Multimedia broadcast multicast data sending/receiving method, apparatus and system
A technology of multimedia broadcasting and multicasting data, which is applied to devices dedicated to receivers, digital transmission systems, store-and-forward switching systems, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
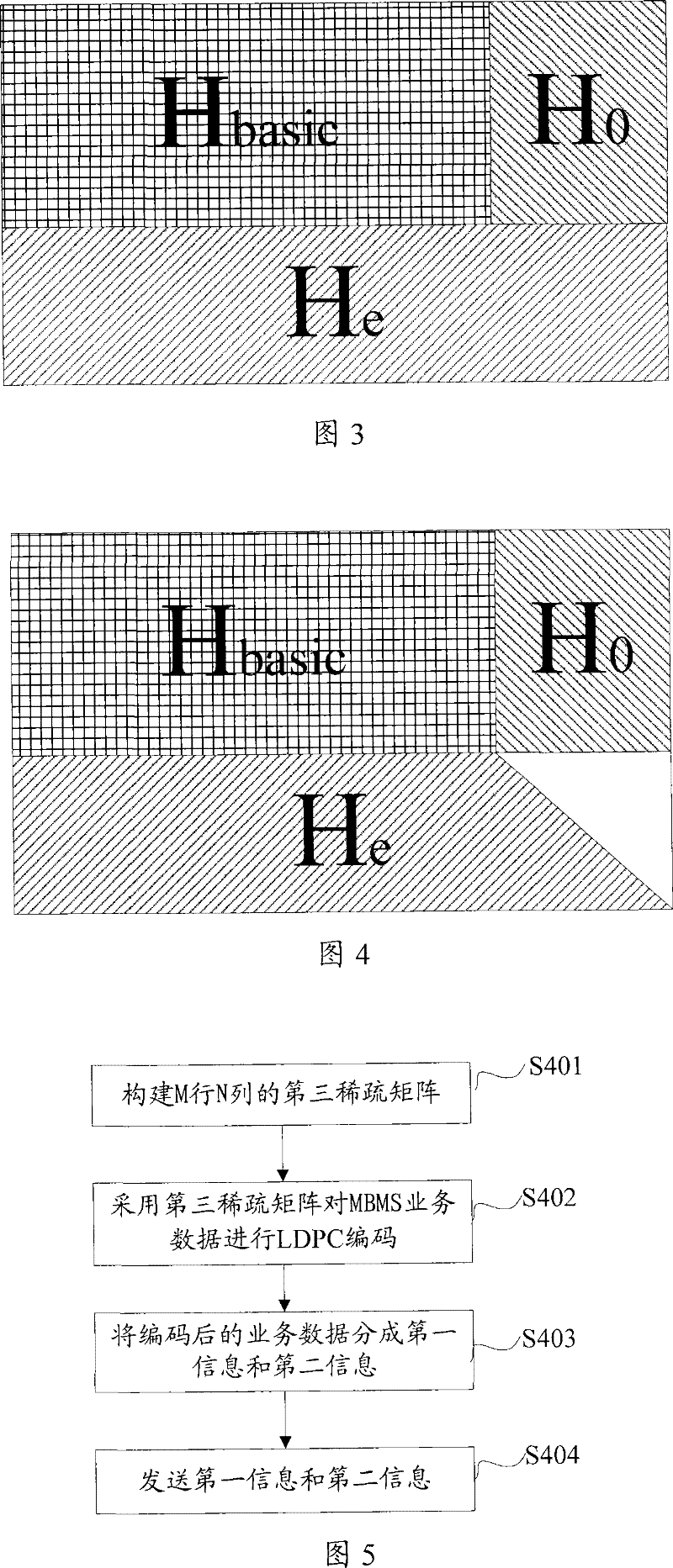
[0054] The basic implementation principle is as follows: construct a first sparse matrix, which is called the base matrix for the convenience of description, so that the multimedia broadcast and multicast data encoded by the base matrix can be correctly decoded by the receiving end with a good channel environment; by expanding the base matrix , to generate a second sparse matrix, which is called an enhanced parity check matrix for convenience of description. For a receiving end with a poor channel environment, it decodes after receiving all the information encoded according to the enhanced parity check matrix, and obtains the transmission data of the MBMS service.
