Organic solvent tolerant protease and producing strain thereof
A technology resistant to organic solvents and organic solvents, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, hydrolytic enzymes, etc., can solve the problems that have not been seen, and achieve the effect of good organic solvent tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] This experiment illustrates the screening procedure for natural strains producing organic solvent-resistant proteases.
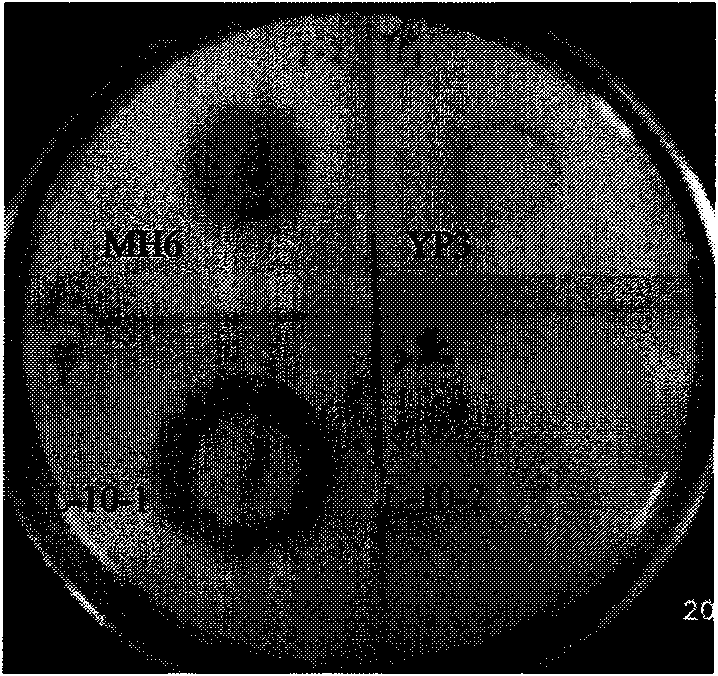
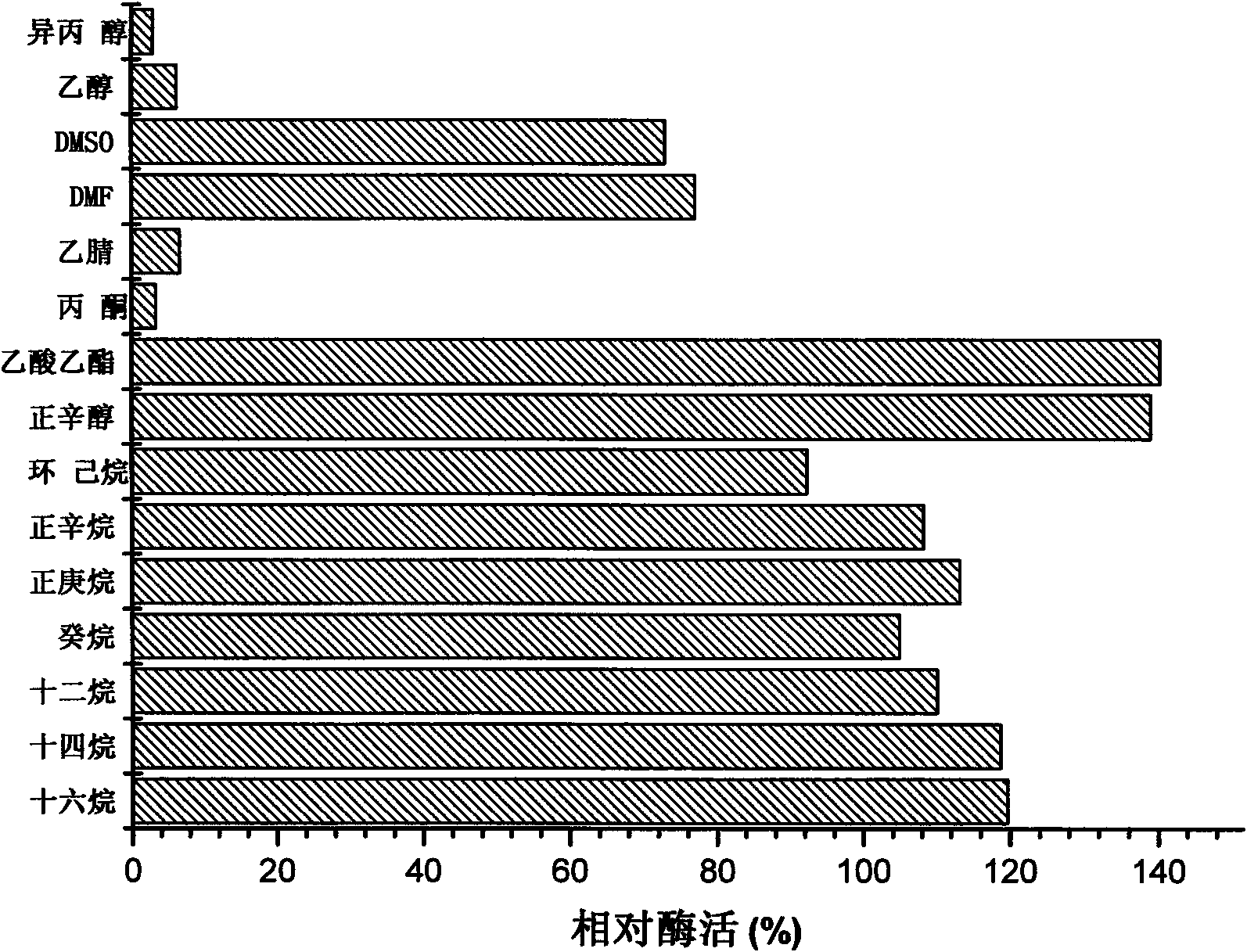
[0027] Preliminary screening: Obtain strains that can tolerate organic solvents and produce protease. Using different concentrations of cyclohexane, DMF, DMSO and other organic solvents as the screening pressure, extremophiles resistant to organic solvents were screened from oily soil samples. Then, the milk agar plate medium was used to screen the protease-producing strains from the above-mentioned extremophiles resistant to organic solvents. According to the ratio of the colonies formed by each strain on the milk agar plate medium to the diameter of the transparent circle, 6 protease high-producing bacteria were preliminarily screened ( figure 1 ). Because these 6 strains can tolerate organic solvents, the protease produced by them is also very likely to have tolerance to organic solvents.
