Conductive paste for solar cell electrode
A solar cell and conductive adhesive technology, which is applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of large FF changes and unavailability, and achieve the effect of improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
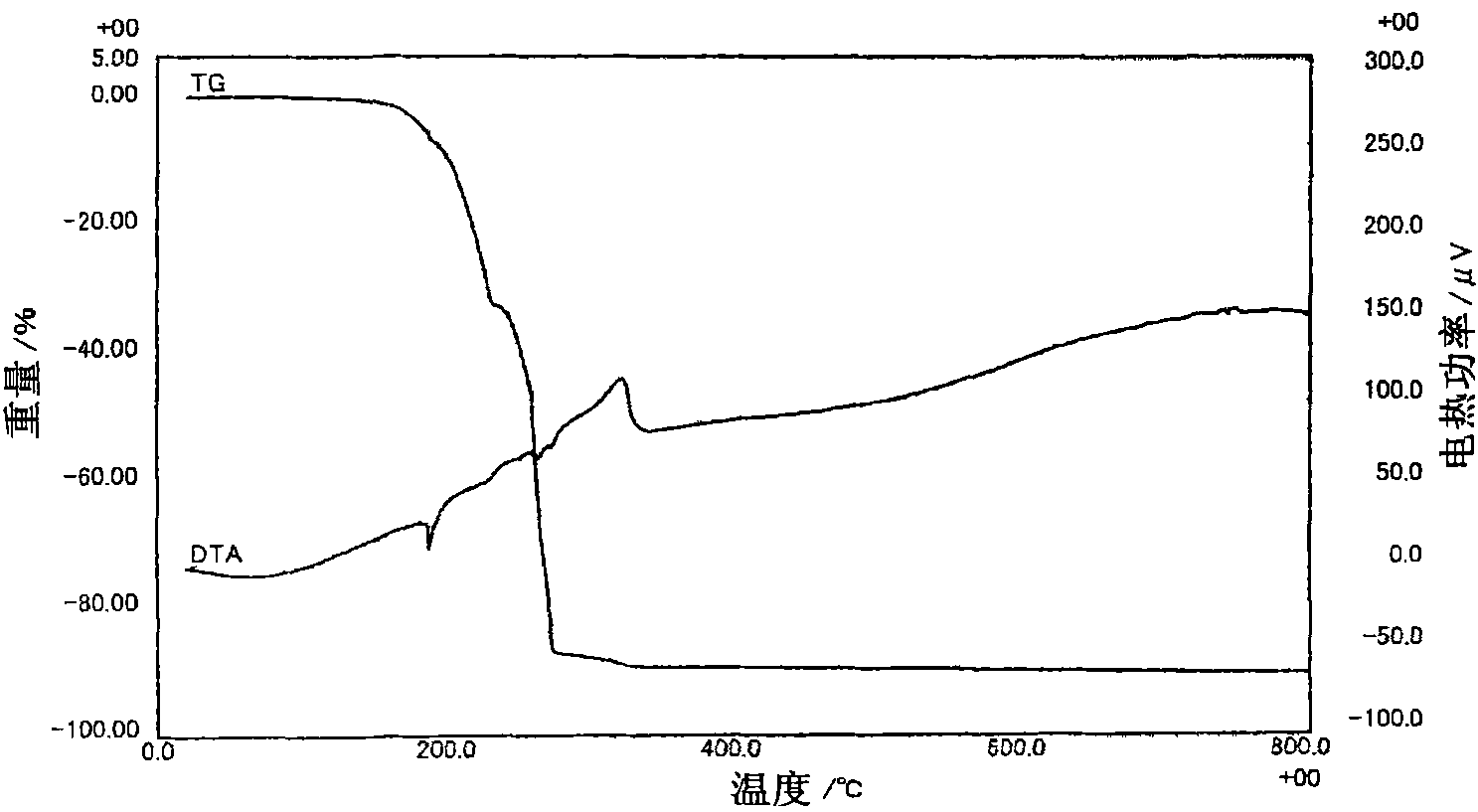
[0096] The present embodiment is an example of using an organometallic compound, ie, an indium acetylacetonate compound, as (A) a substance that turns into a gas in a temperature range of 150 to 800°C. When compared with the case of no addition, it is possible to maintain a high FF over a wide temperature range and obtain an FF with less unevenness by adding a vaporizable substance to the conductive adhesive.
[0097] The composition of the conductive adhesive (expressed in parts by weight) is shown in Table 1. The conductive adhesive was prepared by mixing the ingredients with a planetary mixer and a 3-roll mixer.
[0098] Table 1
[0099]
[0100] *In(C 5 h 7 o 2 ) 3 Indium acetylacetonate. It is amorphous and has an average particle size of 0.2 μm (the same applies to other examples).
[0101] The firing conditions are: the peak temperature is 705°C, 725°C or 745°C, and the firing time is 2 minutes.