[0055] For specific steps, see figure 2 ,include:
[0056] Step S101. Construct a first sparse matrix (base matrix) with M rows and N columns, so that the multimedia broadcast multicast data encoded by the base matrix can be correctly decoded by the receiving end with a good channel environment.
[0057] The spec...
Embodiment 2
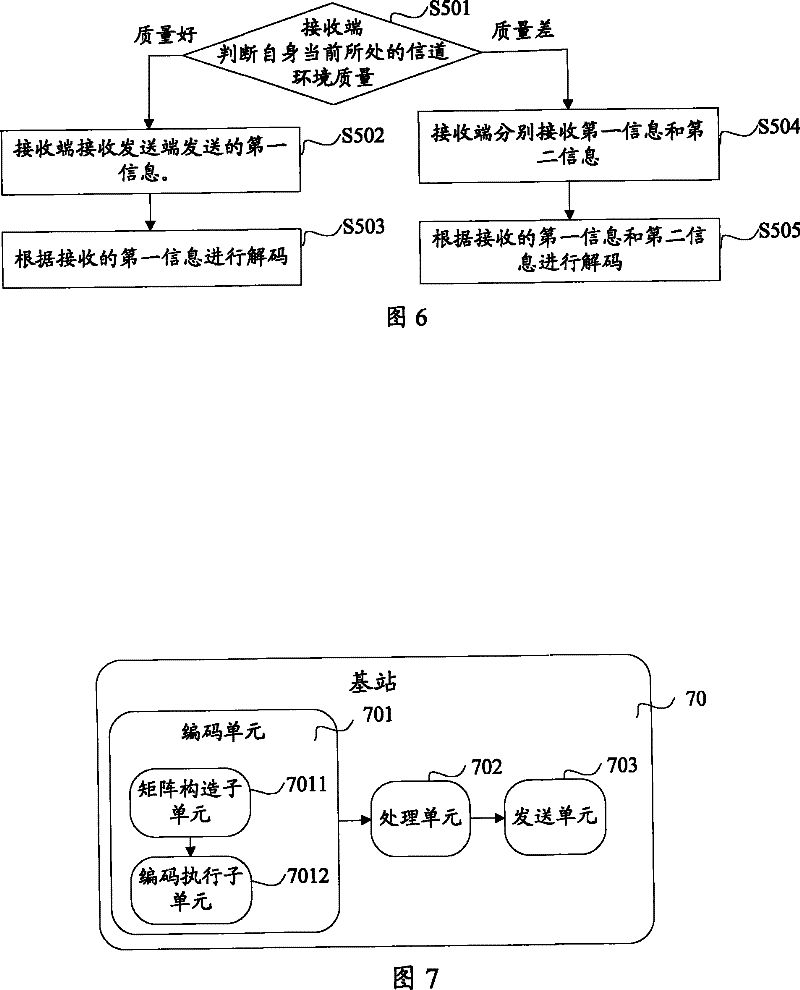
[0086] The basic implementation principle is as follows: construct a sparse matrix, which is called the third sparse matrix for the convenience of description, so that the multimedia broadcast multicast data encoded by the third sparse matrix can be correctly decoded by the receiving end with poor channel environment; The matrix performs LDPC encoding on the multimedia broadcast and multicast data, and divides the encoded service data into first information and second information for transmission, wherein the first information is part of the encoded service data bits, and the receiving end with a good channel environment , it can be correctly decoded only by receiving the first information, and the transmission data of the MBMS service can be obtained.
[0087] Figure 5 The flow chart of the steps for sending the MBMS service data at the sending end provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention specifically includes:
[0088] Step S401, constructing a third sparse matrix...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Figure 6 The flow chart of the receiving end receiving MBMS service data steps provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention; specifically includes:
[0104] Step S501, the receiving end judges the quality of the channel environment where it is currently located.
[0105] In this step S501, the channel environment quality can be characterized by various parameters. For example, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) can be used to characterize the channel environment quality. When the receiving end judges that the current SNR is greater than the set threshold, it is determined that the channel environment quality is good; when the SNR is less than or equal to the set threshold, it is determined as the channel environment quality. Difference.
[0106] When the receiving end judges that the quality of the channel environment it is currently in is good, adopt the first receiving strategy and perform the following step S502;
[0107] When the receiving end judges that the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com