[0028]Re-screening: By testing the protease-producing a...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This experiment illustrates the physiological and biochemical properties and identification of organic solvent-resistant protease-producing bacteria MH6
[0034] The strain Serratia marcescens MH6 is a Gram-negative short bacilli strain, without spores, with perinatal flagella, and the size is 1 μm×1.5~0.7×1.0 μm. After growing in LB medium for 24 hours, the colony is red and the size of the colony is 1.5-2.5 mm. The growth temperature range of the strain is 20-45 DEG C, the optimum growth temperature is 35 DEG C, the growth pH is 5-9, the optimum pH is 8.0, and it grows under aerobic conditions. See its physiological and biochemical properties (Table 1).
[0035] LB medium formula: tryptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 1.0g / L.
[0036] Table 1 Some physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain MH6
[0037] feature
[0038] oxidase reaction
[0039] Note: + (positive): can be used; - (negative): can not be used.
[0040] After BIOLOG ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This experiment illustrates the purification procedure of the organosolvent-resistant protease produced by the strain Serratia marcescens MH6.
[0048] The strain Serratia marcescens MH6 was cultured in the enzyme-producing medium for 28 hours, the obtained fermentation liquid was centrifuged (9000 rpm, 4° C.) for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was taken as the crude enzyme liquid.
[0049] Preliminary purification of organic solvent-resistant protease by ammonium sulfate precipitation. Place the crude enzyme solution in an ice bath, and slowly add (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 to 50% saturation, then centrifuge (9000rmp, 4°C) for 20min, take the supernatant and continue to add (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 To 60% saturation, centrifuge again (9000rmp, 4°C) for 20min, and dissolve the obtained precipitate with Tris-HCl buffer (50mmol / L, pH8.0). After testing, the recovery rate of protease activity in the precipitate reached 69.1%.
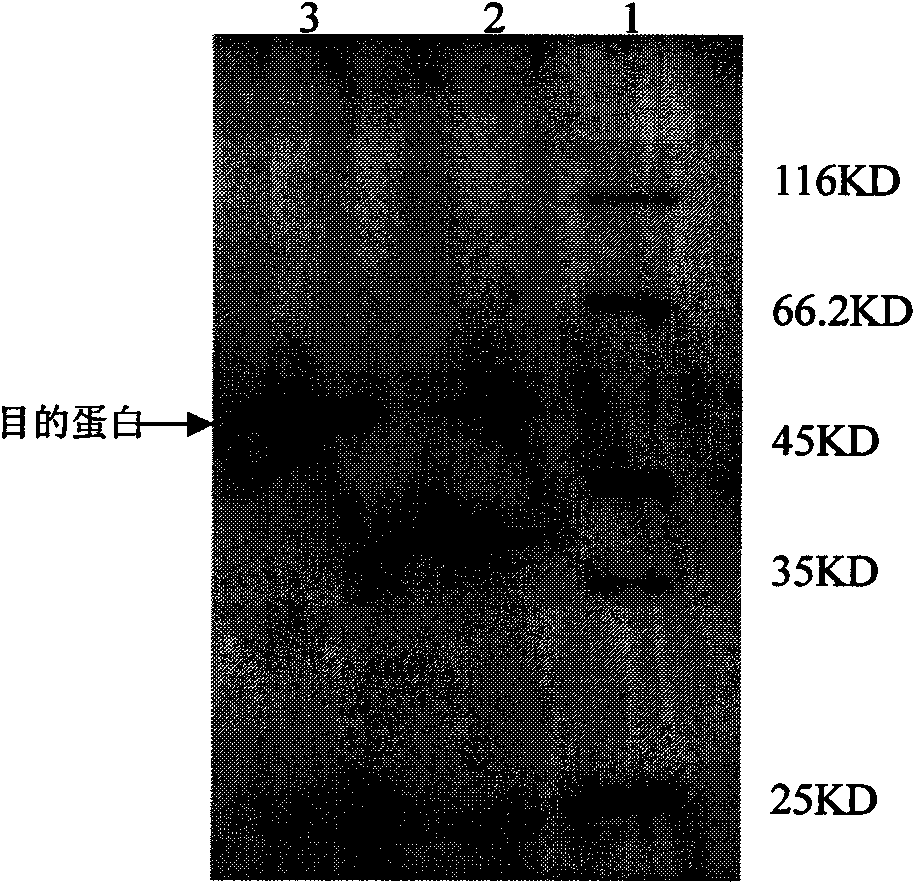
[0050] The organic solvent-resistant protease was further p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com