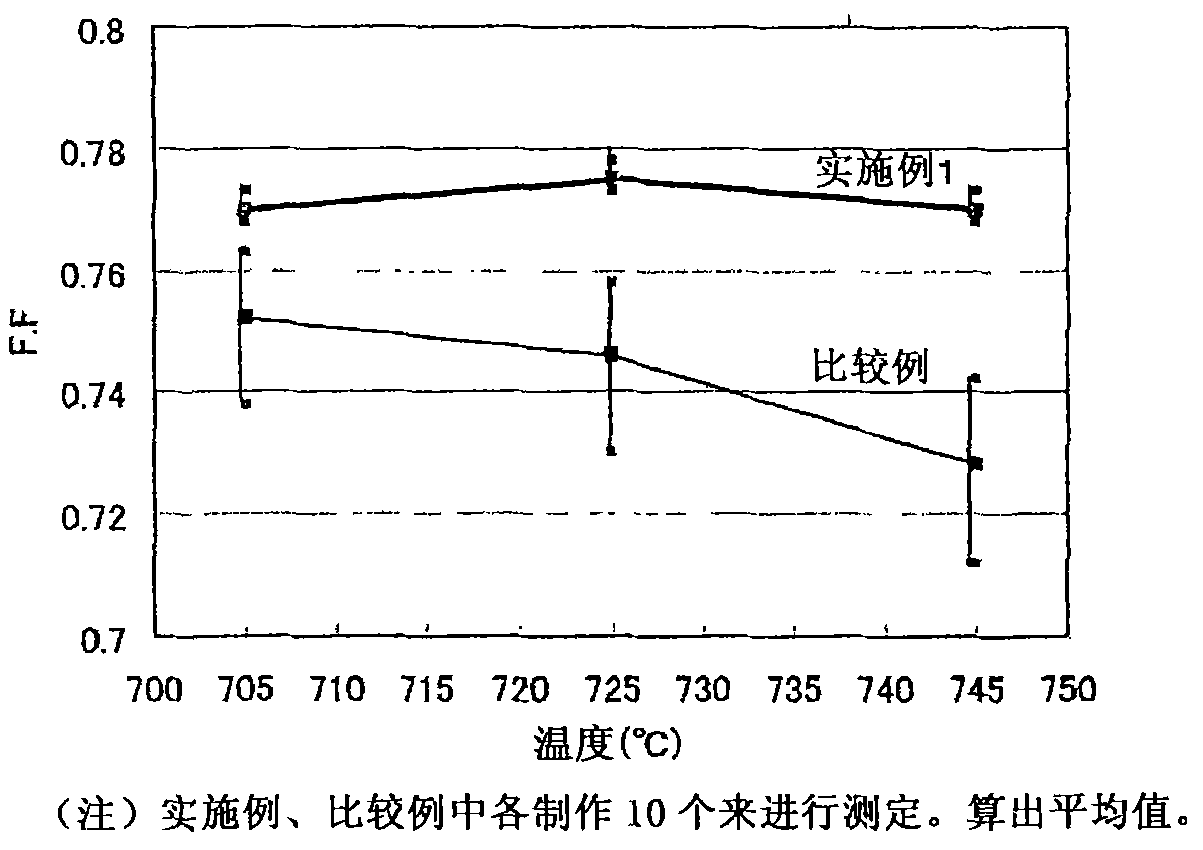
[0102] The FF of the obtained solar cell is shown in image 3...
Embodiment 2
[0104] The present example is an example in which acetylacetonation of indium, which is an organometallic compound, is used as a substance that becomes a gas in a specific temperature range, and the amount of addition thereof is changed.
[0105] The composition of the conductive adhesive (expressed in parts by weight) is shown in Table 2. The conductive adhesive was prepared by mixing the ingredients with a planetary mixer and dispersing with a 3-roll mixer.
[0106] Table 2
[0107]
[0108] The firing conditions are: peak temperature 725°C, firing time 2 minutes.
[0109]Table 2 shows the FF of the obtained solar cell. In Examples 2-1 to 2-3 of the indium-added acetylacetonate compound, high FF was exhibited in any addition amount.
Embodiment 3
[0111] This example is an example in which an organometallic compound, ie, indium acetylacetonate, is used as a substance that becomes a gas in a specific temperature range, and the amount of ZnO as a metal oxide is changed.
[0112] The composition of the conductive adhesive (expressed in parts by weight) is shown in Table 3. The conductive adhesive was prepared by mixing the ingredients with a planetary mixer and dispersing with a 3-roll mixer.
[0113] table 3
[0114]
[0115] The firing conditions are: peak temperature 725°C, firing time 2 minutes.
[0116] Table 3 shows the FF of the obtained solar cell. Examples 3-1 to 3-6 to which ZnO was added showed higher FF than the comparative example to which ZnO was not added. In particular, a high FF is exhibited when ZnO is added in an amount of 0.5 to 15 parts by weight, especially 1 to 15 parts by weight.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com