Markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (nash) and methods of use thereof
A steatohepatitis, non-alcoholic technology, used in disease diagnosis, instrumentation, biomaterial analysis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0153] Correlation of plasma and liver fatty acid composition
[0154] Lipid metabolites expressed as percentage composition of lipid classes were found to be analyzable from blood in relation to hepatic triglyceride content. To determine the potential of blood-based quantities to accurately reflect the fatty acid composition of liver lipid classes, the fatty acid composition of each lipid class was correlated for paired plasma-liver samples derived from normal subjects (from the first set of subjects). The correlation between the fatty acid composition of plasma and liver was excellent for the triglyceride and phosphatidylcholine classes and partially good for the cholesteryl ester class ( figure 2 ). This indicates that plasma fatty acid composition of triglycerides and phosphatidylcholine are accurate indicators of hepatic fatty acid composition of triglycerides and hepatic fatty acid composition of phosphatidylcholine, respectively. Thus, plasma-based fatty acid levels ...
Embodiment 2
[0157] Correlation between hepatic steatosis and liver fatty acid composition
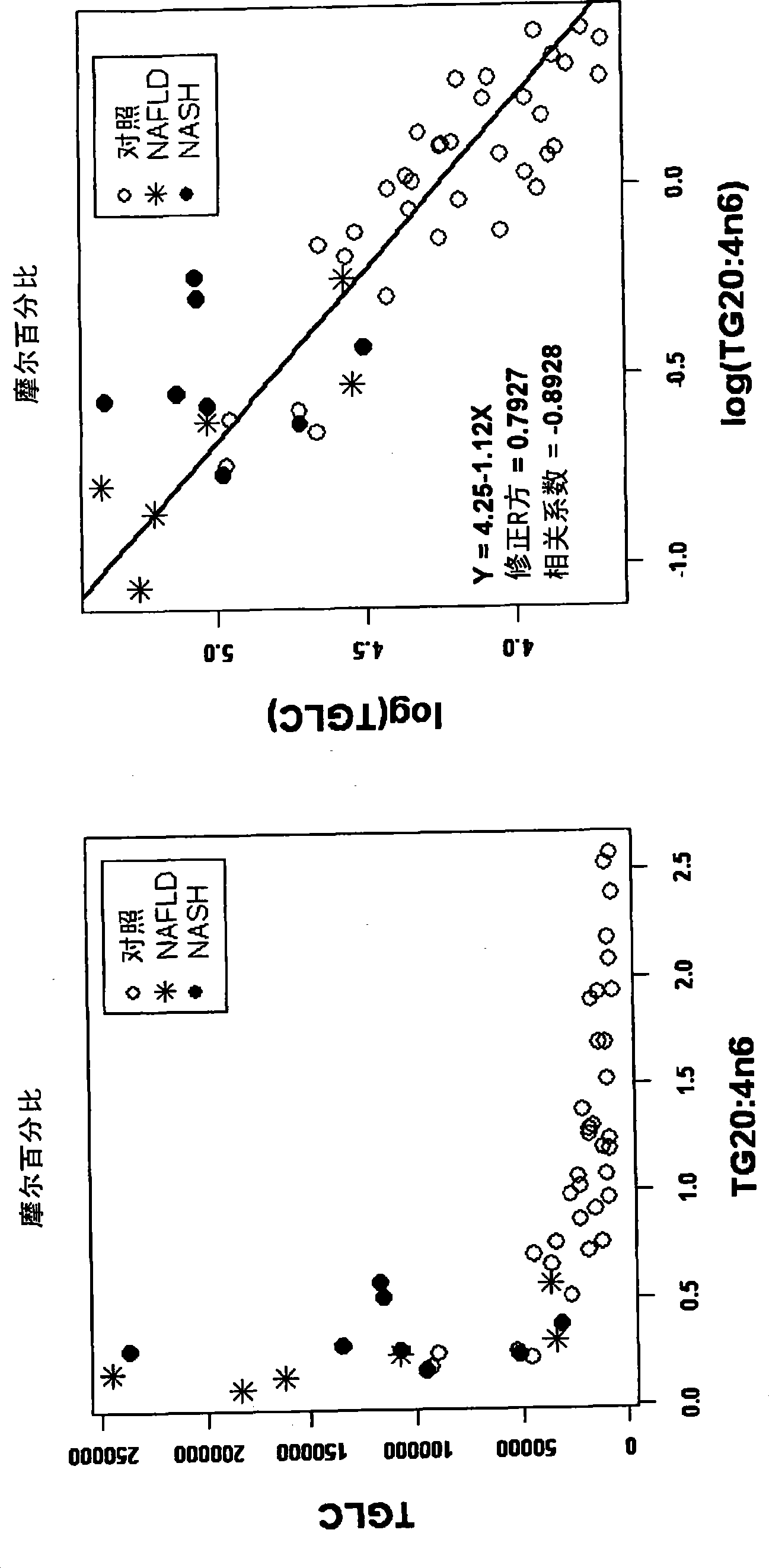
[0158] The first data set was used in this experiment. Liver samples from 49 subjects were assessed for the degree of hepatic steatosis and inflammation. Six subjects were graded as NAFLD and eight subjects were graded as NASH. All other samples were assumed to be normal. use The samples were technically profiled; numerous metabolites were found to be positively or negatively correlated with liver total triglyceride concentrations. In particular, monounsaturated fatty acids are generally positively correlated with steatosis, and essential fatty acids are generally negatively correlated with steatosis. An example of a metabolite that correlates well with total hepatic triglycerides is fatty acid 20:4n6, which is expressed as the percentage of all fatty acids present in the triglycerides ( image 3 ).
[0159] image 3 The relationship between hepatic triglyceride concentration (nmol / g) and t...
Embodiment 3
[0161] Markers of NAFLD and NASH
[0162] The metabolite signatures for NAFLD and NASH in Table 6 were selected based on the observed and / or predicted correlations of the metabolite signatures with liver total triglyceride content. Furthermore, these markers showed some correlation useful in classifying all 16 subjects examined with normal liver function or liver damage.
[0163] Table 6. Blood-Based Lipid Metabolite Markers of Hepatic Steatosis (Mole Percent Based)
[0164] lipid class Positive correlation negative correlation Triglycerides TG14:0 TG15:0 TG14:1n5 TG18:2n6 TG16:0 TG18:3n3 TG18:1n7 TG20:0 TGMUFA TG20:2n6 TT7 TG20:3n6 TGSFA TG20:3n9 TG16:1n7 TG20:4n6 TG20:5n3 TG22:0 TG22:1n9 TG22:2n6 TG22:4n6 TG22:5n3
[0165] TG22:5n6 TG22:6n3 TG24:0 TG24:1n9 TGn3 TGn6 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com