Paenibacillus polymyxa and application thereof
A polymyxa and bacillus technology, applied in the application, bacteria, bacterial peptides and other directions, can solve the problems of damage to the host vascular bundle transport tissue, easy loss of resistance, low resistance, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2 strain identification
[0031] The main morphological and biological characteristics of the strains isolated above are as follows: the cells are rod-shaped, Gram-positive, and move with perinatal flagella. There are oval spores in enlarged cysts, and there is no soluble pigment on nutrient agar. Facultative anaerobic. The colony on the culture medium is thin, expanding in a star shape, with a large amount of bacteria and sticky, and the surface is dull. Growth will adhere to the medium. The optimum temperature for growth is 28-30°C, and the growth temperature range is 15-50°C. The optimum pH for growth is 7.0, and the growth pH range is 5.6-8.5.
[0032] The strain was identified as Paenibacillus polymyxa by FAME fatty acid analysis and named as Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Antagonistic activity of embodiment 3 bacterial strain ZJU0901 to Ralstonia solanacearum
[0034] In this example, the 8 R. solanacearum strains in Example 1 were still used as indicator strains. Add 1ml of the bacterial suspension of the indicated strain to 15ml of NA medium that has been sterilized and melted and cooled to about 45°C, shake well and pour the medium into a sterilized petri dish. Use a sterilized toothpick to pick a single colony of Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901, and spot it on the medium with indicator bacteria. The culture condition is 30°C for 48 hours, and its antagonistic ability is determined according to the diameter of the inhibition zone. Antagonism results are as follows (Table 2):
[0035] Table 2 Antagonistic activity of Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901 to Ralstonia solanacearum strains from different hosts
[0036]
[0037] The above results show that: Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901 has obvious antagonistic activity to other indicator p...
Embodiment 4
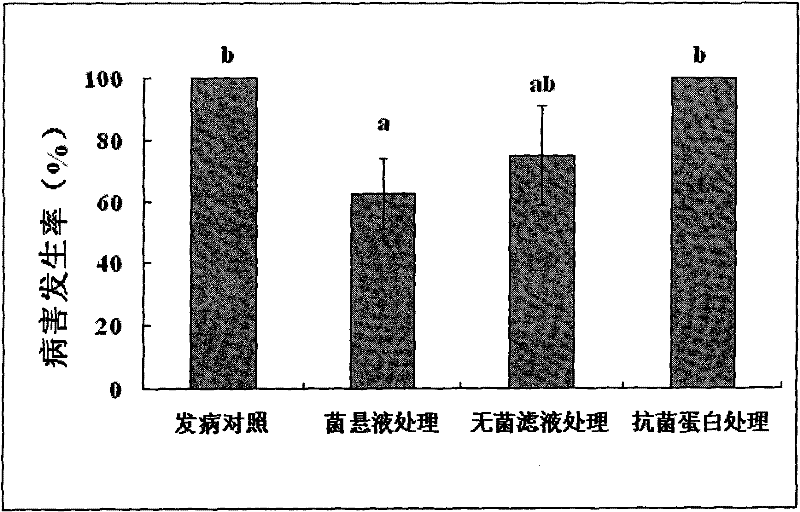
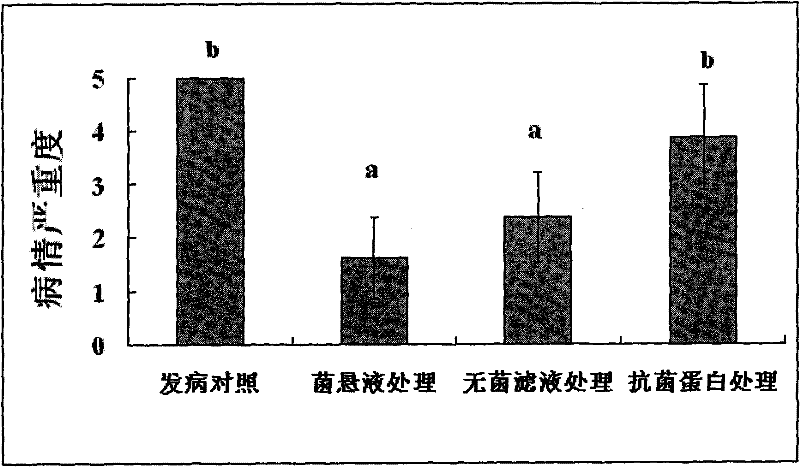
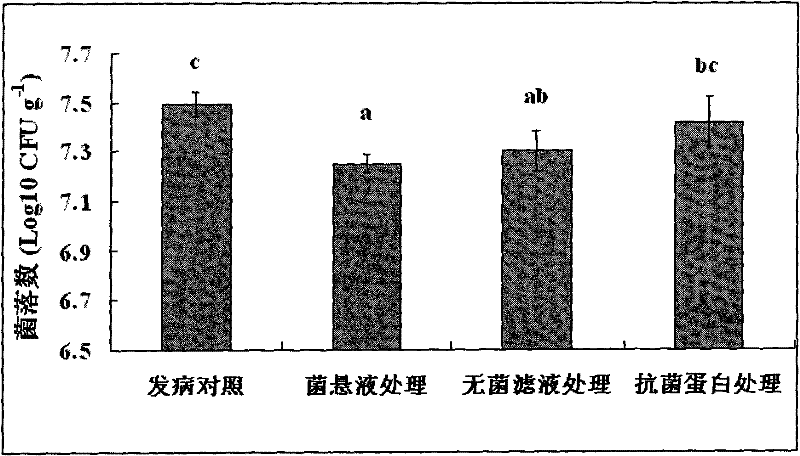
[0038] Antibacterial activity assay of embodiment 4 Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901 different treatments
[0039] The antibacterial activity of Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901 bacterial suspension, sterile filtrate, proteinase K-treated filtrate and high-temperature heat-treated filtrate were determined by the Oxford cup method, and each treatment was set in 3 repetitions, and the specific methods for each treatment as follows:
[0040] (1) Bacterial suspension preparation: Pick a single colony of Paenibacillus polymyxa ZJU0901, inoculate it in NB liquid medium, and culture it with shaking at 170 r / min at 30°C for 24 hours;
[0041](2) Preparation of sterile filtrate: the bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 10,000 r / min for 20 min, the supernatant was taken, and sterilized with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane to obtain a crude extract of antibacterial substances;
[0042] (3) Proteinase K treatment: take 1ml of the sterile filtrate, divide it into 1.5ml centrifuge tubes, add...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com