Cloning vector pGreen-S based on enhanced green fluorescent protein gene deletion as screen marker and construction method thereof
A green fluorescent protein and gene deletion technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reducing the flexibility of genetic recombination, the inability to screen recombinants, and practical limitations, etc., to achieve clear and convenient observation and collection of data, clear contrast, and increased flexibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
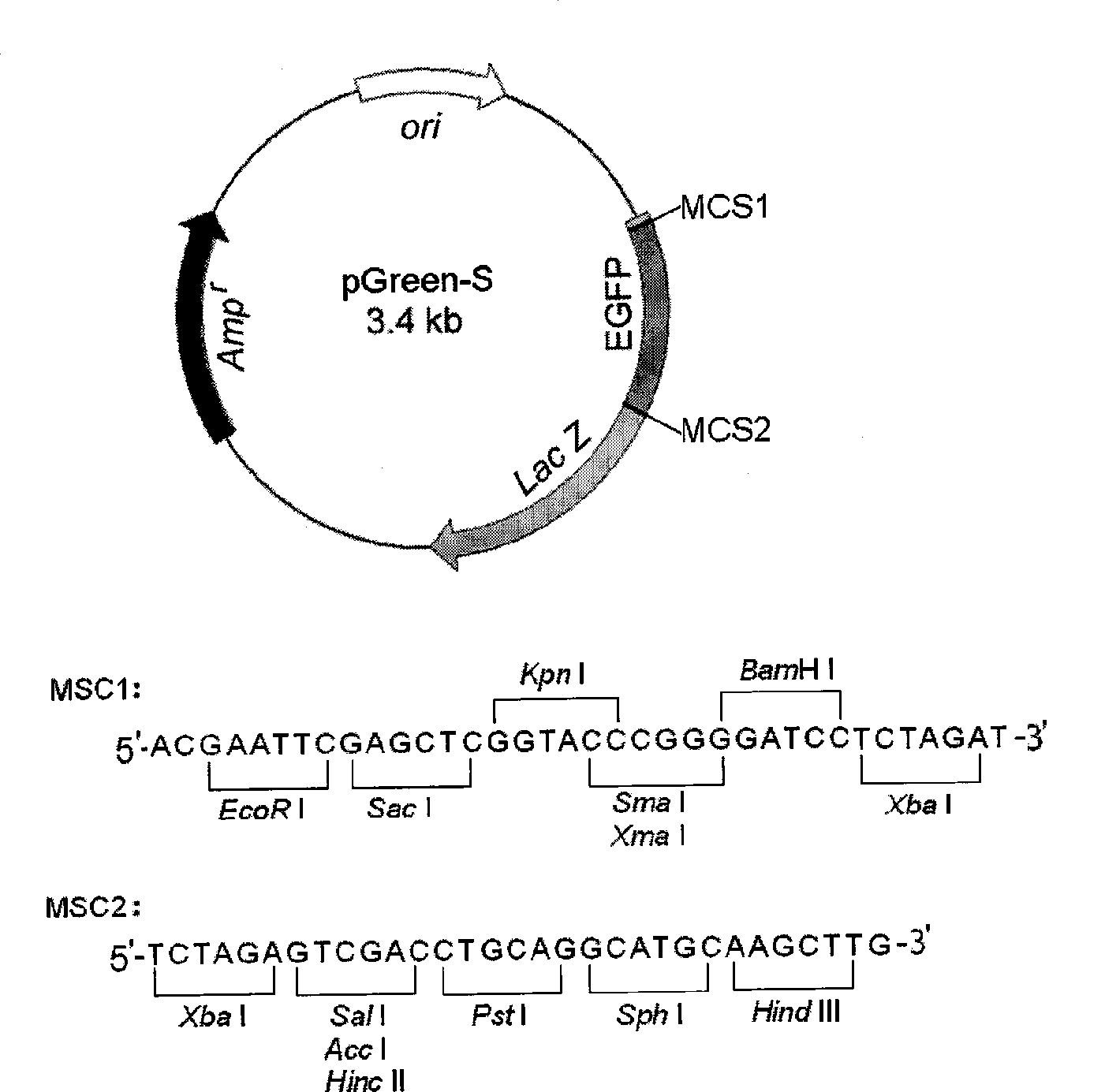
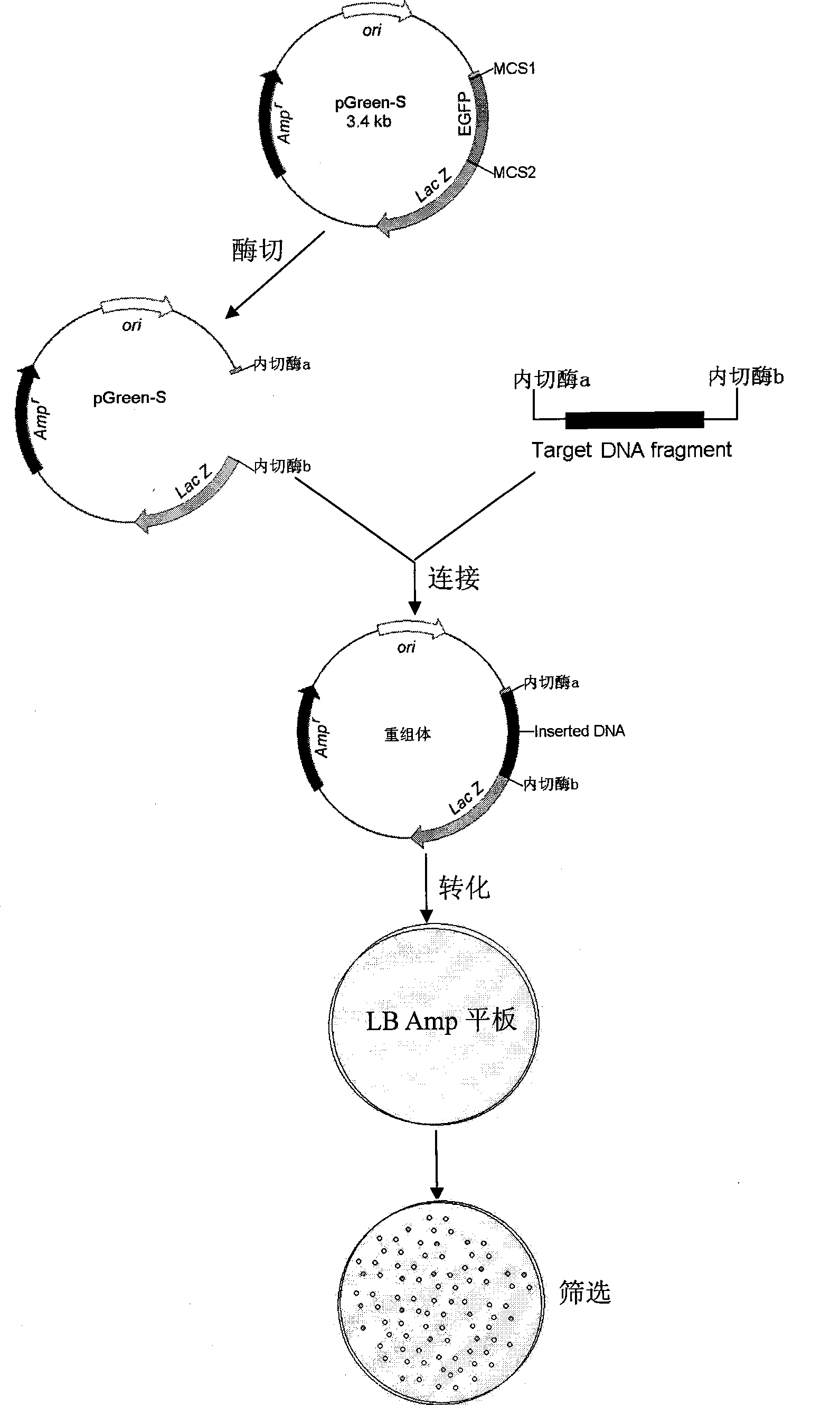
[0033] Example: a cloning vector pGreen-S that utilizes the absence of green fluorescence of enhanced green fluorescent protein as a marker to screen recombinants is the Xba I that inserts the enhanced green fluorescent protein gene (enhanced green fluorescent protein, EGFP) forward into the pUC18 vector Enzyme cut site obtained. The pGreen-S vector construction process is as follows:
[0034] 1. Construction of pGreen-S vector
[0035] According to the EGFP gene sequence, a pair of upstream and downstream primers were designed, and the EGFP gene was amplified by PCR using the plasmid pEGFP-N1 (Clontech) as a template. Primers are as follows:
[0036] Upstream primer: 5′-GCAC TCTAGA TATGGTGAGCAAGGGCG-3′
[0037] Downstream primer: 5′-GCTA TCTAGA TTACTTGTACAGCTCGTCCA-3′
[0038] Both upstream primers and downstream primers contain Xba I restriction endonuclease sites.
[0039] A 0.73 kb gene fragment was amplified, digested with Xba I, and ligated with the pUC18 plasmid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com