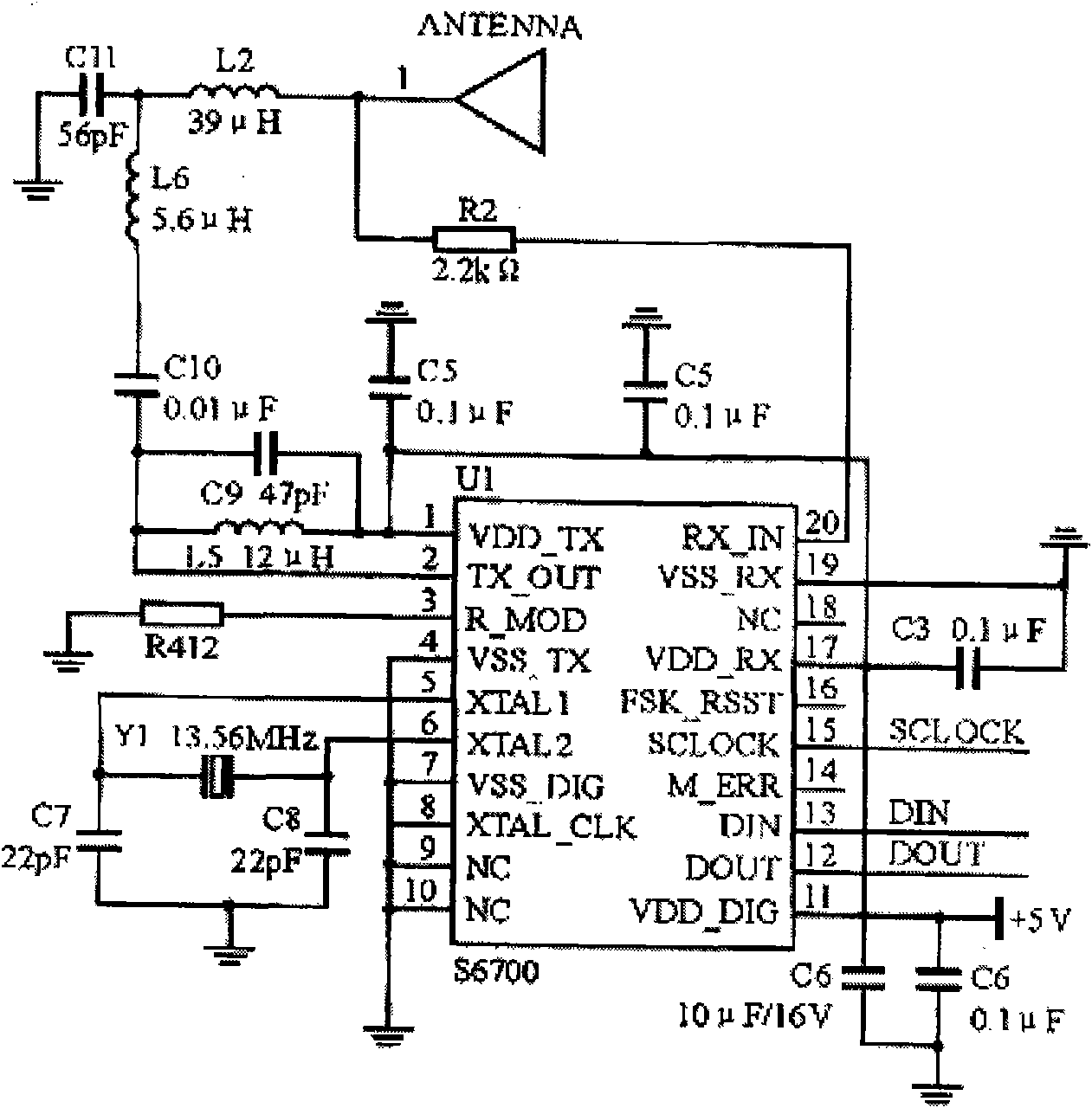
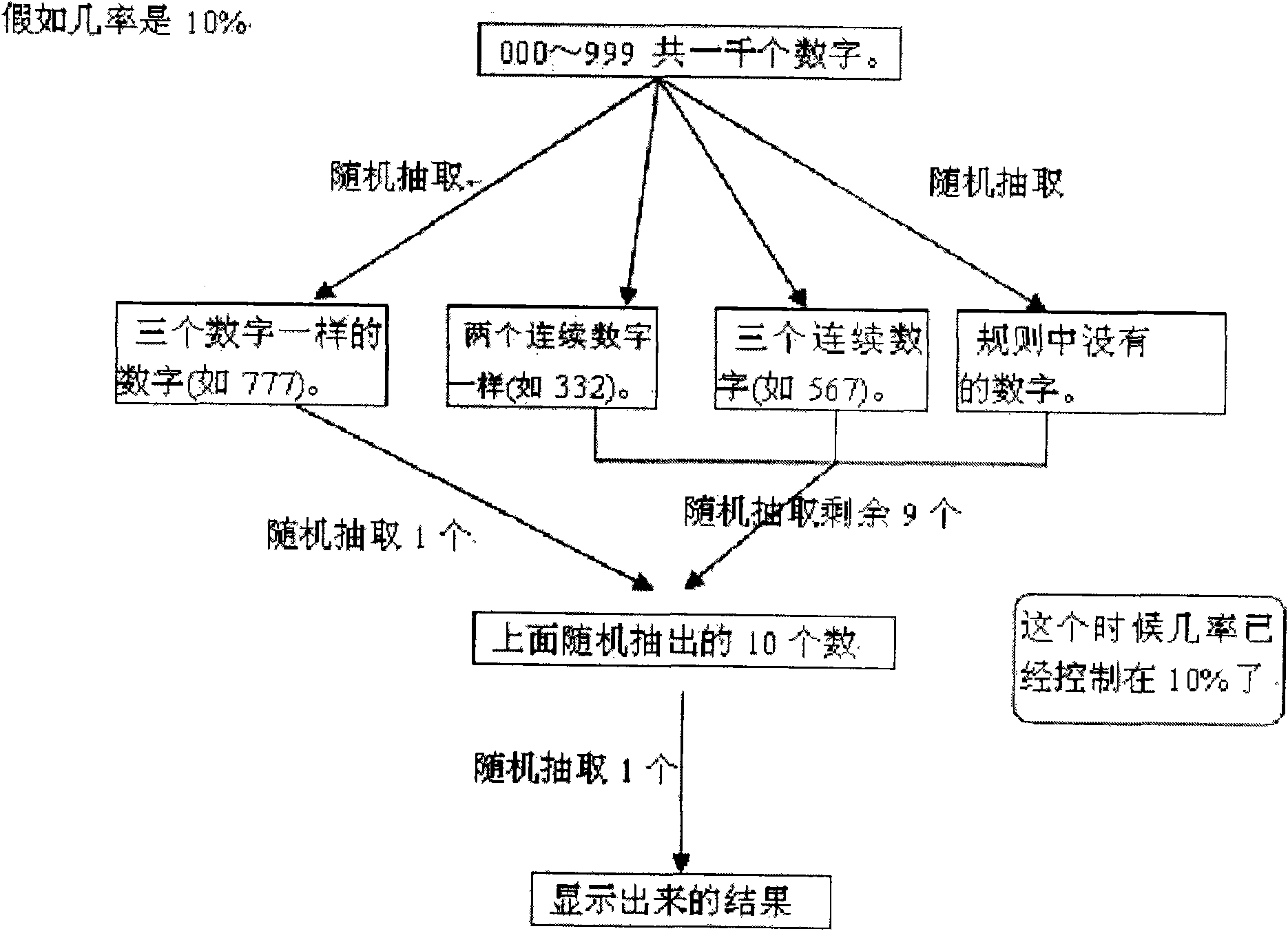
RFID security system
A security system and memory technology, applied in the field of RFID security systems, can solve problems such as hidden dangers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] For example, at first, find out three numbers, p, q, r,
[0069] [068] Wherein p, q are two different prime numbers, and r is a number that is mutually prime with (p-1)(q-1)......
[0070] [069] p, q, r these three numbers are the private key
[0071] [070] Then, find out m, so that rm==1mod(p-1)(q-1).....
[0072] [071] This m must exist, because r and (p-1)(q-1) are relatively prime, and can be obtained by the method of rolling and dividing.....
[0073] [072] Come again, calculate n=pq.......
[0074] [073] The two numbers of m and n are the public key
[0075] [074] The encoding process is, if the data is a, it is regarded as a large integer, assuming a
[0076] If a>=n, just a is represented as s carry (s<=n, usually gets s=2 ^ t),
[0077] [076] Then each digit is less than n, and then segmented coding...
[0078] [077] Next, calculate b==a^m mod n, (0<=b
[0079] [078] b is the encoded data......
[0080] The process of decoding is to calculate ...
Embodiment 2
[0107] To change a 64-bit plaintext input block into a 64-bit ciphertext output block, the key used is also 64 bits. The main flow chart of the entire algorithm is as follows:
[0108] Its function is to reassemble the input 64-bit data block bit by bit, and divide the output into two parts, L0 and R0. Each part is 32 bits long. The replacement rules are shown in the following table:
[0109] 58, 50, 12, 34, 26, 18, 10, 2, 60, 52, 44, 36, 28, 20, 12, 4,
[0110] 62, 54, 46, 38, 30, 22, 14, 6, 64, 56, 48, 40, 32, 24, 16, 8,
[0111] 57, 49, 41, 33, 25, 17, 9, 1, 59, 51, 43, 35, 27, 19, 11, 3,
[0112] 61, 53, 45, 37, 29, 21, 13, 5, 63, 55, 47, 39, 31, 23, 15, 7,
[0113] The 58th digit that is about to be input is changed to the first digit, the 50th digit is changed to the second digit, ..., and so on, and the last digit is the original 7th digit. L0 and R0 are the two parts after the transposition output. L0 is the left 32 bits of the output, and R0 is the right 32 bits. F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com