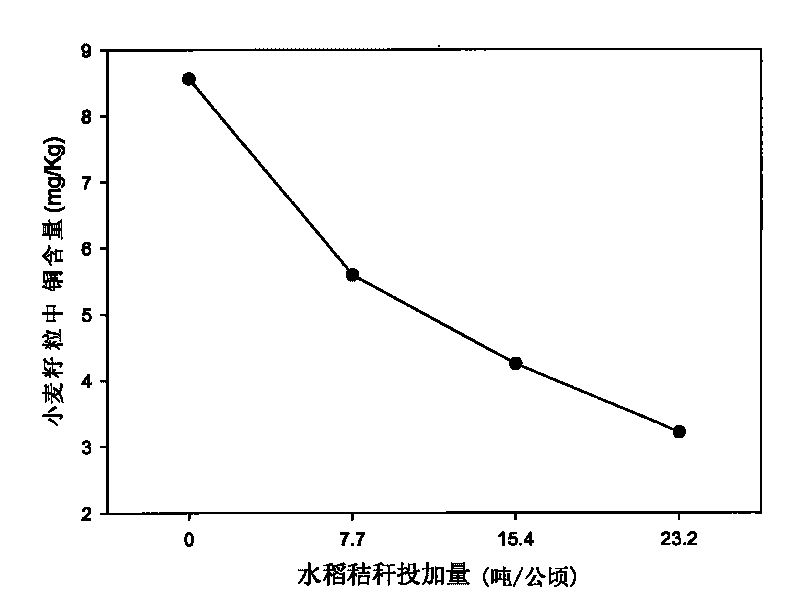
[0021] The 2cm rice straw is applied to the surface layer (0-20cm) of the cadmium-contaminated soil, mixed evenly, and the application rate is 0, 7.7, 15.4, 23.2 tons / ha, and wheat is sown three months later. The grains are harvested after the wheat has matured. The grains were dried at 65°C for about 48 hours, crushed by a stainless steel grinder, and passed through a 60-mesh nylon sieve. Cadmium and copper in wheat grains were digested with nitric acid-perchloric acid and determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry.
[0022] The contents of copper and cadmium in wheat grains planted and harvested after soil remediation are shown in image 3 , Figure 4 , the application of rice straw can significantly reduce the content of copper and cadmium in wheat grain. The copper content in the grain was 8.56mg kg by the control treatment -1 Reduced to 3.21mg kg -1 , decreased by 62.5%, reaching the level required for pollution-free agricultural products (see image 3 ). Th...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Apply 2cm-long rice straw to the surface layer (0-20cm) of cadmium-contaminated soil, mix evenly, and apply 0, 5.2, 10.3, 15.4 tons / ha, and sow pak choi three months later. After the pakchoi matured, the aboveground parts were harvested, and the yield of pakchoi was recorded. Plant samples were dried at 65°C for about 48 hours, pulverized by a stainless steel pulverizer, and passed through a 60-mesh nylon sieve. Cadmium and copper in the shoots of Chinese cabbage were determined by nitric acid-perchloric acid digestion and atomic absorption spectrophotometry.
[0025] The output of pakchoi planted in repaired soil is as follows: Figure 5 shown. The application of rice straw can significantly increase the yield of pakchoi, with a maximum increase of 126.5%. The contents of copper and cadmium in the aboveground part of Chinese cabbage are shown in Image 6 , Figure 7 . The application of rice straw can significantly reduce the content of copper and cadmium in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com