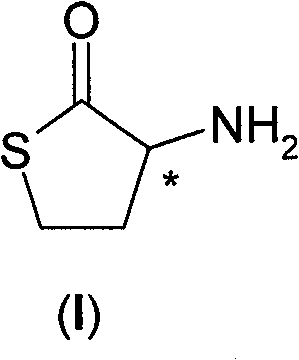
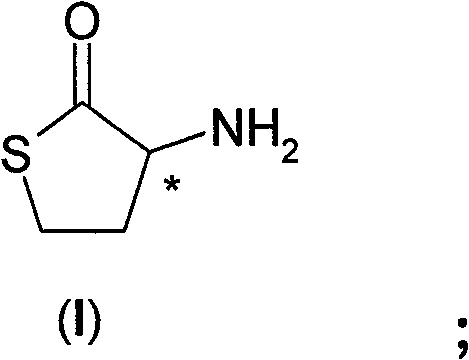
Process for the resolution of homocysteine-thiolactone
A homocysteine and thiolactone technology, applied in organic chemistry and other fields, can solve the problems of difficult amide cracking, low yield, expensive use, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 - Splitting (Method 1)
[0048] R,S-HCT hydrochloride (154 g) and acetone (2500 mL) were charged to the reactor, triethylamine (139 mL) was added and stirred for 1 hour. Triethylamine hydrochloride was filtered off and the pale yellow filtrate was recharged to the reactor along with L-(+)-mandelic acid (114 g). Solids started to precipitate immediately; the suspension was cooled to 10° C. for 1 hour and then filtered. S-HCT mandelate (118 g dry weight) was obtained while leaving the mother liquor for the racemization process.
[0049] S-HCT mandelate was charged to the reactor along with acetone (1500 mL), and hydrochloric acid 37% (44 mL) was added to the stirred suspension. Stirring was continued at 15°C for 1 hour, and the solid was filtered and washed with acetone. S-HCT hydrochloride was obtained (60.5 g dry weight, 78.5% yield), [α] D =+21.9°.
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 - Splitting (Method 1)
[0051]R,S-HCT hydrochloride (154 g), methanol (3000 ml) and (-)-di(toluoyl)-L-tartaric acid (145 g) were charged to the reactor, and the mixture was stirred until completely dissolved , then triethylamine (139 mL) was added dropwise at 20°C. Stirring was continued at the same temperature for 1 hour, then the precipitate was filtered and washed with methanol; the mother liquor was kept for the racemization process. The precipitate was recharged to the reactor along with acetone (1500 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, then filtered to obtain L-HCT di(toluoyl)tartrate (120 g dry weight).
[0052] S-HCT di(toluoyl)tartrate was resuspended in acetone (1500 mL), and to the stirred suspension was added 37% hydrochloric acid (40 mL). Stirring was continued at 15°C for 1 hour, and the resulting product was filtered and washed with acetone. Obtain 55.5 grams of L-HCT hydrochloride (dry weight, 72% yield), [α] D =+22.1°.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 - Racemization (Method 1)
[0054] The mother liquor from Example 1 was acidified to pH 1 with 37% hydrochloric acid, then concentrated to dryness under vacuum. The residue was dissolved in acetic acid (150 mL), salicylaldehyde (2 mL) was added and the solution was heated to 50°C for 5 hours, then cooled to 5°C for 2 hours. The resulting solid was filtered and washed well with acetone to obtain racemic R,S-HCT hydrochloride (65.5 g dry weight).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com