One-step template-free method for preparing a great amount of monodisperse ZnS hollow nanospheres
A monodisperse, zinc sulfide technology, applied in the direction of zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide, etc., can solve the problems of many preparation steps, high cost, affecting large-scale applications, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Preparation of Monodisperse ZnS Nanohollow Spheres
[0024] Zinc acetate and thiourea were used as reactants. The detailed experimental process is as follows:
[0025] Dissolve 1.6 mmol of zinc acetate in 40 ml of distilled water, then add 40 mmol of thiourea to the solution, and stir at room temperature until the solution is clear, prepare 4 parts of clear solutions according to the method described, and transfer the resulting solutions to polytetrafluoroethylene After sealing in the lined stainless steel reaction kettle, heat the reaction kettle to 140, 170, 180 or 200°C respectively to decompose thiourea and react with zinc acetate for 5 hours, wash the precipitate with distilled water for 3 times, and then put it in a vacuum drying oven Dry at 60±2°C for 6 hours to obtain monodisperse zinc sulfide nano hollow spheres.
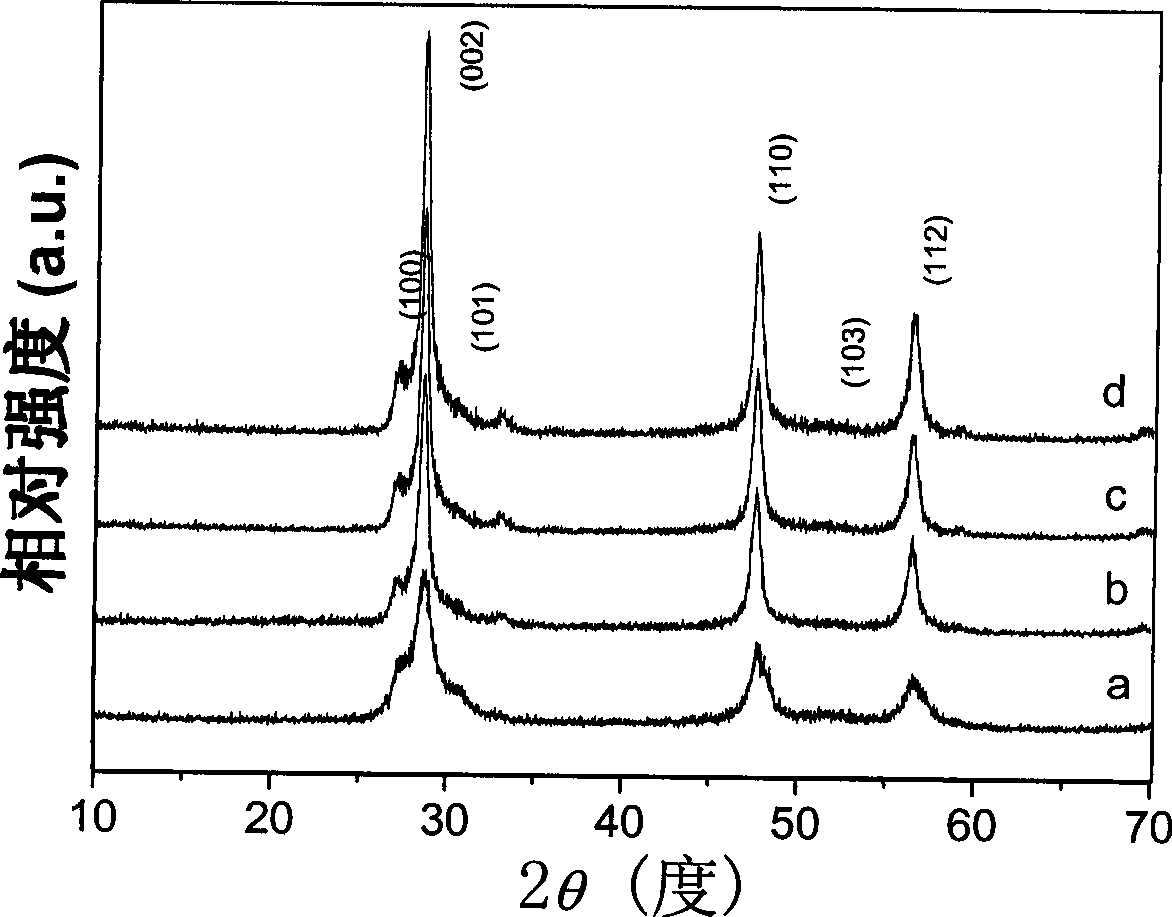
[0026] The phase structure of the prepared samples was characterized by XRD. The XRD patterns of ZnS samples prepared at different temperatures a...
Embodiment 2
[0033] In order to test the influence of reaction time on the sample morphology, the reaction temperature was fixed at 140° C., and other reaction conditions such as the amounts of zinc acetate and thiourea were exactly the same as in Example 1 except that the reaction time was different. The results showed that the samples prepared at 1 h were solid spheres with a radius of 100 nm. As the reaction time increased to 5 hours, the morphology of the sample changed to a uniform core-shell structure, the radius increased to 200 nm, and the surface became rough. The morphology of the sample prepared after 10 hours is a hollow sphere with double shells. As the reaction temperature was further increased up to 24 h, a completely hollow structure with larger grain size and thicker shell was finally obtained. From the above results, it can be deduced that the growth mechanism of hollow spheres is the Ostwald aging process, that is, the gradual cavitation process in which small grains gr...
Embodiment 3
[0035] In order to check the influence of the amount of thiourea on the shape of the sample, except that the amount of thiourea takes different values between 20-60mmol, other reaction conditions such as: the amount of zinc acetate (1.6mmol), reaction Temperature (140 ℃), reaction time (5 hours), the amount of water (40 milliliters) etc. are all identical with embodiment 1. The results show that when the amount of thiourea is reduced to 20mmol, the prepared samples are aggregates of nanoparticles, which is due to the reduction of thiourea reduces the amount of complexes it forms with zinc ions, thus zinc ions in the solution Homogeneous nucleation; when the amount of thiourea increased to 60mmol, the prepared samples were nano-solid spheres, because too much thiourea prevented the Ostwald aging process. In experiments, it was found that the optimum amount of thiourea was 30-50 mmol.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com