Production of novel bacterial exopolysaccharides by using Phyllobacterium sp.nov.921F bacterial strain
A technology of bacteria and strains, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, and methods based on microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
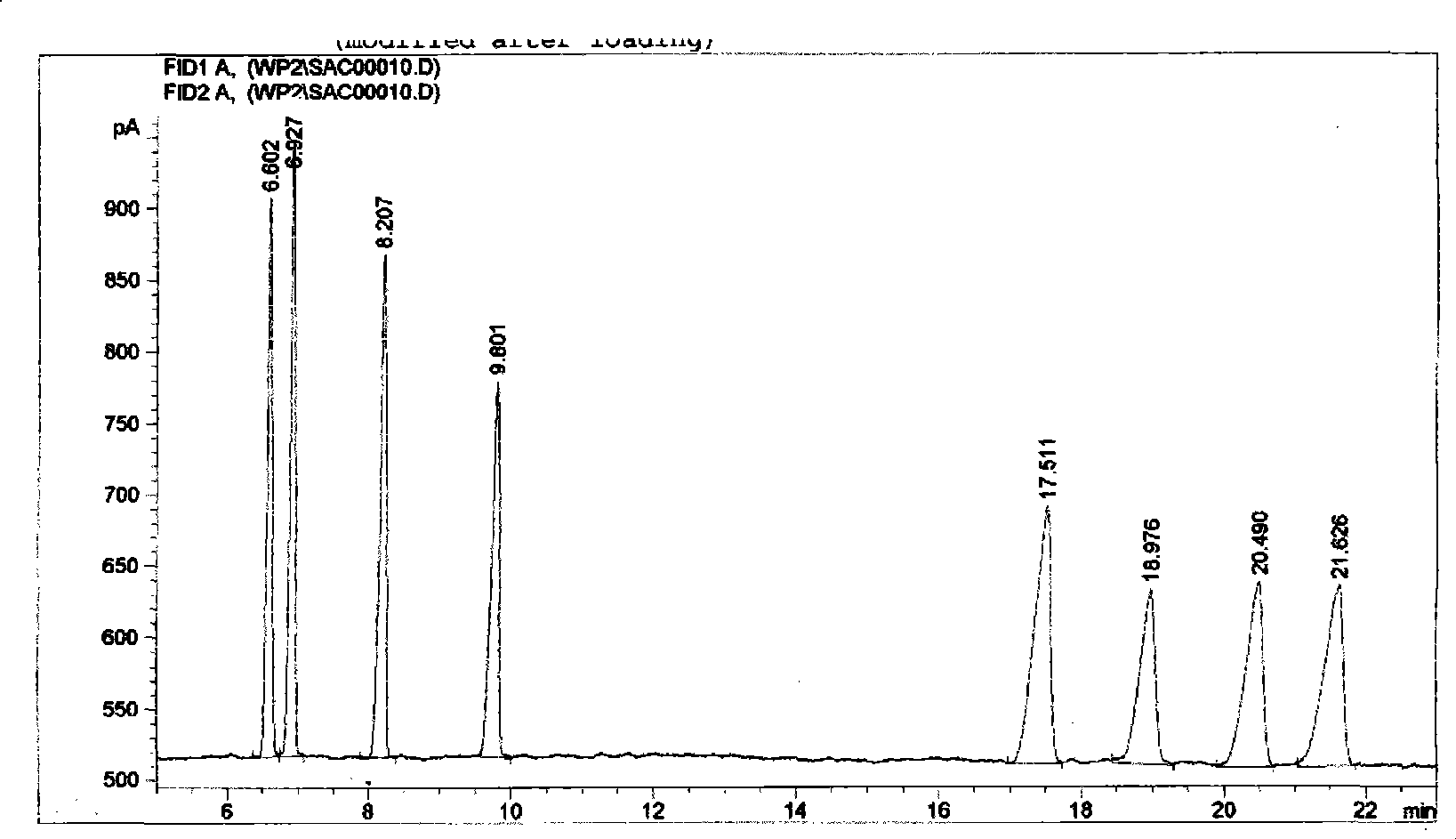
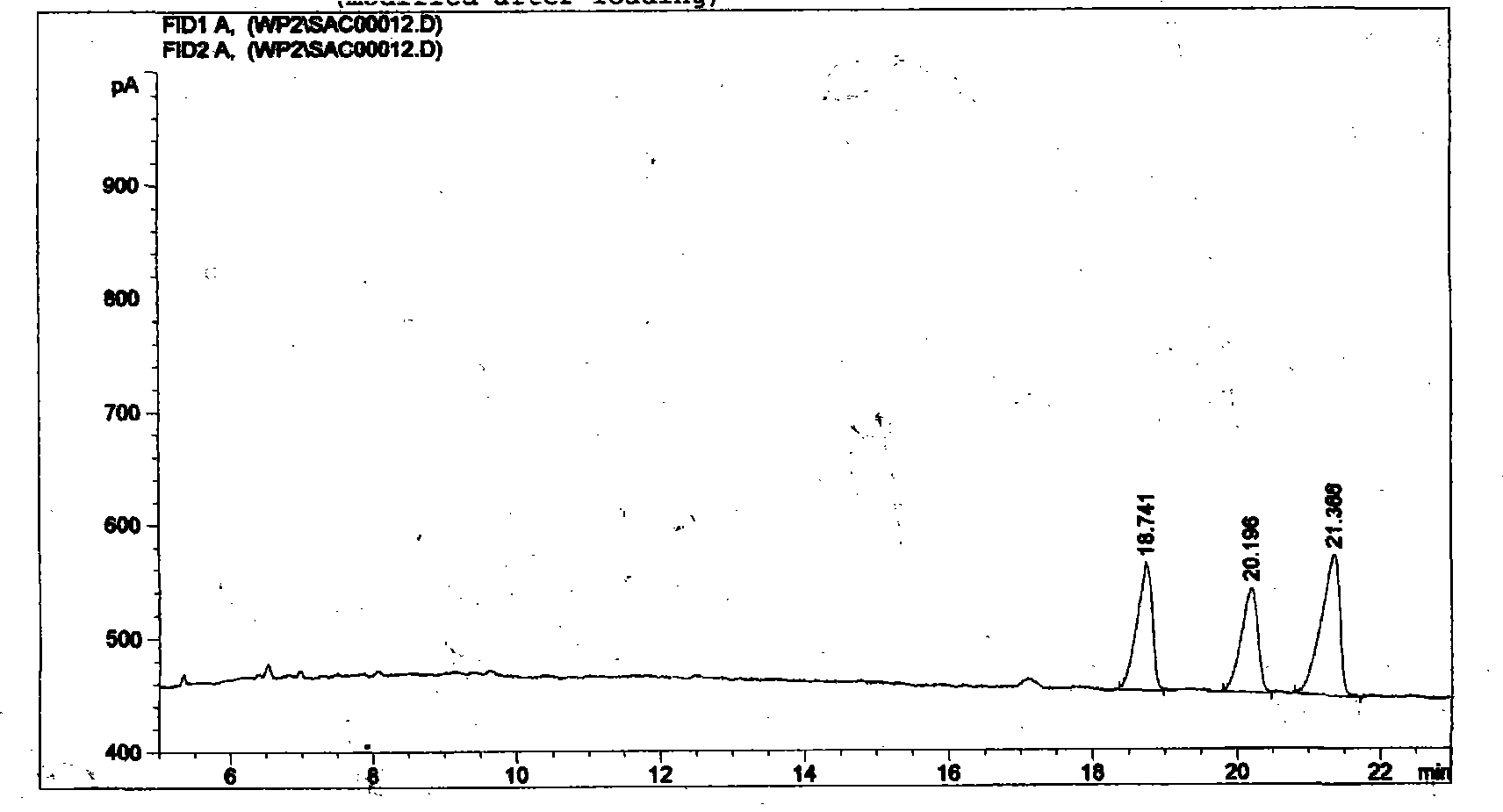
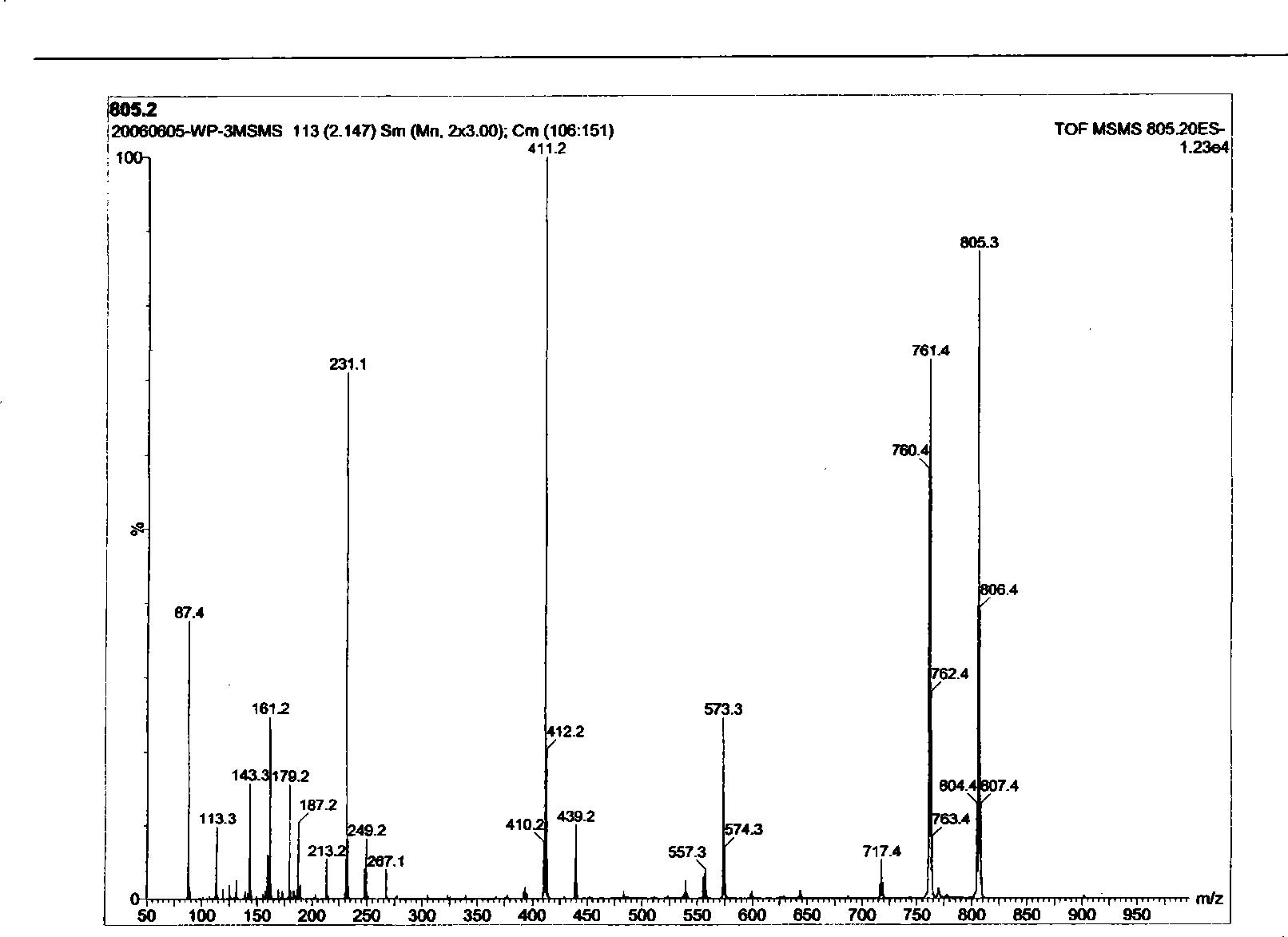
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] 1. Isolation and purification of strains:
[0012] The acquisition of the Phyllobacterium sp.nov.921F bacterial strain of the present invention: collect fungal fruiting body samples from the remaining veins of Changbai Mountain, add to 25ml enrichment medium (sucrose 2g, NaNO 3 1g, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g, MgSO 4 0.5g, NH 4 Cl0.5g, FeSO 4 0.01g, H 2 O 1000ml, pH7.2) Erlenmeyer flask, 30 ℃, 160r / min shake flask culture 3d. Then the enriched culture solution was properly diluted with sterile physiological saline, and 0.2ml was taken to coat the primary screening separation medium (sucrose 10g, NaNO 3 1g, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g, MgSO 4 0.5g, NH 4 Cl 0.5g, FeSO 4 0.01g, agar 15g, H 2 O 1000ml, pH7.5) plate. Inverted culture at 30°C for 48 hours, a viscous milky white colony on the selected plate was obtained, and a bacterium capable of producing exopolysaccharide was obtained.
[0013] 2. Identification of strains:
[0014] The isolated strain was identified according...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com