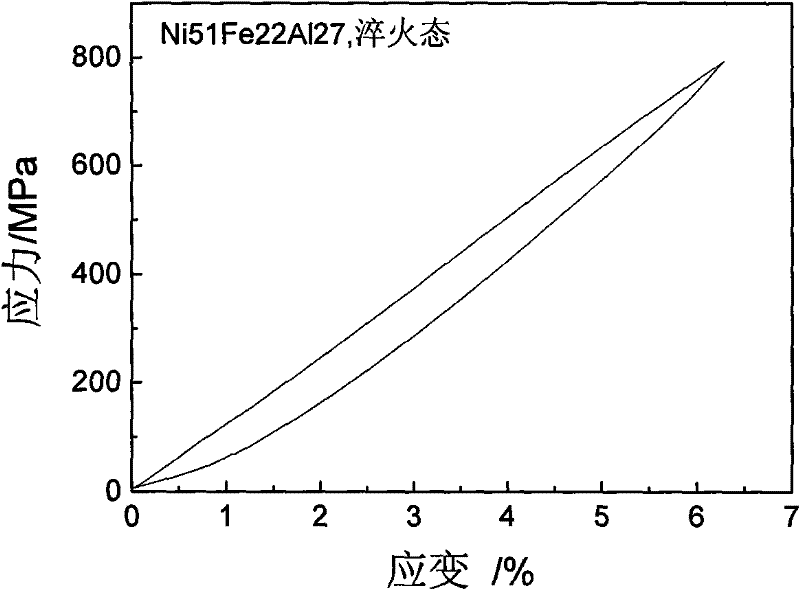
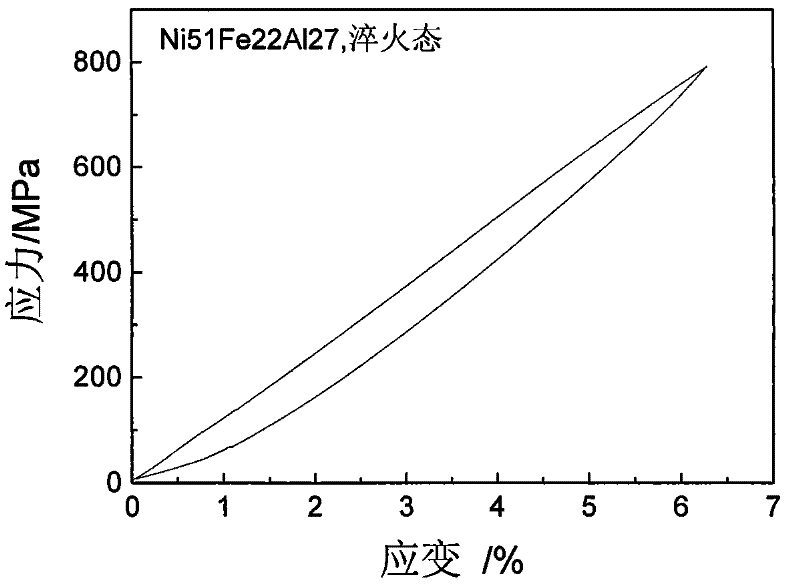
A kind of ni-fe-al alloy with linear superelasticity and preparation method thereof
A ni-fe-al, superelastic technology, applied in the field of alloy materials, can solve the problems of difficult precise control of composition, limited alloy research and development, limited cold deformation ability, etc., to achieve easy raw materials, expanded application temperature range, excellent superelasticity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Step 1) Weigh the components according to atomic percentage: nickel (Ni) is 56.5%, iron (Fe) is 18.5%, aluminum (Al) is 25%, and these three powders are placed in a mixing tank and mixed evenly.
[0021] Step 2) Pressing the powder into shape with a pressing pressure of 500 MPa.
[0022] Step 3) Vacuum sintering at a sintering temperature of 1280° C., holding time for 2 hours, and cooling with the furnace.
[0023] Step 4) Heating the alloy sintered billet to 1280° C. and keeping it warm for 2 hours, taking it out and immediately performing quenching treatment.
[0024] For the Ni prepared above 56.5 Fe 18.5 al 25 The mechanical properties of the alloy were tested, and it was found that the quenched state of the alloy showed complete linear superelasticity, and the elastic recovery was 4.3%.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Step 1) Weigh the components according to atomic percentage: nickel (Ni) is 56.5%, iron (Fe) is 18.5%, aluminum (Al) is 25%, and these three powders are placed in a mixing tank and mixed evenly.
[0027] Step 2) Pressing the powder into shape with a pressing pressure of 500 MPa.
[0028] Step 3) Vacuum sintering at a sintering temperature of 1280° C., holding time for 2 hours, and cooling with the furnace.
[0029] Step 4) Heating the alloy sintered billet to 1200° C. and keeping it warm for 16 hours, taking it out and immediately performing quenching treatment.
[0030] For the Ni prepared above 56.5 Fe 18.5 al 25 The mechanical properties of the alloy were tested, and it was found that the quenched state of the alloy showed complete linear superelasticity, and the elastic recovery was 4.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Step 1) Weigh the components according to atomic percentage: nickel (Ni) is 56%, iron (Fe) is 19%, aluminum (Al) is 25%, and these three powders are placed in a mixing tank and mixed evenly.
[0033] Step 2) Pressing the powder into shape with a pressing pressure of 500 MPa.
[0034] Step 3) Vacuum sintering at a sintering temperature of 1280° C., holding time for 2 hours, and cooling with the furnace.
[0035] Step 4) Heating the alloy sintered billet to 1280° C. and keeping it warm for 2 hours, taking it out and immediately performing quenching treatment.
[0036] For the Ni prepared above 56 Fe 19 al 25 The mechanical properties of the alloy were tested, and it was found that the quenched state of the alloy showed complete linear superelasticity, and the elastic recovery was 4.2%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com