Automatic hot galvanizing technique for steel fastener
A fastener and hot-dip galvanizing technology, applied in hot-dip galvanizing process, metal material coating process, coating, etc., can solve problems such as high operating cost, irregular nut direction, shortened zinc pot life, etc., to reduce Workers' labor intensity, guaranteed accuracy and strength, and the effect of reducing galvanizing temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
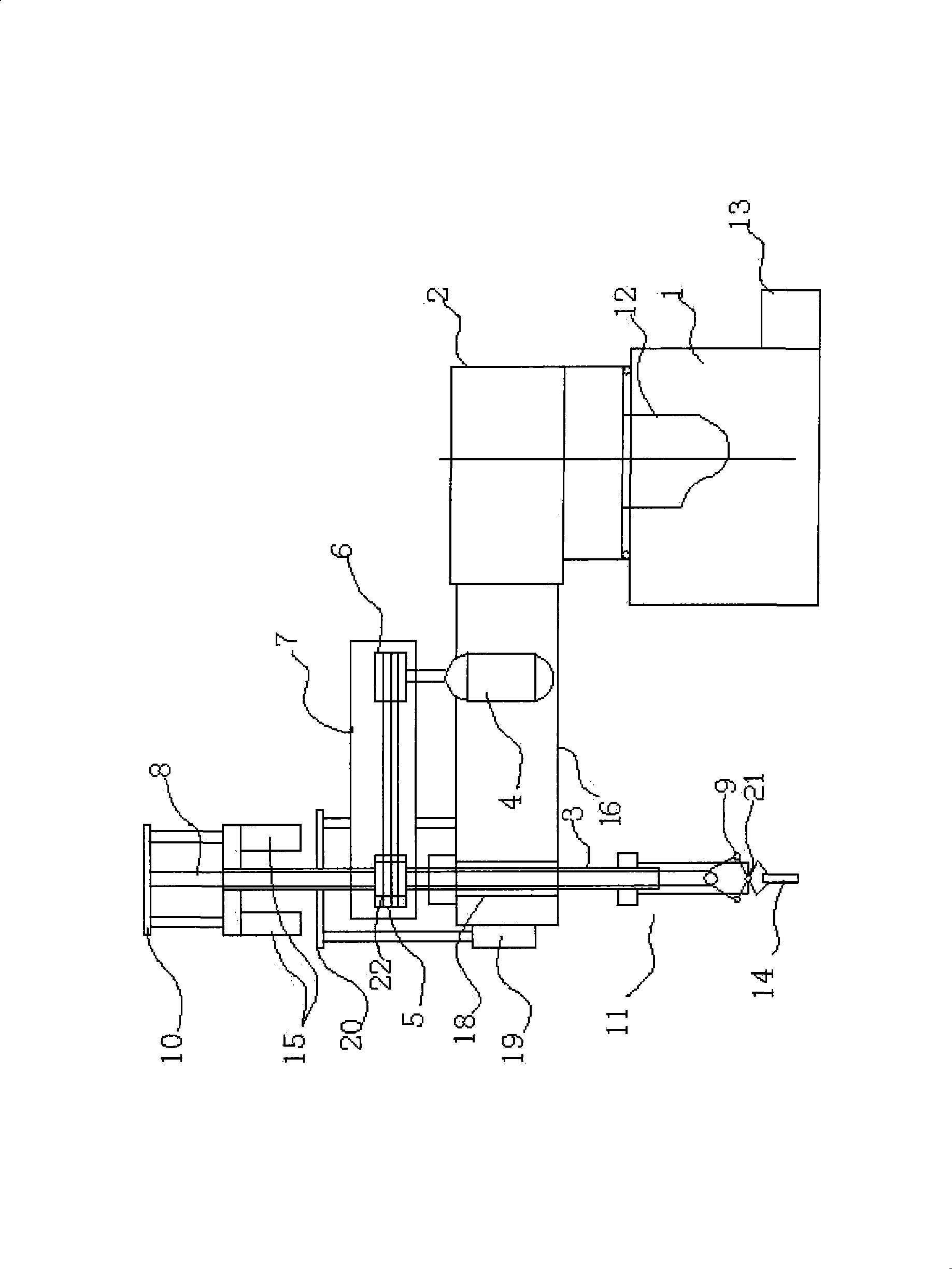
Image
Examples
Embodiment
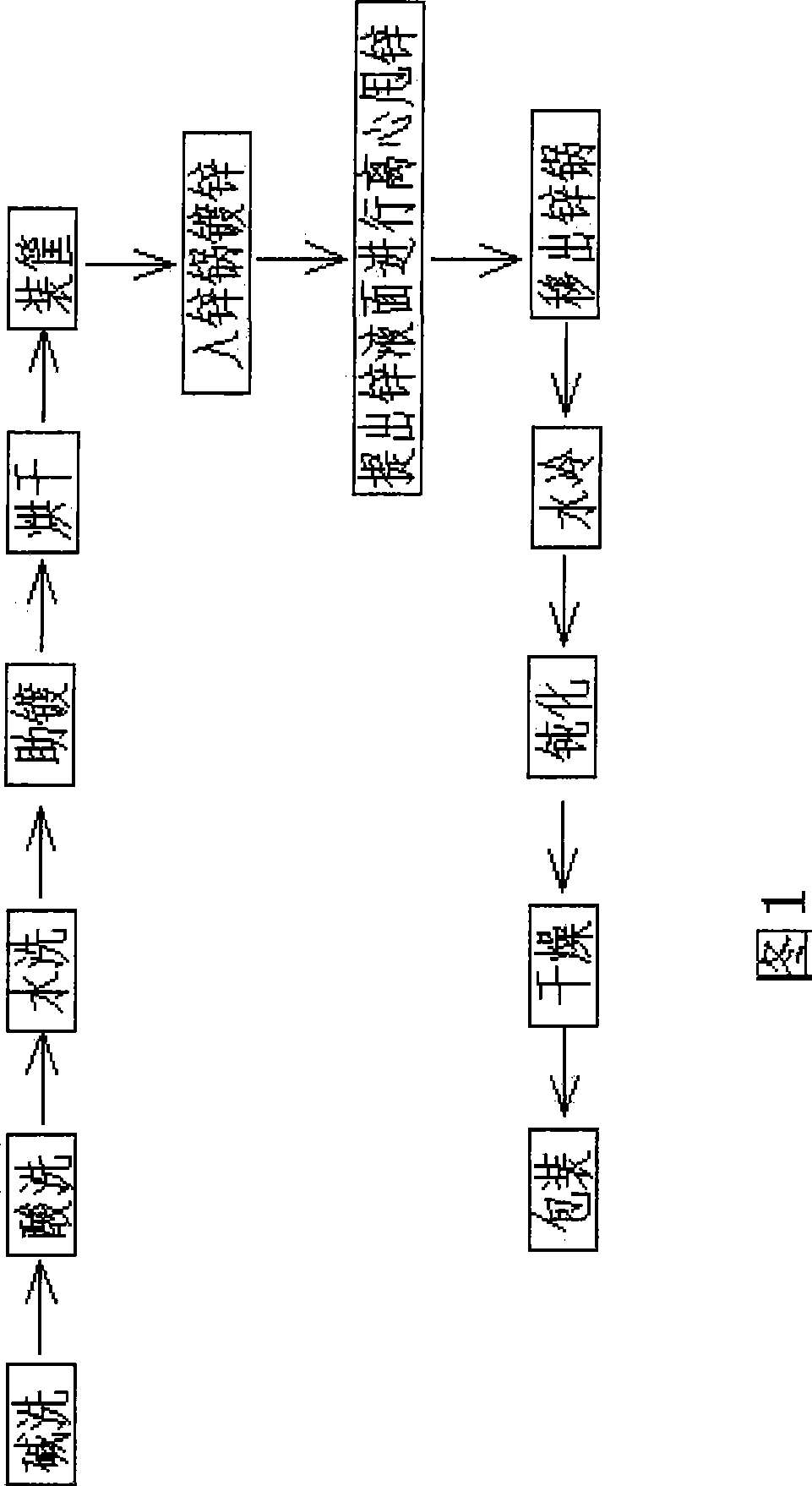
[0034] Figure 1 shows a flow chart of an automatic hot-dip galvanizing process for steel fasteners. The process includes alkali cleaning, pickling, water washing, plating aid, drying, loading into baskets, galvanizing in the zinc pot, centrifugal zinc rejection after the zinc liquid level is raised, removal from the zinc pot, water cooling, passivation, drying, and packaging Waiting for the process. in,
[0035] Alkali cleaning: Put the workpiece into the lye tank, adjust the alkali cleaning time according to the degree of oil pollution on the surface of the workpiece, and clean the residual alkali on the surface with clean water after washing;
[0036] Pickling: Put the above-mentioned alkali-washed and water-washed workpieces into a hydrochloric acid tank for derusting, and the time depends on the degree of corrosion on the surface of the workpieces;
[0037] Washing: the workpiece after pickling is washed to remove residual acid;
[0038] Helping plating: put the above-m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com